Zoloft
David Bloom, MD
- Chair, Department of Urology, and Jack Lapides Professor of
- Urology, University of Michigan Medical School,
- C. S. Mott Children? Hospital,
- Ann Arbor, Michigan
One of the most important issues bipolar depression dsm code safe zoloft 25mg discuss with the woman considering pregnancy after a diagnosis of breast cancer is whether a future pregnancy will adversely affect her prognosis anxiety quotes order zoloft paypal. The main consideration is whether a relapse during pregnancy would impose signifcant risk anxiety jittery feeling purchase generic zoloft the woman or her unborn child anxiety 4 year old symptoms buy zoloft 25 mg line. Early relapse within the frst two years portends an aggressive clinical course and relapse in this timeframe during pregnancy depression definition merriam webster buy zoloft 25 mg with visa. An analysis of the risk of relapse is useful when considering recommendations of this nature; a woman with a very small risk of breast cancer relapse poses little problem anxiety 101 purchase 25mg zoloft fast delivery, whereas a young woman whose cancer has aggressive features might receive strong recommendations against early pregnancy. There is no evidence that pregnancy increases relapse risk, so there is no medical reason terminate an unplanned pregnancy in a mother in the absence of evidence of relapse. Breastfeeding Women should also be informed that surgical interventions and radiotherapy may result in a reduced milk fow the infant and radiotherapy may affect the elasticity of the nipple, making it more diffcult for the infant latch and suckle effciently. It is generally accepted that clinical trials are an essential component of the process of fnding better treatments for breast cancer and that there is indirect evidence that women who participate in clinical trials have better outcomes than women given similar treatments outside trials. There are large-scale national and international collaborations for31 clinical trials such as the Australian New Zealand Breast Cancer Trials Group available Management of early breast cancer 157 Chapter 10: Special issues New Zealand specialists and women. In New Zealand there are rigorous standards for the provision of complete and appropriate information regarding clinical trials and for written informed consent. These include the requirement make clear that entry into a trial remains voluntary and subsequent access treatment should not be affected by the decision participate or not. A high participation rate in clinical trials will enable questions of scientifc importance be answered more rapidly. Well-conducted clinical trials set high standards of practice for participating centres, with very careful audit and review of many aspects of the treatment process. The websites of the following groups provide information and/or links and some protocols of ongoing trials. Few alternative or complementary therapies have been tested in rigorous randomised clinical trials. The Cancer Society of New Zealand website indicates that more than 60% of New Zealanders use complementary therapies at least once a year ( The website lists sources of information and links other websites regarding the use of complementary and alternative therapies. How complementary therapy interacts with conventional treatment is largely unknown, so care should be exercised when using both concurrently. Increased complication rates from some treatments, including infection and lymphoedema after surgery, have been noted in association with obesity. Disposal of tissue the disposal of tissue may be of particular signifcance Maori, so health practitioners should approach this issue with sensitivity and awareness. Culturally appropriate disposal of tissue following surgery or investigations should be available, if requested. Health practitioners should also be aware that Pacifc people may wish be buried as a whole person if they are die. If a mastectomy is chosen, it may have implications for whether the woman chooses retain the tissue postoperatively. Provision needs be made during surgery and following pathological evaluation of tissue for its return the individual. Considerations for Maori and Pacifc peoples are discussed further in Chapter 2, General principles of care. Recommended practice in relation determining the preference of Maori and Pacifc women for disposal of tissue is included in a good practice point in that section of the guideline. Good practice point Practitioners should consult with Maori and Pacifc women with early breast? If tissue banking is planned for research purposes, especially if testing for heritable genetic traits is planned, clinicians should follow the national guidance on this issue. It describes how the clinical questions were developed, the literature review that was undertaken, and the process by which the reviewed evidence was developed into recommendations and good practice points. Further discussion limited the areas of interest those within scope and of major importance for patients. In patients with early breast cancer what advice, communication and information methods are most effective? What is the effectiveness of psychosocial support for breast cancer patients and their families? What is the effectiveness of a multidisciplinary team/coordinator of care in patients with early breast cancer? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of lumpectomy versus quadrantectomy? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of excising the axillary, supraclavicular and internal mammary nodes versus no excision? Is there any evidence that carrying out breast reconstruction immediately is more or less effective than delayed reconstruction? In patients with early breast cancer does venous access the arm on the side of axillary surgery increase the risk of lymphoedema on that side when compared with venous access on the opposite side? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of mastectomy plus radiotherapy versus mastectomy alone? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of mastectomy plus radiotherapy plus a boost dose of radiotherapy versus mastectomy plus radiotherapy without a boost dose of radiotherapy? In patients with early breast cancer does the use of paclitaxel or docetaxel in addition chemotherapy improve patient outcome when compared with chemotherapy alone? In patients with early breast cancer does the use of trastuzumab in addition chemotherapy improve patient outcome when compared with chemotherapy alone? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of chemotherapy provided before surgery radiotherapy compared with chemotherapy provided after surgery radiotherapy? In patients with early breast cancer what is the diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility of scoring systems for oestrogen and progesterone receptors? In women with early breast cancer does the use of endocrine therapy (tamoxifen, ovarian suppression, ovarian ablation) alone or in addition chemotherapy improve patient outcome when compared with no treatment or chemotherapy alone? In patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of endocrine therapy + chemotherapy radiotherapy surgery versus endocrine therapy radiotherapy surgery? In premenopausal patients with early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of one endocrine therapy versus other forms of endocrine therapy? What is the effectiveness of adjuvant therapy with bisphosphonates compared with adjuvant therapy without bisphosphonates in patients with early breast cancer when outcomes are disease free survival or local recurrence, or distant recurrence, or overall survival? What is the effectiveness of adjuvant therapy with bisphosphonates compared with adjuvant therapy without bisphosphonates in patients with early breast cancer in terms of bone density as an outcome measure? In patients who have completed therapy for early breast cancer what is the effectiveness of mammography versus follow-up without mammography? The exception this approach is where the guideline of interest is assessed as being of poor quality, where there is considerable controversy, or where there are additional research and outcomes of interest not covered by the existing guideline. The evidence from these guidelines would be considered in conjunction with, and in places an extended, evidence search. A Considered Judgment