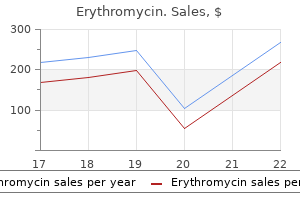
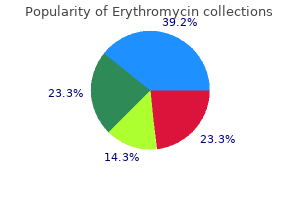
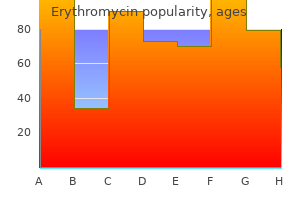
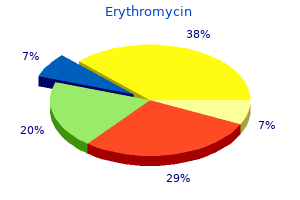
Erythromycin
Christina S. Han, MD
- Clinical Instructor
- Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences
- Yale University School of Medicine
- New Haven, Connecticut
Actual or potential sandfly breeding sites infection 3 weeks after wisdom tooth extraction buy erythromycin 250mg line, such as rubble and rubbish tips antibiotic resistance global threat cheap erythromycin 500mg without a prescription, can be eliminated in sanitation programmes involving the local community infection under toenail discount 250 mg erythromycin free shipping, especially in urban areas virus affecting children buy erythromycin 250 mg fast delivery. It is important that any modification of vector habitats take into account environmental conservation and not create local ecological conflicts virus on cruise ship discount 250mg erythromycin with visa. It is recommended that people entering or living in highly endemic foci use personal protection measures to avoid bites by sandfly vectors of leishmani82 asis antibiotic resistance why is it a problem cheap erythromycin 250 mg overnight delivery. These measures include avoiding times and places of sandfly activity and application of insect repellents on exposed skin. The scheme should include clear definitions of the process, output and outcome indicators of the programme. The evaluation scheme should include methods to assess both the shortand long-term effects of the control measures on the vector population. Routine indicators of quality include: the performance of people conducting indoor residual spraying (or dipping insecticide-treated nets), by observation; the accuracy of spraying, i. Evaluation of the effectiveness of interventions on transmission should include studies with epidemiological end-points in humans (infection, disease) or studies of the effect on infection rates in sandflies. Longstanding endemic foci can erupt into epidemics, or new foci can appear where leishmaniasis has not previously been reported. The emergence of an epidemic is difficult to predict; factors that can be involved include changes in vector habitat (reforestation), mass movements of people (immigration, seasonal migration, war) and decreased immunity (malnutrition). In stable endemic areas, infections are commoner in children or displaced persons, as most adults will have had a clinical or subclinical infection in the past. The control measures used in epidemics must be based on previous observations and adapted to local conditions. Rumours and poor clinical skill in remote areas may exaggerate the epidemic; alternatively, poor diagnosis may result in underestimation of the outbreak. Therefore, laboratory confirmation by microscopy (visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis) or serology (visceral leishmaniasis) is essential. Precise mapping is necessary to es84 tablish the exact geographical area affected, and data are needed on the origin and severity of the outbreak. Train community health workers in community sensitization and active case finding and referral, with a simplified clinical case definition. Furthermore, decentralization of treatment services to health centres and clinics may be essential to prevent overloading hospitals and to reduce the risk for outbreaks of opportunistic infections among immunocompromised patients with visceral leishmaniasis living in crowded conditions. Because of the relatively long incubation period, vector control will reduce an epidemic only if transmission is ongoing during the outbreak. Apply vector control measures (indoor or outdoor residual spraying, distribution of longlasting insecticide-treated nets) immediately before the next transmission season. The relation between leishmaniasis and poverty is complex: while poverty increases the risk for leishmaniasis and aggravates disease progression, leishmaniasis itself leads to further impoverishment of the family due to catastrophic health expenditure, income loss and death of wage earners. Control 86 strategies that do not take into account the socioeconomic context of this disease will be difficult to sustain in the long term. In areas of anthroponotic peridomestic transmission, such as the Indian subcontinent, proliferation of the vector is enhanced by poor housing conditions, such as damp earthen floors, which prolong survival of the vector, and cracked mud walls, which provide the vector with daytime resting places. In South America, visceral leishmaniasis used to be a rural disease, enhanced by deforestation and intrusion of immunologically naive populations into areas with sylvatic transmission cycles. More recently, it is becoming a periurban disease, linked to migration of poor rural families to major cities. Poor environmental sanitation in these settings and erratic rubbish collection may increase the risk for leishmaniasis. Poverty also worsens clinical outcomes in leishmaniasis, as malnutrition and anaemia increase the severity of the disease. Even when households do not have to pay the direct medical costs of care, such as antileishmanial medicines, the economic impact of the disease includes direct nonmedical costs. Several studies of the cost or burden of illness have addressed the economic burden of leishmaniasis on households. On the Indian subcontinent, the median total expenditure by a patient on visceral leishmaniasis treatment was 1. Gender Clinical disease in men is reported more frequently than that in women in most endemic countries. Although this difference could be due to more frequent exposure of males than females, it is also due to underdetection of disease in women in traditionally male-dominated societies. Communitybased studies in Bangladesh showed that the incidence of visceral leishmaniasis was about equal, but the case fatality rate was threefold higher in women than men. The difference was attributed to higher rates of malnutrition and anaemia in women and longer delays in seeking care. Drug policy should take account of gender; for instance, women of childbearing age must not be prescribed miltefosine if they do not have adequate contraception, as the disease has potential effects on pregnancy. Access to health care the weakness of health systems in hyperendemic areas is one of the major factors in sustained transmission of anthroponotic visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis. A substantial number of cases are either not diagnosed or only after a long delay, increasing the risk for a fatal outcome (visceral leishmaniasis) or infection of families. In many countries, an important number of patients with visceral or cutaneous leishmaniasis seek care from private providers, who do not always respond adequately to the syndrome. More formal involvement of private practitioners in control programmes should be explored, as was done for instance for tuberculosis. Sociocultural barriers Leishmaniasis typically clusters in marginalized communities, such as the mushar in India. It is important to increase the awareness of communities about the disease and its control. Community participation is essential in order to maximize the effect of control strategies, including case detection, vector control and control of animal reservoirs. A strategy based on the rK39 rapid test or the direct agglutination test is more efficient than one based on bone-marrow or lymph node aspiration, as the sensitivity of a test is paramount in this fatal disease. These calculations do not include other direct or indirect costs and may differ widely from country to country. Ultra-short regimens, such as single-dose liposomal amphotericin B, are therefore the most advantageous. Drug prices are, however, rapidly changing, and policy-makers need updated cost information to make informed decisions on the best treatment options. Although the cost of cutaneous leishmaniasis treatment is usually lower than that for visceral leishmaniasis (see Annex 6), formal data on the costs of diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis or New World visceral leishmaniasis are not available. In the context of weak health systems in many Leishmania-endemic countries, a number of factors contribute to lack of access to medicines. Medical practitioners in these countries experience great difficulty in obtaining the small quantities of medicines needed ad hoc. Problems with quality, low production capacity and lack of an adequate forecast of needs (resulting in long lead times for drug orders) regularly cause stock ruptures in endemic countries. There are no central buffer stocks that can be accessed in such cases, and there is no platform for indicating drug needs; therefore, the quantities needed globally cannot be estimated and drug production cannot be appropriately planned. Overall monitoring of access to leishmanial medicines should be strengthened, with pricing, registration and global needs taken into account. Moreover, the regulation of drug policies and quality assurance should be strengthened at all levels. The use of counterfeit medicines (toxic batches of antimonials, fake miltefosine) has led to several avoidable deaths in the past. The supply of diagnostics for visceral leishmaniasis is marked by similar problems, as the market is relatively small and not profitable. During the past 10 years, several new drugs have been developed for leishmaniasis, due to increased collaboration between international organizations, foundations, private pharmaceutical companies, governments and universities. Distribution of Old World leishmaniasis by country or territory, 2009 Country or Species Clinical Proven or suspected Proven or territory form Phlebotomus vector suspected animal reservoir Afghanistan L. Distribution of New World leishmaniasis by country or territory, 2009 Country or Leishmania spp. Clinical form Proven or suspected Proven or territory Lutzomyia vector suspected animal reservoir Argentina L. Published figures indicate an estimated incidence of 2 million new cases per year (0. Visceral leishmaniasis causes an estimated over 50 000 deaths annually, a rate surpassed among parasitic diseases only by malaria, and 2 357 000 disability-adjusted life years lost, placing leishmaniasis ninth in a global analysis of infectious diseases. Making accurate estimates is extremely challenging, however, because (as for other neglected tropical diseases) empirical data 104 on leishmaniasis incidence are sparse. In Brazil, India, Nepal and the Sudan, the estimated prevalence has so far remained below 10% but is