Form was then prepared, taking into account the quality volume,4 consistency, applicability and clinical impact of the evidence available. Systematic reviews of the literature were not conducted for four topic areas of the guideline: axillary clearance following sentinel lymph node biopsy; genetic testing; considerations for Maori and other ethnic groups; and information provision. Recommendations were graded based on the level which they were supported by the evidence (described in the following sections). Toward the completion of the guideline process additional searches were undertaken for very relevant data published since the completion of the original literature searches. Management of early breast cancer 165 Chapter 11: General section: methods Special issue: trastuzumab While this guideline did restrict its searches published evidence due both methodological and resource concerns, unpublished studies were included in the review of the literature regarding the role of trastuzumab-based regimens. This was because that discussion in the current scientifc literature focuses heavily on unpublished data. Including this unpublished data was necessary in this case be as inclusive as possible. An overall summary level of evidence was assigned each study, as follows: Very high quality ++ assigned when all or most validity criteria met High quality + assigned when some criteria met and where unmet criteria are not likely affect the validity, magnitude or precision, or applicability of the results markedly Low quality assigned when few or none of the criteria met. Intermediate grades (++, +) were assigned when the overall study quality fell between the three categories listed above. For every study included in the evidence review, the level of evidence assigned is listed alongside the citation in the reference list at the end of the guideline. Step 3: Developing recommendations the grading of the recommendations was based on the quality of the evidence, which does not equate the importance of the recommendation. Ian Campbell received fnancial support from AstraZeneca attend as guest speaker at the St Vincents Biennial Breast Cancer meeting in February 2009; from Pfzer attend the San Antonio Breast Cancer Convention 2009; from Roche attend the St Gallen International Breast Cancer Consensus Conference and International Breast Cancer Study Group meeting in 2007, and the San Antonio Breast Cancer Convention in 2006; from Novartis attend the San Antonio Breast Cancer Convention in 2005 and fourth European Breast Cancer Conference Zofast and International Steering Group meeting in Hamburg in 2004. Anita Frew received sponsorship from Roche Pharmaceuticals attend the Society of Hospital Pharmacists of Australia/New Zealand Healthcare Pharmacists Association conference in 2006. Gavin Harris received sponsorship attend the New Zealand Pathologists Conference in 2005. Lyndell Kelly received fnancial support from Novartis attend the Breast Cancer meeting in Cairns and from Schering Plough attend a New Zealand Association of Cancer Specialists conference. Cheryl MacDonald received fnancial support from Roche attend the ninth National Breast Care Nurses meeting in Australia. David is a member of the Breast Special Interest Group of the New Zealand Association of Cancer Specialists. Andrew Simpson received sponsorship from Roche, Novartis, Eli Lily, Sanoti-Aventis and Pfzer attend conferences and educational meetings, including the American Society Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, and World Lung Cancer Congress. The T, N and M categories (tumour, nodes and metastases, respectively) are assessed by the combination of physical examination and imaging such as mammography. Additional notes from the Guideline Development Team: the prognosis of patients with pN1a is similar that of patients with pN0. Management of early breast cancer 177 Appendix B: Verbal prompts assist when raising specifc concerns with people with cancer Body image concerns Cancer certainly changes how we feel about ourselves, and I would like hear if you have particular concerns about the way the cancer and treatments might affect your body how you look and how you feel? It is important have a sense of how troublesome these symptoms are for you, and how much they are affecting your life. Management of early breast cancer 179 Appendix C: Websites providing information on breast cancer and treatment Organisations with websites providing information on breast cancer and treatment include. Those suggested offer credible and responsible information, but we cannot guarantee that the information on the websites is correct, up date or evidence based. We advise you discuss any information you fnd with your health care practitioner. The content is based on the unpublished BreastScreen Aotearoa treatment standards. Macroscopic handling of the specimen: general comments General points Various comprehensive international guidelines for pathology cut-up and reporting exist and are a useful reference. Frozen section Frozen section examination of breast tissue has a limited role in management of patients with palpable breast lesions and is rarely indicated in the management of clinically impalpable lesions. Frozen sections should not be performed in cases where the subsequent pathological examination is likely be compromised. Surgical specimen the surgical team should provide information regarding the source of the specimen (ie, which breast and which quadrant a diagram and a standardised form are often useful); appropriate clinical and imaging fndings such as calcifcation, stellate or cystic lesions; the results of previous biopsy procedures and signifcant operative fndings. The surgeon taking the specimen should ensure that the specimen/s are orientated using radio-opaque markers (where the specimen will be X-rayed) or sutures enable the pathologist and radiologist orientate the specimen correctly. If further tissue is removed after the main specimen, further clips/sutures should be placed indicate the new margin or any area of concern. Fixation On receipt in the laboratory, the tumour should be incised as quickly as possible allow timely fxation. Suboptimal fxation can impact on tumour grading and the results of receptor testing. Management of early breast cancer 181 Appendix D: Pathology guidance for early management of breast cancer Margins of excision For local excision specimens the tissue should be measured in three dimensions and weighed. Any lesion present within the specimen should be described and its maximum dimensions recorded in millimetres. The distance the nearest radial, superfcial and deep margins should be measured. For mastectomy specimens, the distance from the nipple and the quadrant where the lesion is located should also be mentioned. Where multiple lesions are present, the distance between the two or more lesions should be recorded in millimetres. Local excision specimens should have their margins painted mark the various excision margins prior incision. Occasionally an impalpable lesion may not be visible on mammography or specimen radiography. If ultrasound was used for preoperative localisation, ultrasound of the specimen may be necessary confrm removal of the lesion. Blocks should be selected from the area of the radiological abnormality, which can be identifed either by slicing and re-radiographing the slices or by using a localisation device in which a grid reference is used locate the area of interest. A sample radiograph may also be of assistance in some instances for palpable lesions. Wide local excision specimens For wide local excision specimens containing impalpable/palpable lesions, blocks should be taken show the size of the lesion, the relationship the nearest margin or margins and associated disease processes. Detailed assessment of the distance of in situ or invasive carcinoma from the radial margins in particular should be made. There is evidence that detailed margin assessment may have an impact on local recurrence rates. Mastectomy specimens For mastectomy specimens some laboratories in addition blocks assessing lesion size and proximity margins may also favour sampling from quadrants and the nipple. Sections of skin are also important, particularly in the setting of infammatory breast carcinoma. Large lymph nodes should be sliced at 2 mm 3 mm thickness, perpendicular the long axis.