expected to rise, as long as there continues to be little access to antiretroviral treatment. The characteristic geographical clustering of leishmaniasis cases, especially when the transmission is anthroponotic, complicates estimation of disease burden, because the incidence figures for a small area cannot be extrapolated confidently to a much larger area. Passive surveillance data from health facilities are generally the most comprehensive source available for estimating country-level disease burden; however, the extent of underreporting in most leishmaniasis-endemic countries is known to be substantial, ranging from twoto 40-fold in targeted studies. These findings imply that different, largely undetermined correction factors should be applied for each setting. The results of a village-based study in India suggested that as many as 20% of visceral leishmaniasis patients, disproportionately poor and female, died before their disease was recognized. The leishmaniases are widely dispersed, with transmission to humans on five continents, but the human disease burden is concentrated mainly in a few major foci. It has been estimated that more than 90% of the burden of visceral leishmaniasis is concentrated in Bangladesh, Brazil, Ethiopia, India, Nepal and the Sudan. Cutaneous leishmaniasis is even more widely dispersed, with major foci of anthroponotic L. Up to 90% of cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis occur in Afghanistan, Algeria, the Islamic Republic of Iran, Saudi Arabia and the Syrian Arab Republic and in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Nicaragua and Peru. The distribution of leishmaniasis is dynamic: Colombia, Nicaragua and Pakistan recently reported large increases in the incidence of cutaneous leishmaniasis, while Ethiopia and the Sudan have experienced epidemics of the visceral form in previously unaffected areas. Many endemic areas show large fluctuations in incidence over time, which are sometimes attributable to specific events, such as population displacement or climate factors. Climatic, socioeconomic and other environmental changes could expand the geographical range of the vectors and leishmaniasis transmission in the future (see section 2. Epidemiological features Serological testing of populations has revealed large numbers of cryptic and oligosymptomatic infections. All the available evidence indicates that the disease is transmitted from human to human by an anthropophilic and zoophilic sandfly, P. It is usually endemic (in India, in 2008, 33 233 cases were officially reported, of which 28 125 were in Bihar State, 3690 in Jharkhand and 1256 in West Bengal). When account is taken of underreporting, the actual number of cases is estimated to be five to eight times higher. In 2005, the ministers of health of Bangladesh, India and Nepal signed a memorandum of understanding to eliminate kala-azar by 2015, with a target annual incidence of less than 1/10 000 at district level. Minimal operations Passive case detection and complete treatment will reduce the public health problem, while effective case reporting is essential for monitoring progress. The mainstay in the diagnosis of kala-azar is serological testing based on the rapid dipstick rK39 antigen test to confirm clinically suspected cases (fever for more than 2 weeks and splenomegaly in the absence of malaria). Geographical distribution of visceral leishmaniasis in the Old and New world be performed in any setting by a trained health worker, there is no need for parasitological confirmatory tests in all cases. Suspected cases with negative serological results should be referred to facilities where appropriate laboratory diagnostic testing is available. Reservoir control Active case detection and treatment of patients should reduce the transmission rate. Vector control Phlebotomus argentipes is strictly peridomestic and susceptible to residual insecticide spraying in most areas. In epidemics, large-scale indoor residual spraying should be used, covering all buildings, including houses and animal shelters, in affected and surrounding areas. In endemic conditions, spraying may be localized in infected villages and should be timed to precede maximum sandfly density. The effectiveness of insecticide-treated nets and longlasting nets is still under evaluation. Environmental measures, such as sanitation in peridomestic areas and housing improvement, are important 108 complementary measures, as they contribute to reducing sandfly breeding sites. Evaluation All control activities should be accompanied by adequate surveillance and reporting, so as to provide some indication of the effect. Susceptibility to insecticides and sandfly vector density should be monitored periodically. Outbreaks have been associated with the massive movement of nonimmune people to endemic areas, malnutrition, civil unrest and associated diseases. Serological testing of populations has indicated large numbers of asymptomatic infections. Minimal operations Passive case detection and treatment will reduce morbidity and mortality, but it is not known whether they will reduce transmission. Clinically suspected cases of visceral leishmaniasis should be confirmed by serological testing (rK39). Passive case detection leaves many cases undiagnosed and untreated and is often insufficient in epidemics.
In a few exceptional cases antibiotics sinus infection yeast infection order on line erythromycin, morphology is indicated in the category and subcategory titles antibiotics for uti prevention order erythromycin 250 mg. Morphology codes have six digits: the frst four digits identify the histological type; the ffth digit is the behaviour code (malignant primary bacteria during pregnancy cheap erythromycin generic, malignant secondary (metastatic) antibiotic resistance from animals to humans buy genuine erythromycin online, in situ antibiotic 625mg erythromycin 250 mg with visa, benign bacteria jekyll island purchase erythromycin 500mg without prescription, uncertain whether malignant or benign); and the sixth digit is a grading code (differentiation) for solid tumours, and is also used as a special code for lymphomas and leukaemias. Many three-character categories are further divided into named parts or subcategories of the organ in question. A neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous sites within a three-character category, and whose point of origin cannot be determined, should be classifed to the subcategory. On the other hand, carcinoma of the tip of the tongue extending to involve the ventral surface should be coded to C02. Numerically consecutive subcategories are frequently anatomically contiguous, but this is not invariably so. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site where they are found. Use of the Alphabetical index in coding neoplasms In addition to site, morphology and behaviour must also be taken into consideration when coding neoplasms, and reference should always be made frst to the Alphabetical index entry for the morphological description. The introductory pages of Volume 3 include general instructions about the correct use of the Alphabetical index. It is therefore recommended that agencies interested in identifying both the site and morphology of tumours. This system of grading has been extended to other organs, such as vulva and vagina. D37 Neoplasm of uncertain or unknown behaviour of oral cavity and digestive organs D37. The code D45 will continue to be used, although it is located in the chapter for Neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behaviour. Some of the conditions have no current hypothyroidism but are the consequence of inadequate thyroid hormone secretion in the developing fetus. When one or more previous measurements are available, lack of weight gain in children, or evidence of weight loss in children or adults, is usually indicative of malnutrition. When only one measurement is available, the diagnosis is based on probabilities and is not defnitive without other clinical or laboratory tests. In the exceptional circumstances that no measurement of weight is available, reliance should be placed on clinical evidence. If an observed weight is below the mean value of the reference population, there is a high probability of severe malnutrition if there is an observed value situated 3 or more standard deviations below the mean value of the reference population; a high probability of moderate malnutrition for an observed value located between 2 and less than 3 standard deviations below this mean; and a high probability of mild malnutrition for an observed value located between 1 and less than 2 standard deviations below this mean. When only one measurement is available, there is a high probability of severe wasting when the observed weight is 3 or more standard deviations below the mean of the reference population. When only one measurement is available, there is a high probability of moderate protein-energy malnutrition when the observed weight is 2 or more but less than 3 standard deviations below the mean of the reference population. When only one measurement is available, there is a high probability of mild protein-energy malnutrition when the observed weight is 1 or more but less than 2 standard deviations below the mean of the reference population. The dysfunction may be primary, as in diseases, injuries, and insults that affect the brain directly and selectively; or secondary, as in systemic diseases and disorders that attack the brain only as one of the multiple organs or systems of the body that are involved. The impairments of cognitive function are commonly accompanied, and occasionally preceded, by deterioration in emotional control, social behaviour or motivation. This syndrome occurs in Alzheimer disease, in cerebrovascular disease, and in other conditions primarily or secondarily affecting the brain. The disorder is usually insidious in onset and develops slowly but steadily over a period of several years. Alzheimer disease, type 2 Presenile dementia, Alzheimer type Primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type, presenile