Those same surveys have revealed depression symptoms light headed zoloft 100mg, however mood disorder bipolar order on line zoloft, that residents are concerned about mosquitoes because of the pest factor and those concerns would be sufficient depression levels discount zoloft 50mg fast delivery motivate a certain level of behavior change (Rosenbaum depression xanax order generic zoloft, et al mood disorder lamp discount 50 mg zoloft with mastercard. Yet most dengue control programs continue depression definition dsm iv tr discount zoloft amex function under the assumption that providing more information will motivate behavior change; date, this has not occurred in a sustainable fashion. Residents desire for clean water can facilitate water storage behaviors that are favorable preventing mosquito breeding. A broader environmental management approach also paves the way for greater intersectoral collaboration through advocacy and reduction in duplication of efforts. The rapid reporting of suspected cases and the submission of blood samples taken at the appropriate times and sent in good condition the laboratory depend upon trained and informed health care professionals. Health institutions such as hospitals and clinics must then be prepared for an increase in the number of patients and, during an emergency, the management of an influx of very large numbers of patients. Dissemination of this information in a timely fashion intersectoral groups such as a dengue commission can then guide decisions intensify routine control actions or implement an emergency response using data rather than responding political pressure. Clinical surveillance should at minimum be based upon a passive surveillance system, with an active surveillance system, as described earlier, a goal work toward. A national laboratory service that can perform, at minimum, basic diagnostic tests. Incorporation of the subject of dengue and health into formal education systems School-based education programs are believed be the single best way inculcate future generations of homeowners with a sense of responsibility for environmental management. However, few vector control programs have been able sustain school-based activities due, in part, academic requirements that have led a full curriculum. Development of curricula in partnership with curriculum specialists from the Ministry of Education should go a long way toward increasing acceptance of health curricula by teachers and principals. Critical analysis of the use and function of insecticides Most national dengue prevention and control programs rely on the use of various insecticides control larval and adult stages of Ae. Typically, program budgets allocate most funds staff salaries, the purchase of chemicals, and the purchase of equipment apply the chemicals. These unrealistic perceptions of the costs of the various components continue result in programs that rely on the use of chemicals given that those purchases account for a significant portion of the budget, leaving little funding available for implementation of other components of the program. The use of chemicals has an important role and function in a comprehensive, integrated dengue prevention and control program. But how, when, and where each type of chemical is used must be critically evaluated prior its use, and the norms guiding its use rigorously enforced (see Najera and Zaim, 2002). For example, there are many appropriate uses for larvicides (temephos sand granules is the most commonly used larvicide) in both routine and emergency response Ae. However, its effectiveness at the community, or operational, level needs be evaluated for each of the containers currently treated with larvicides so that it is used in the most effective manner, and supplies can be maintained for treating those containers where it is most needed. Given the high costs of purchasing the chemicals and equipment, and the labor costs apply them, the operational effectiveness of all types of space spraying must be evaluated and guidelines for their appropriate use enforced as a result of those evaluations (see Reiter and Nathan, 2001). A final activity that should be part of chemical control activities is routine monitoring of insecticide susceptibility. Larval control the use of larvicides prevent larval development in water-holding containers is an essential component of the vast majority of national programs in the region of the Americas. At times, however, the use of larvicides has been indiscriminate, with containers of all sizes, from bottle caps lying about the back yard large water storage containers such as 55-gallon drums and cement tanks, being treated with the chemical. This indiscriminant use of larvicides can lead larval resistance the chemical. In some countries, use of the larvicide in domestic water containers used for storing drinking water has also generated homeowner resistance its use. Program staff in a number of countries readily acknowledges passive resistance temephos. They relate stories of homeowners who remove the chemical once vector control field workers leave the premises, as well as homeowners who actively resist use of the chemical by prohibiting its placement in water containers (interviews by L. Should a cycle be missed due lack of the larvicide, mosquitoes will continue reproduce in containers with little intervention from either residents or government vector control staff. The continued application of chemicals by vector control staff also reinforces community perceptions that the government is responsible for all facets of vector control, with little no responsibility residing with residents. This perception has resulted in limited sustained community involvement in environmental management efforts and community demands for mosquito control methods that may not be effective in the affected area. Adult control Studies have shown that space spraying is relatively ineffective as a routine control strategy (Clark et al. However, factors keep in mind are that the killing effect is transient, with mosquito populations usually recovering within one or two weeks; it is variable in its effectiveness because the aerosol droplets may not penetrate indoors where adult mosquitoes are resting; and the application procedure is costly. All space spraying methods must be evaluated for field efficacy regardless of whether they are being used for routine or emergency actions. Decisions use space sprays and the method for application should be made only after these evaluations have been conducted. Training is needed in communication skills so that all levels of health staff, from vector control field workers health promotion staff nurses and physicians, provide consistent and correct information. Training in the social sciences is especially important for the development of control strategies that are effective, congruent with residents daily living circumstances, and sustainable. This may mean modifying a current recommended method make it more amenable adoption or developing a new method. For example, families that have already experienced cases of dengue in the household may ignore messages encouraging individuals seek medical care since the dengue case was successfully treated at home, that is, the family member recovered and did not suffer more severe disease. Another example of a deceptively simple message commonly seen in educational materials throughout the region is that of covering water storage drums or barrels. The message is so general that it is meaningless and, therefore, impossible implement. Since many families already cover water storage containers, the message has little relevance a large segment of the target audience, despite the fact that most do not properly cover containers prohibit the entry of mosquitoes. Correcting this situation requires an understanding of behavior change theories, ways develop effective mosquito control methods with community input and active participation, and an ability communicate specific messages related treatment seeking. Emergency preparedness, establishing mechanisms, and plans face outbreaks and epidemics Emergency response is a short-term response epidemic situations. Emergency actions are intended be intense, short-term activities that rapidly reduce the adult mosquito population as a means reduce transmission of the virus. Unfortunately, political support for dengue programs oftentimes reflects an emergency response; that is, attention and resources are provided when the country is in the middle of an epidemic, but such support disappears once the epidemic has ended. Although countries may have an emergency plan, they may not be well prepared implement it given that routine actions are already limited. This lack of preparedness can severely impair an effective response during an epidemic. All members should understand their roles and responsibilities during an emergency period. While no studies have shown that space spraying effectively interrupts an epidemic, control methods that reduce the number of potentially infected mosquitoes should be considered during an emergency. Examples of Best Practices Examples of best practices for each of the 10 elements of the Decalogue were solicited from individuals knowledgeable about dengue prevention and control programs in the Americas (results are presented in Table 2). An example was selected if the practice had been expanded beyond a pilot phase (with the exception of DengueNet) as a result of demonstrated effectiveness and had some reported level of sustainability. Individuals involved in the development and/or implementation of the practice were then contacted and asked contribute a five-page description of the best practice, the process used develop the practice, where appropriate, and evidence that the practice was effective and being sustained. List of Best Practices for the 10 Elements of a Comprehensive, Integrated Dengue Prevention and Control Program Essential Program Element Best Practice 1. Weekly Epidemiological Report produced by the Venezuelan Ministry of Health and Social Development 3. Effective community participation Social mobilization of city residents for dengue control, Brazil Community participation elements in the practices from Brazil, Mexico, and Dominican Republic 4. Use of the key container and key premise basic services indices for surveillance and vector control actions, Vietnam 2. Management and control of 55-gallon drums used for water storage, Dominican Republic 5. Critical analysis of the use and function of No best practice identified insecticides 9. Formal health training of professionals Development of the environmental health technician position and training program, Honduras 10. Emergency preparedness No best practice identified While a best practice specifically addressing broad-based community participation was not received, community participation was addressed in the best practices from Brazil, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic. Community participation was key the successful development and adoption of appropriate Ae. And in Brazil, the social mobilization campaign was successful in motivating residents participate in a day of special dengue clean up activities. These best practices provide examples of how invite community 24 participation in the development of control methods and sustain that motivation through implementation. Should countries in the same region experience an epidemic, neighboring countries will be able track the number of cases and deaths and prepare for a potential emergency response depending upon the serotype circulating. Although DengueNet is currently used for historical data analysis, it is still under development and is in the process of being field tested in several countries in the Americas. Currently, global dengue statistics from 1955 2001 can be accessed on DengueNet. As countries begin entering data into DengueNet, real-time updates of standardized epidemiological and virological data will become available. A key objective is ensure that data of the highest possible quality are reported in a timely manner DengueNet. The first 2 meeting on DengueNet implementation was held July 9-11, 2002, in Puerto Rico. The specific objective was launch pilot testing by building on the existing reporting systems and network of dengue laboratories in the Americas. Purpose and objective Forty participants (surveillance epidemiologists and laboratory specialists) from 15 countries participated in this first meeting. The overall objective was describe and demonstrate DengueNet prospective users and develop a framework for DengueNet implementation with emphasis placed on quality of data and active participation of national programs. The first defined the epidemiological data and reporting requirements for DengueNet, modifications needed its present format, identification of countries for pilot testing, and roles and responsibilities of national and international partners. Data collection Epidemiological data: Countries will provide these data by epidemiological week at the state/department level for the large countries and at the island level for island countries. DengueNet will calculate the proportion of the total number of isolations of each serotype as a percentage of total number of isolations of all four serotypes isolated in the country for the time period for which they are provided. General considerations Only the central level of each country will provide data (one source of data per country). The data entered during the pilot testing period will include a disclaimer stating that the system is being tested and that the data for this period are provisional. Roles and responsibilities of the partners in this network Countries will collect, validate, and provide epidemiological and laboratory data, and they will designate the participating centers. Country participation A major outcome of the meeting was that all the representatives of countries in the Americas expressed interest in participating in the DengueNet pilot test, and the representatives of Southeast Asian countries indicated interest in having the system expanded include their region. The participants will follow up with their country authorities obtain official authorization participate in DengueNet. The pilot testing of DengueNet in the Americas will be conducted over a three six-month period. The lessons learned will be built into the implementation framework for high burden countries in the Southeast Asian and Western Pacific regions in 2003. Pilot test data should provide a better indication of how the data are being used. Special attention needs be paid surveillance efforts along national borders. At the first meeting on DengueNet implementation in July 2002, representatives of all participating countries from the Americas expressed interest in participating in the pilot test of DengueNet and the representatives of countries from Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific expressed interest in having DengueNet pilot test expanded include their countries. Evidence that the practice works DengueNet will provide national and international public health authorities with epidemiological and virological information by place and time that can guide public health prevention and control actions. Being able monitor virus transmission and circulating serotypes by place and time during inter-epidemic periods will be useful for early warning of dengue activity in neighboring states/countries, and will provide time for planning increased Ae. In addition, DengueNet contains valuable historical and current data that may be useful for public health researchers support their research and that national and international agencies could use for advocacy purposes. Password protected capability for Critical Permits timely collection and remote data entry in a standard analysis of standardized format into DengueNet via the (comparable) epidemiological Internet directly by national health and virological data from officials affected countries worldwide. A major challenge the success of epidemiological surveillance systems in most countries is reliable, rapid transmission of data from local areas the central level. In addition, entomological data are included during reporting periods when dengue activity has increased. The entomological data can be triangulated with the epidemiological data since data are reported from the state level. The weekly epidemiological report includes a high level of analysis for epidemiological and, when included, entomological data using tables, graphs, and text succinctly summarize the data. Both suspected and confirmed cases are reported since in dengue endemic countries it is important report suspected cases based upon a clinical diagnosis; reporting only laboratory confirmed cases will mask the actual level of dengue transmission, particularly during epidemics. Epidemiological information is an essential component for the proper planning and evaluation of health services. Aegypti, commonly the container index?the percentage of water-holding 34 containers positive for Ae. These data are necessary regardless of whether the actions are routine or an emergency response. Therefore, the weekly epidemiological report provides systematic, opportune, and informative data that can be used make administrative decisions for the prevention and control of the disease.
Buy zoloft 50 mg mastercard. Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder.