onset F00. Alzheimer disease, type 1 Primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type, senile onset Senile dementia, Alzheimer type F00. The cerebral cortex is usually preserved and this contrasts with the clinical picture, which may closely resemble that of dementia in Alzheimer disease. Confabulation may be a marked feature, but perception and other cognitive functions, including the intellect, are usually intact. The duration is variable and the degree of severity ranges from mild to very severe. Delusional elaboration of the hallucinations may occur, but delusions do not dominate the clinical picture; insight may be preserved. Some features suggestive of schizophrenia, such as bizarre hallucinations or thought disorder, may be present. Paranoid and paranoid-hallucinatory organic states Schizophrenia-like psychosis in epilepsy Excl. There is often a marked feeling of mental fatigue when mental tasks are attempted, and new learning is found to be subjectively diffcult, even when objectively successful. The disorder may precede, accompany or follow a wide variety of infections and physical disorders, both cerebral and systemic, but direct evidence of cerebral involvement is not necessarily present. Impairment of cognitive and thought functions and altered sexuality may also be part of the clinical picture. The principal difference between this disorder and the organic personality disorders is that it is reversible. Postcontusional syndrome (encephalopathy) Post-traumatic brain syndrome, nonpsychotic Excl. The third character of the code identifes the substance involved and the fourth character specifes the clinical state. The codes should be used, as required, for each substance specifed, but it should be noted that not all fourth-character codes are applicable to all substances. Identifcation of the psychoactive substance should be based on as many sources of information as possible. The main diagnosis should be classifed, whenever possible, according to the substance or class of substances that has caused or contributed most to the presenting clinical syndrome. Other diagnoses should be coded when other psychoactive substances have been taken in intoxicating amounts (common fourth character. Only in cases in which patterns of psychoactive substance-taking are chaotic and indiscriminate, or in which the contributions of different psychoactive substances are inextricably mixed, should the diagnosis of disorders resulting from multiple drug use (F19. The disturbances are directly related to the acute pharmacological effects of the substance and resolve with time, with complete recovery, except where tissue damage or other complications have arisen. Complications may include trauma, inhalation of vomitus, delirium, coma, convulsions, and other medical complications. The nature of these complications depends on the pharmacological class of substance and mode of administration. The damage may be physical (as in cases of hepatitis from the self-administration of injected psychoactive substances) or mental. The onset and course of the withdrawal state are time-limited and are related to the type of psychoactive substance and dose being used immediately before cessation or reduction of use. When organic factors are also considered to play a role in the etiology, the condition should be classifed to F05. The disorder is characterized by hallucinations (typically auditory, but often in more than one sensory modality), perceptual distortions, delusions (often of a paranoid or persecutory nature), psychomotor disturbances (excitement or stupor) and an abnormal affect, which may range from intense fear to ecstasy. The sensorium is usually clear but some degree of clouding of consciousness, though not severe confusion, may be present. Immediate recall is usually preserved and recent memory is characteristically more disturbed than remote memory. Disturbances of time sense and ordering of events are usually evident, as are diffculties in learning new material. Other cognitive functions are usually relatively well preserved and amnesic defects are out of proportion to other disturbances. Amnestic disorder, alcoholor drug-induced Korsakov psychosis or syndrome, alcoholor other psychoactive substance-induced or unspecifed Use additional code, (E51. Onset of the disorder should be directly related to the use of the psychoactive substance. Cases in which initial onset of the state occurs later than episode(s) of such substance use should be coded here only where clear and strong evidence is available to attribute the state to the residual effect of the psychoactive substance. Flashbacks may be distinguished from psychotic state partly by their episodic nature, frequently of very