Department of Ultrasound depression and sex order zoloft 50 mg overnight delivery, Institute of Radiology depression vs anxiety purchase discount zoloft on-line, Hospital das Clinicas anxiety 7 question test purchase zoloft without a prescription, Medical School of University of Sao Paulo? These techniques take advantage of changed soft tissue elasticity in various pathologies depression medication for teens cheap zoloft 50mg amex yield qualitative and quantitative information that can be used for diagnostic purposes anxiety yoga purchase 25mg zoloft overnight delivery. Measurements are acquired in specialized imaging modes that can detect tissue stiffness in response klinische depression definition generic zoloft 100mg online an applied mechanical force (compression or shear wave). Ultrasound-based methods are of particular interest due its many inherent advantages, such as wide availability including at the bedside and relatively low cost. Several ultrasound elastography techniques using different excitation methods have been developed. In general, these can be classified into strain imaging methods that use internal or external compression stimuli, and shear wave imaging that use ultrasound-generated traveling shear wave stimuli. While ultrasound elastography has shown promising results for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis, new applications in breast, thyroid, prostate, kidney and lymph node imaging are emerging. Here, we review the basic principles, foundation physics, and limitations of ultrasound elastography and summarize its current clinical use and ongoing developments in various clinical applications. Key words: Elastography; Ultrasound; Strain Imaging; Shear Wave Imaging; Liver; Breast; Thyroid; Kidney; Prostate; Lymph nodes. It has been further of being an inexpensive, versatile, and widely developed and refined in recent years enable available modality that can be used at the bedside, quantitative assessments of tissue stiffness. For applications such as liver fibrosis assessment or breast instance, many solid tumors are known differ lesion characterization. This is applied normal (perpendicular surface, first column), shear (tangential surface, second column), and bulk (normal inward or pressure, third column) forces used in ultrasound elastography. In shear wave imaging (b), particle motion is perpendicular the direction of wave propagation, with shear wave speed cS related shear modulus G. In B-mode ultrasound (c), particle motion is parallel the direction of wave propagation, with longitudinal wave speed cL related bulk modulus K. While it is G as: technically easy convert between E and G via equation 9, estimations of these values depend on the =? A S giving suitable tissue contrast for elastography recent consensus advocates reporting results as shear measurements. Excitations methods include quasi-static mechanically-induced displacement via active external compression or passively-induced physiologic motion (orange), dynamic mechanically-induced compression via a thumping transducer at the tissue surface produce shear waves (green), and dynamic ultrasound-induced tissue displacement and shear waves by acoustic radiation force impulse excitation (blue). Since this the excitation are measured perpendicular the method is not dependent on superficially applied acoustic radiation force application or parallel the compression, it may be used assess deeper located 1D transient elastography excitation; the shear wave organs [1]. It is the most widely the manually or physiologically applied stress is used and validated technique for assessment of liver not quantifiable, but by assuming uniform normal fibrosis, and it is often used by clinicians in the office. Typically, using time-motion ultrasound (based on multiple low strain (stiff tissue) is displayed in blue, and high A-mode lines in time at different proximal locations strain (soft tissue) is displayed in red, although the assembled form a low quality image) locate a color scale can vary depending on the ultrasound liver portion 2. The examiner takes repeated this is an alternative approach for measuring measurements with the following criteria for strain. Measurement of the shear wave speed and reported provide a quantitative estimate of results in qualitative and quantitative estimates of tissue elasticity. This creates a near cylindrical shear wave without large vessels or dilated bile ducts. A number of these can be traced back general sonography limitations such as shadowing, reverberation, and clutter artifacts, or the operator-dependent nature of free-hand ultrasound systems [6, 21]. Similarly, tissue attenuation decreases ultrasound signal as a function of depth, limiting accurate assessment of deeper tissue or organs. Fluid or subcutaneous fat also attenuates propagation of the external stimulus applied at the skin surface. In principle, these manufacturer system another a difficult task [4, 6, assumptions violate conventional models that 19, 21, 22]. The assumption that tissue is isotropic stimuli, such as strain elastography, are the most (homogeneous) is violated at tissue interfaces, where challenging reproduce. Measurements in these shear wave reflection at structural interfaces may lead modes are highly subjective since the magnitude of incorrect speed estimates [2]. Similarly, the applied stress is difficult control with operator incompressibility is incorrect since tissues can lose dependent manual compression and the inherent volume when compressed (usually in the form of variability of physiologic motion when used as a fluids). In which introduces a dependency of shear wave speed addition, the extent of stress induced by an operator on excitation frequency. The in general is also susceptible internal sources of adoption of elastography new clinical applications, stress. For example in liver such as characterizing highly heterogeneous tumor applications, it is preferable measure stiffness in the masses or organs, will likely require the adoption of right lobe over the left lobe minimize internal more complex modeling that accounts for tissue stimulations generated by the nearby palpating heart viscoelasticity [25, 26]. In the highly heterogeneous microenvironment, which case of elastography modes that utilize internal contains stiff elastic regions. Since cardiac motion score being the most widely used histopathologic can confound elastography measurements, it is grading system. According this system, the fibrosis recommended sample measurements in the right stages are: F0= normal liver, F1= minimal fibrosis, F2= liver lobe, which has shown the most reliable results significant fibrosis, F3= severe fibrosis and F4= [38, 39]. Major complications, liver capsule, with measurements obtained 4-5 cm such as bleeding, hemobilia, bile peritonitis, deep the skin and within a minimum 1-2 cm of liver bacteremia, sepsis, pneumothorax, hemothorax and parenchyma limit refraction of the pulse. Furthermore, the patient needs be Inter-observer agreement among pathologists in coached in breathing (to stop breathing at the end of grading liver fibrosis/cirrhosis is also not perfect, normal expiration or inspiration) so measurements with kappa statistic ranging from 0. In phase 1 of the high but lesser priority for treatment owing study optimal stiffness cut-off values for identification relatively lower risk of complications [36]. Summary of cut-off values for fibrosis staging according manufacturers/literature. Shear wave speed was estimated endoscopy as the reference standard found that a in pairs of phantoms (one soft and one hard phantom) shear wave velocity cut-off value of 3. Summary of ultrasound elastography studies assessing malignancy of masses in the liver, breast, thyroid, kidney, prostate, and lymph nodes. Among other causes, right heart failure can lead hepatic venous congestion with consecutive elevation of liver stiffness due the could be more accurate. The equipment does not provide was the most specific of the 3 modalities B-mode images, which can limit selection of an (specificity=95. Since fat has a correspond a greater probability of malignancy, constant elastic modulus over various compressions, with scores 1-3 indicating a probably benign lesion, the ratio is a semi-quantitative measurement that and scores 4-5 requiring a biopsy. This study showed based on maximum stiffness (93%, 81%, respectively) excellent sensitivity and specificity (100% and 95%, and on mean stiffness (94%, 71%, respectively) (Table respectively) in differentiating malignant from benign 3, [74]). The lesion is shown as an oval, with colors indicating lesion stiffness (blue=increased, red=decreased) compared the surrounding tissue. With increasing Tsukuba score (1-5), lesions have a higher probability of malignancy. In this system, red color represents stiff tissue and blue color reflects soft tissue. The suspicious hypoechoic lesion (shown within rectangle on B-mode image) has an irregular border, angular margins, is slightly wider than tall and shows posterior acoustic shadowing. The elastogram suggested malignant etiology due increased stiffness (red/yellow/green) and ductal adenocarcinoma was confirmed on subsequent biopsy. The increased shear wave speed in the differentiate between malignant and benign breast surrounding tissues is relevant help characterize lesions. Thyroid ultrasound strain imaging studies can Additional areas needing further research include the be classified by the types of stimuli and scoring determination of appropriate cut-off values of strain systems. It is semi-quantitative thyroid stiffness index (strain in important distinguish the subset of thyroid nodules background normal thyroid / strain in thyroid that are malignant, as morbidity and mortality from nodule) [85, 87]. The Asteria criteria is based on four thyroid cancer increases with disease stage. The nodule appears hypoechoic with ill-defined borders on anatomical B-mode image. The elastogram shows normal thyroid tissue encoded with blue color (soft tissue) and the nodule with red color (stiff tissue), suggesting a malignant nodule. Transverse B-mode image (left) shows small heterogeneous thyroid nodule (lesion within region of interest) with ill-defined margins and microcalcifications in the right thyroid lobe, suggesting malignant etiology. In order for these promising = 88%, positive predictive value = 75%, negative preliminary results gain widespread clinical predictive value = 91%) [78]. Both these conditions can lead obligation of lifetime thyroid hormone replacement extensive morbidity, mortality, and high health care from an unnecessary total thyroidectomy. Allograft renal interstitial disease in the literature: can lead renal transplant failure. Currently, biopsy Manual external compression in strain imaging is the standard method for renal fibrosis staging. Strain imaging has also been used assess Ultrasound elastography cannot be performed native kidneys, although the difficulty of applying on nodules with a calcified shell because the sound external compression the native kidney in the waves do not penetrate the calcifications evaluate retroperitoneal location can limit the accuracy of the central non-calcified portion of interest [86]. Furthermore, studies have shown significant and potentially be confused with benign cysts [109]. In contrast the above promising results, although a direct comparison of the studies is difficult Wang et al. Also, the reported sensitivity and specificity of 88% and 54% respectively negative correlation between shear wave velocity and (Table 3, [112]). About 180,890 new linear structures since glomeruli are spherical and cases of prostate cancer are expected be diagnosed proximal/distal tubes have convoluted shape. The vascular interfaces, decreasing the shear wave core biopsy is conducted in a spatially systematic way velocity, thus, lowering elasticity values. The untargeted biopsy has limitations such as anisotropy is 40% in the medulla and 22% in the procedure-related complications (bleeding and cortex [115], since the cortex anatomy is not organized infection), false negative results [121], and a high rate in linear structures. Analysis of resultant tissue sextant biopsy samples (samples obtained from 6 deformation is used generate an elastogram. Hypoechoic of 96%, 85%, 48%, 99% and 95%, respectively (Table 3, lesions were classified as suspicious and mean tumor [119]). The which carry an intrinsic risk of inadvertently applying detection rates for the combination, systematic and excess compression because of the often end-fire targeted biopsies were 46. Differentiating abnormal lymph nodes in benign Strain imaging depends on the operator, who conditions such as infection or inflammation from manually compresses the prostate using the malignant conditions such as metastatic disease or transducer probe perform the exam. It is difficult primary malignances such as lymphoma is clinically maintain uniform compression over the entire important. However, up 30% of lymph nodes less compression, it is more difficult for strain imaging than 5 mm have been shown have malignant detect prostate cancers that have sparse architecture infiltration in lung, esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, or are located in areas distant from the posterior and rectal cancers [137]. However, these Doppler findings can be plane acquisition; signal attenuation in enlarged difficult assess with small lymph nodes and have prostates which make the evaluation of the anterior not increased sensitivity [137]. Also, in ultrasound has shown centripetal inhomogeneous general correlating elastograms with histology is enhancement with perfusion defects in malignant challenging since the biopsy specimen is a long tract, lymph nodes in distinction the centrifugal not a single round structure as represented as stiff homogeneous enhancement of benign lymph nodes, areas on the elastogram. Most studies show good results, with an standard for diagnosis of lymph node malignancy. This can be done with superficial lymph nodes However, some studies showed mixed results. Full volume imaging could also facilitate infiltration is focal and the benign portion of the registration and fusion of data from various imaging lymph node is unknowingly sampled. However, a separate reactive processes do not change the stiffness of study assessing 89 biopsy-proven cervical lymph lymph nodes and may be barely distinguishable from nodes (37 benign: reactive, histiocytic necrotizing the adjacent soft tissue [137, 143]. These properties lymphadenitis, tuberculosis; 52 malignant: various could aid selection of lymph nodes for biopsy (Figure primary sites) with strain imaging showed high 10) and may provide needle guidance on the sampling sensitivity but low specificity for differentiating regions if for example a volumetric stiffness map benign from malignant lymph nodes, with could be generated. With lymph nodes, the surrounding score yielded a high specificity of 100% with a subcutaneous fat or the sternocleidomastoid muscle sensitivity of 83% (Table 3, [146]). For example, one study assessed 53 ranging from assignment of 4 8 total pattern scores lymph nodes in the setting of upper gastrointestinal [143]. A recent malignancy, with a sensitivity of 83% and specificity meta-analysis of 9 studies including strain imaging of of 96% (Table 3, [138]). B-mode image (left) of a cervical lymph node shows a hypoechoic rounded lymph node. The establishment of a programme for the1 ongoing development of formal guidelines for cancer care was specifed in this plan. In 2005, breast cancer was the most common site of cancer registration for women, with an age-standardised rate of 92 cases per 100,000 females. Please note that while this guideline has used the term women in its recommendations, individual clinical judgments should be utilised determine where a recommendation applies men. It should be noted that the management of women with more advanced breast cancer is beyond the scope of the guideline, so has been excluded. Furthermore, the guideline does not cover all clinical scenarios or medical emergencies. Management of early breast cancer v About the guideline Target audience the guideline is intended primarily for the providers of care for women with early breast cancer. It is also expected that the guideline will have implications for health service provider organisations and funders, and may be accessed by women with early breast cancer. Maori health needs and outcomes should be considered and explicitly addressed throughout the guideline process. It is important differentiate between involving Maori in the guideline development process (the aim of which is encourage participation and partnership), and specifcally considering Maori health issues pertinent that guideline topic at all stages of the guideline development process. Although Maori participation in guideline development aims ensure the consideration of Maori health issues by the guideline team, this is no guarantee of such an output; the entrenched barriers Maori may encounter when involved in the health care system (in this case guideline development) need be addressed. In addition, it is expected that Maori health is considered at all points in the guideline in a less explicit manner. The different types of evidence appraised included, but was not limited, existing guideline research, systematic reviews and randomised controlled trials.