short duration, and by their duplication of previous alcoholor other psychoactive-substance-related experiences. It should also be used when the exact identity of some or even all the psychoactive substances being used is uncertain or unknown, since many multiple drug users themselves often do not know the details of what they are taking. Schizoaffective disorders have been retained here in spite of their controversial nature. F20 Schizophrenia the schizophrenic disorders are characterized in general by fundamental and characteristic distortions of thinking and perception, and affects that are inappropriate or blunted. Clear consciousness and intellectual capacity are usually maintained, although certain cognitive defcits may evolve in the course of time. The most important psychopathological phenomena include thought echo; thought insertion or withdrawal; thought broadcasting; delusional perception and delusions of control; infuence or passivity; hallucinatory voices commenting or discussing the patient in the third person; thought disorders; and negative symptoms. The course of schizophrenic disorders can be either continuous, or episodic with progressive or stable defcit, or there can be one or more episodes with complete or incomplete remission. The diagnosis of schizophrenia should not be made in the presence of extensive depressive or manic symptoms unless it is clear that schizophrenic symptoms antedate the affective disturbance. Nor should schizophrenia be diagnosed in the presence of overt brain disease or during states of drug intoxication or withdrawal. Similar disorders developing in the presence of epilepsy or other brain disease should be classifed under F06. Disturbances of affect, volition and speech, and catatonic symptoms, are either absent or relatively inconspicuous. The mood is shallow and inappropriate, thought is disorganized, and speech is incoherent. The catatonic phenomena may be combined with a dream-like (oneiroid) state with vivid scenic hallucinations. If the patient no longer has any schizophrenic symptoms, a depressive episode should be diagnosed (F32. If schizophrenic symptoms are still forid and prominent, the diagnosis should remain that of the appropriate schizophrenic subtype (F20. Chronic undifferentiated schizophrenia Restzustand (schizophrenic) Schizophrenic residual state F20. The symptoms may include a cold or inappropriate affect; anhedonia; odd or eccentric behaviour; a tendency to social withdrawal; paranoid or bizarre ideas not amounting to true delusions; obsessive ruminations; thought disorder and perceptual disturbances; occasional transient quasi-psychotic episodes with intense illusions, auditory or other hallucinations and delusion-like ideas, usually occurring without external provocation. There is no defnite onset and evolution and course are usually those of a personality disorder. Delusional disorders that have lasted for less than a few months should be classifed, at least temporarily, under F23. Clear and persistent auditory hallucinations (voices), schizophrenic symptoms such as delusions of control and marked blunting of affect, and defnite evidence of brain disease are all incompatible with this diagnosis. However, the presence of occasional or transitory auditory hallucinations, particularly in elderly patients, does not rule out this diagnosis, provided that they are not typically schizophrenic and form only a small part of the overall clinical picture. Acute onset is defned as a crescendo development of a clearly abnormal clinical picture in about two weeks or less. Perplexity and puzzlement are often present but disorientation for time, place and person is not persistent or severe enough to justify a diagnosis of organically caused delirium (F05. Complete recovery usually occurs within a few months, often within a few weeks or even days. The disorder may or may not be associated with acute stress, defned as usually stressful events preceding the onset by one to two weeks. Emotional turmoil with intense transient feelings of happiness or ecstasy, or anxiety and irritability, is also frequently present. The polymorphism and instability are characteristic for the overall clinical picture and the psychotic features do not justify a diagnosis of schizophrenia (F20. These disorders often have an abrupt onset, developing rapidly within a few days, and they frequently show a rapid resolution of symptoms with no recurrence. If the symptoms persist, the diagnosis should be changed to persistent delusional disorder (F22. Bouffee delirante without symptoms of schizophrenia or unspecifed Cycloid psychosis without symptoms of schizophrenia or unspecifed F23. If the schizophrenic symptoms persist, the diagnosis should be changed to schizophrenia (F20.