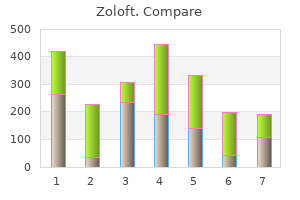
Overall anxiety vision problems order zoloft overnight, 60% rated treatment as very effective depression kjv zoloft 25 mg on-line, most of the remaining rated moderately effective mood disorder genetic factors generic 25 mg zoloft with visa, at week 1 anxiety while driving 50 mg zoloft with visa, (p=0 depression test webmd purchase zoloft 100mg line. Group 2: 4% as the association of Cromoglycate plus nafazoline Tetrizoline (antihistamine) plus decongestive imidazoline imidazoline derivate (decongestive) anxiety kit buy 50 mg zoloft, present in 5% solution (N = effective treatments for 20) vs. Epinastine ed cat hair, cat chloride, edetate epinastine vs vehicle: showed prompt onset (3 dander; dust sodium, 0. Invest mention symptoms of age not four times daily (N = -up at was lower on day 3 in and pranoprofen were No meaningful differences 4. Suggests 1993 ac rosso d by a bilateral age of ophthalmic solution up at treated eye showed ophthalmic solution efficacy. Placebo solution, and / Conjunctival alleviation of the signs Research, seasonal 1 drop in eye 4 after 7 inflammation / allergic and symptoms of allergic Palo Alto, allergic times a day for 7 days. Patients placebo redness scores at allergic received an allergen 3, 10, and 20 minutes disease challenge 27 after challenge, within the minutes after (p<0. Claritin in tablet ne, in the Patanol-Claritin shown be significantly Claritin hip or and history form (N = 15) vs. Placebo, ne, placebo: first 2 hours: the treatment of placebo in treatment of Bausch al seasonal one drop bilaterally and 0. The prognosis is progressively worse with increasingly worse symptoms, especially with systemic symptoms such as occupational asthma. If symptoms include anaphylactic symptoms, then complete removal from exposure is indicated (see Work-related Asthma Guideline). Anaphylaxis is also a rare potential among those with severe allergies, especially when combined with a high exposure. In others, work-up and evaluation for concomitant asthma and consideration of exposure modification and/or removal from work is indicated. In others, immunotherapy is indicated, in which case treatments every 1-2 weeks for a period of many months up approximately 2 years may be indicated. In some cases, measurements of those agent(s) may be indicated help quantify the exposure and guide treatment. Occasionally, the exposures may be reduced and following the measured exposure levels may be of assistance. Azelastine and 14 significantly in total potentially valuable addition for improved allergic 7. Target with allergic allergen-specific severe in the treatment expression on conjunctival project rhinoconjunc conjunctival group vs. No history and for total daily dose superior the placebo outdoor environment in which group showing mention of diagnosis of Azelastine, 1. Placebo improvements in itchy matching the nasal eyes / ears / throat / spray given twice palate and cough were daily (N = 67). Azelastine with azelastine, additive clinical benefit groups had enter mention of 0. Placebo 1spray per symptom for total Azelastine groups nostril twice daily ocular symptoms report taste (N = 151). No fall for at the placebo each eye 6 times a significance between least 2 years; group. Outcomes assessed and after increase in nasal objective method posterior dropout rate. There was a multiple correlation between analogue scale and Copyright 2017 Reed Group, Ltd. No statistically significant reduction between groups in terms of symptoms reduction, (p=002671). No significant results do not clearly support an decreasing nasal years; nostril (N = 15) vs. Sodium at baseline three main eye indicate that the therapeutic details for (Score = Medica with a two azelastine Cromoglycate and after symptoms: itching, use of azelastine eye drops in randomization, 6. Placebo, with placebo group: effective and safe alternative tivitis; levocabasti identical the yes vs no: 39 vs. Patients (Score = unrestricte allergic range of allergen challenge itching with the with a topical ophthalmic not well 5. All randomized treat, one of the three solutions: Copyright 2017 Reed Group, Ltd. Baroody Crosso Sponsored N = 20 with age range Azelastine No follow Allergen and diluent Nasal allergen challenge Data suggest pre 2008 ver by seasonal of 20 42 hydrochloride up challenges were lower releases histamine at the site of treatment with (Score = Trial GlaxoSmit allergic years. On scientific the side ipsilateral advisory the nasal challenge, Copyright 2017 Reed Group, Ltd. Azelastine and after itching, lacrimation, drops provide rapid, dose supported by (Score = Blind No from years for 0. Azelastine and days 7 symptoms: itching, drops are well tolerated and allocation 5. Meltzer, Doubl No N = 294 men Mean age Azelastine qd Follow-up the two Azelastine Azelastine nasal spray 0. These groups patients reported during the 2 also showed significant improved years prior. Rhinoconjunctivitis evaluation of the severity and a for 3 weeks (Score = from a history of 33. Mean scores olopatadine Follow-up at for ocular hyperemia: and baseline, and days day 14: 0. Early phase confirming the results obtained ne Riderca tivitis; following eye (N = reaction 30 minutes at nasal level. Clinical after challenge: total Immunolog changes were symptom score and iche e assessed 5, 10, 15, total number of Allergiche) 20 minutes after inflammatory cells was foundation allergen challenge less in the treatment. Topical be superior in each nostril and nasal scores by treatment usually results in a placebo. The compared systemic drops (1 drop in cetirizine rescue was treatment and can avoid each eye 2 4 higher in placebo adverse events usually times daily) and patients, from day 0 associated with anti nasal spray, one 7 (4. A clinical sign one-half the recommended prick test nedocromil Nedocromil sodium (overall signs of dose of fexofenadine. Solution, 1 drop in 2, and on groups had significantly solution used in conjunction Data suggest 3. It primarily begins in childhood [592, 689], thus is largely considered non-occupational. It may be worsened by non-specific hyperreactivity due wind, dust and sunlight. By inference, treatments recommended for other allergic eye diseases are also recommended for vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Keratonconjunctivitis) age cromoglycate treatment groups the treatment of seasonal efficacy. Placebo levocabastine group well-tolerated for the suggest from the Janssen Treatm 1 drop / eye 4 (22 days) vs. The specific chemical(s) involved, its concentration, quantity and duration of exposure are critical in determining extent of, and limiting the insults of, the injury. Rapid, initial management is likely the most critical aspect