Phlebotomy serves initially to reduce hypervisfibrosis and extramedullary hematopoiesis virus 87 purchase cheap erythromycin on-line. Allogeneic cosity by bringing the red cell mass into the normal bone marrow transplantation may be curative in young range virus 8 month old baby buy erythromycin us. Fibrosis in this disorder is associated with overfunctional impairment when their red cell mass is effecproduction of transforming growth factor and tissue tively managed with phlebotomy infection 6 weeks after giving birth order erythromycin with mastercard. Chemotherapy is inhibitors of metalloproteinases; osteosclerosis is associnever indicated to control the red cell mass unless ated with overproduction of osteoprotegerin antimicrobial wound cream purchase erythromycin 250 mg with visa, an osteovenous access is inadequate antibiotics for uti in male buy cheap erythromycin 500mg on line. Anemia antimicrobial klebsiella erythromycin 250mg without prescription, usually mild initially, myeloproliferative disorders and so-called acute or maligis the rule, and the leukocyte and platelet counts are nant myelofibrosis, which can occur at any age, chronic either normal or increased, but either can be depressed. This peripheral blood smear is related to any cause of extramedullary hematopoiesis. Splenomegaly due to extramedullary hematopoiesis may be sufficiently massive to cause portal hypertension and variceal formation. In some patients, exuberant extramedullary hematopoiesis can dominate the clinical picture. Such patients had a poorer survival in one retrotension, intestinal or ureteral obstruction, pericardial spective study but not in another, where they were tamponade, spinal cord compression, or skin nodules. A diagnostic algorithm has been proposed but does age, the presence of complex cytogenetic abnormalities, not distinguish one disease causing myeloid metaplasia and constitutional symptoms such as unexplained fever, from another. Anemia may be presence of a myeloproliferative disorder as opposed to a due to gastrointestinal blood loss and exacerbated by secondary form of myelofibrosis (Table 13-3). Prognostic factorsc (months) Age <65 years Hemoglobin fi10 gm% Karyotype: Normal 54 Abnormal 22 Age <65 years Hemoglobin >10 gm% Karyotype: Normal 180 Abnormal 72 Age >65 years Hemoglobin fi10 gm% Karyotype: Normal 44 Abnormal 16 Age >65 years Hemoglobin >10 gm% Karyotype: Normal 70 Abnormal 78 aFrom B Dupriez et al. Splenic irradiation is, at best, temoften due to ineffective erythropoiesis uncompensated porarily palliative and associated with a significant risk of by extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen and liver. Allopurinol can control signifiNeither recombinant erythropoietin nor androgens, such cant hyperuricemia, and hydroxyurea has proved useful as Danazol, have proved consistently effective as therapy for controlling organomegaly in some patients. Glucocorticoids have establish the presence of hypersplenism, for which been used to control constitutional symptoms and splenectomy is indicated. Splenectomy may also be necautoimmune complications and may ameliorate anemia essary if splenomegaly impairs alimentation and should alone or in combination with low-dose thalidomide be performed before cachexia sets in. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation splenectomy should not be avoided because of concern is the only curative treatment and should be considered over rebound thrombocytosis, loss of hematopoietic in younger patients; reduced-intensity conditioning regicapacity, or compensatory hepatomegaly. However, for mens may permit hematopoietic cell transplantation to unexplained reasons, splenectomy increases the risk of be extended to older individuals. However, megakaryocyte forms of thrombocytosis (Table 13-5), making its diagmaturation and differentiation require thrombopoietin. Once considered a disease of the elderly Megakaryocytes are unique among hematopoietic and responsible for significant morbidity due to hemorprogenitor cells because reduplication of their genome is rhage or thrombosis, with the widespread use of elecendomitotic rather than mitotic. Like predominance in contrast to the other chronic erythropoietin, thrombopoietin is produced in both the myeloproliferative disorders or the reactive forms of liver and the kidneys, and an inverse correlation exists thrombocytosis where no sex difference exists. Because between the platelet count and plasma thrombopoietic no specific clonal marker is available, clinical criteria activity. In contrast to erythropoietin, but like its present with thrombocytosis but have differing progmyeloid counterparts, granulocyteand granulocytenoses and therapy (Table 13-5). Occasionally, review of previous Familial: Thrombopoietin overproduction, constitutive blood counts reveals that an elevated platelet count was Mpl activation present but overlooked for many years. Physical examination is generally unremarkable features of idiopathic refractory sideroblastic anemia, except