of the management and conveys subsequently improved prognosis when rapidly executed. Uncontrolled studies suggest better outcomes with longer duration of irrigation [699]. Medications (including topical creams) Copious Irrigation is recommended for chemical eye exposures. It is also recommended begin irrigation promptly while others attempt identify the specific chemical(s)/agent(s), concentration(s) and duration of exposure. Irrigation should also be used until Morgan lens, if indicated, is available for more severe injuries. Mild discomfort from solution and irrigation Benefits: Limiting extent of burn/injury, earlier relief of pain Frequency/Dose/Duration: Tap water is most commonly available and should be used if that is the most readily available solution, especially for first line, in-plant settings. Generally use topical anesthetic anesthetize the eye when available, as it will assist in better tolerance of irrigation. Indications for Discontinuation: Only after extensive irrigation, usually at least 1-2 liters has been used flush out the chemical. The pH should be checked after discontinuing irrigation assure that additional irrigation is not needed maintain pH neutrality. Rationale: There are no quality studies identifying use compared with non-use of irrigation. Once irrigation is underway, tailoring of further irrigation, including possible use of an irrigating system. Postoperative Indications: High volume exposures and/or highly alkaline/acidic and/or high-risk injuries. It is recommended begin irrigation immediately after eye exposure (see Copious Irrigation above), rather than waiting for setting up an irrigation system. Harms: Mild moderate discomfort from the irrigating system Benefits: Potential further limit extent of burn/injury beyond that obtainable without the system for more severe exposures Frequency/Dose/Duration: Generally use a balanced salt solution. Reassess and consider additional fluid depending on chemical, concentration, dose, duration of contamination, severity and clinical effects. For alkali burns, 2 liters wide open is recommended, then 50mL/hr until pH in eye cul-de-sac is neutral. If balanced salt solution unavailable, tap water may be substituted until balanced salt available or transit definitive care from an in plant setting. Rationale: There are no quality studies comparing use with non-use of irrigating systems. Irrigating systems, including Morgan Lenses are minimally invasive, have minimal adverse effects, are low cost and are selectively recommended for chemical eye exposures. In Cochrane Library, we found and reviewed 12 articles, and considered 1 for inclusion. Medications (including topical creams) Artificial tears or lubricants are selectively recommended for treatment of patients with chemical ocular burns. Postoperative Indications: Chemical ocular burns of sufficient size and pain, and particularly among those with inadequate tearing. Benefits: May provide sufficient tears reduce symptoms and potentially improve healing. Frequency/Dose/Duration: Prn Indications for Discontinuation: Resolution of symptoms Rationale: There are no quality trials of artificial tears for chemical ocular burns. Patients with more extensive burns tend have greater need for artificial tears. Artificial tears are inexpensive, noninvasive, and have low adverse effects and are recommended particularly for those patients with inadequate tears. In PubMed we found and reviewed 623 articles, and Copyright 2017 Reed Group, Ltd. Data (score = buffered saline Research Funds treated Control group (N = 14 time in all three more functions suggest 4. Minocycline twice a day (60 percentage in the antibiotic injection of alkali burns. China (grant mg/kg or 30 mg/kg) (N = high-dosage character, as Minocycline number: unknown) vs Group 3 14 group reduced shown in this (60mg/kg) bid 3030901009015 consecutive days of significantly study and in significantly, Shi-you Zhou) minocycline (60 mg/kg or 30 compared the other reports. N=35 eyes 5 groups according 24h, Average Subconjunctival Randomization De Saline vs Supported by of 35 severity of burns. There was treated with membrane preservative-free artificial a difference in amniotic suspension tears in 1 eye (N = 10). Strength of Evidence Recommended, Insufficient Evidence (I) Level of Confidence Low? Postoperative Indications: Chemical ocular burns Benefits: Reduced pain, decreased inflammatory response. Of the 78 articles considered for inclusion, 6 human randomized trials and 27 animal randomized trials and 4 systematic studies met the inclusion criteria. Comments: Glucocorticosteroid drops have been used for treatment of chemical burns, sometimes in conjunction with vitamin C. Rats aged ten (N = 14) vs Group 2 were as evident as injury can inflammation in rats 12-week-old Vehicle alone (N = early as day 3. Medications (including topical creams) Glucocorticoid ophthalmic drops are recommended for select treatment of chemical ocular burns. Postoperative Indications: Moderate severe chemical ocular burns Benefits: Reduced pain, decreased inflammatory response. Rationale: There are no quality trials for treatment of chemical ocular burns with ophthalmic glucocorticoid drops. These medications are used attempt reduce the inflammatory process associated with healing chemical burns. These drops are low cost, not invasive, associated with low moderate risks and are recommended for more severely affected patients. No quality trials for treatment of chemical ocular burns with ophthalmic glucocorticoid drops were found. When into the media, first week and Saline award National anesthetized (Decadron) every corticosteroids given was either after. The burn has Eye Institute, albino hour, 12 times per daily for six first days, or unaffected or stabilized without Biomedical rabbits by day, plus mixture fourth or fifth week actually somewhat increasing research placing a of neomycin following the burn, did inhibited by the frequency and support grant, filter paper sulfate and not have an adverse steroids at the severity of Eye research disc (7 mm in dexamethasone effect on the cornea. Data Normal with one eye ulceration in oxygen corneal perforation suggest oxygen Saline patched (N = 14) group, not statistically in rabbits and may therapy may delay vs Control group, significant. Mean delay ulceration of corneal ulceration received difference of ulceration the cornea in severe alkali chloramphenicol was 13. Prednisolone cysteine / and drugs, namely between all Prednisolone acetate 1% eye Prednisolone: 3. Control, one drop treatment groups or of normal saline scores of each group six times per day given by individual (N = 5). Devices Eye patching is selectively recommended for treatment of chemical ocular burns.