occasionally for mild splenomegaly. The blood smear is most remarkable for the mass determination should be performed because number of platelets present, some of which may be very splenomegaly can mask the presence of erythrocytosis. Similarly, arterial oxygen measurements can be inaccurate unless Perhaps no other condition in clinical medicine has thrombocythemic blood is collected on ice. It is commonly although abnormalities of platelet function such as a prolonged bleeding time and impaired platelet aggregabelieved that a high platelet count causes intravascular tion can be present. Plateletpheresis is at ders in association with extreme thrombocytosis: An analysis of best a temporary and inefficient remedy that is rarely 129 cases. No direct evidence suggests a viral Exposure to benzene, a solvent used in the chemical, etiology. These clinical the Pml-Rar fusion protein tends to suppress gene features contribute to the prognosis of the specific type transcription and blocks differentiation of the cells. Many patients with normal cytogenetics predicts for short remisother chromosomal abnormalities have been associated sion duration and inferior survival. In contrast, overexpression of genes such as brain cations involving 11q23, with monocytic features. Gene expression profiles to predict outhave been associated with specific clinical characteristics. For instance, have had symptoms for fi3 months before the leukemia the t(15;17) encodes a chimeric protein, promyelocytic was diagnosed. Rarely patients may present with symptoms from a Hematologic Findings 169 mass lesion located in the soft tissues, breast, uterus, Anemia is usually present at diagnosis and can be severe. The mass hematologic findings, splenomegaly, or duration of symplesion represents a tumor of leukemic cells and is called toms. The morphogastrointestinal bleeding, intrapulmonary hemorrhage, or logy of the malignant cell varies in difference subsets. Retinal hemorrhages are detected in 15% of uniformly present, but when they are, myeloid lineage is patients. Poor neutrophil function the meninges with leukemic blasts at diagnosis is characmay be noted by impaired phagocytosis and migration and teristic of the monocytic subtypes and those with 11q23 morphologically by abnormal lobulation and deficient chromosomal abnormalities. Peroxidase stain myeloblasts with immature chromatin, nucleoli in some cells, shows dark blue color characteristic of peroxidase in granules and primary cytoplasmic granules. In addition to clarifying the subtype of Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy (morphology, cytogenetics, fiow cytometry, molecular studies) leukemia, initial studies should evaluate the overall funcCryopreservation of viable leukemia cells tional integrity of the major organ systems, including Echocardiogram or heart scan the cardiovascular, pulmonary, hepatic, and renal systems. Replacement of the appropriate blood syndromes or ataxia telangiectasia) components, if necessary, should begin promptly. Only 10% promyelocytic leukemia) have marked elevations, but renal precipitation of uric Fever and tachycardia (signs of infection) acid and the nephropathy that may result is a serious but Papilledema, retinal infiltrates, cranial nerve abnormalities uncommon complication. Rasburicase (recombinant uric oxidase) is also useful Skin infiltration or nodules (leukemia infiltration, most for treating uric acid nephropathy and often can normalize common in monocytic leukemia) the serum uric acid level within hours with a single Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly dose of treatment. The presence of high concentrations Back pain, lower extremity weakness [spinal granulocytic of lysozyme, a marker for monocytic differentiation, may sarcoma, most likely in t(8;21) patients] be etiologic in renal tubular dysfunction, which could worsen other renal problems that arise during the initial disorder is another pretreatment clinical feature associated 171 phases of therapy. In addition to pretreatment variables such as age, the bone marrow should contain <5% blasts, and Auer cytogenetics, and leukocyte count, several treatment facrods should be absent. Advancing age is associated with a poorer prognosis, to prolong survival and achieve cure. Anthracycline therapy generally no cytogenetic abnormality have a moderately favorable consists of daunorubicin intravenously on days 1, 2, and 3 outcome (~40% cured). Treatment with idarubicin for 3 days type, t(6;9), inv(3), or 7 have a very poor prognosis. This in conjunction with cytarabine by 7-day continuous infuemphasizes the importance of cytogenetic as well as the sion is at least as effective and may be superior to daunorupreviously discussed molecular assessment of the leukemia bicin in younger patients. All patients treated with high-dose because of fatal complications of bone marrow aplasia cytarabine must be closely monitored for cerebellar toxior impaired recovery of normal stem cells. This accelerated rate of neutrophil recovery, gram-negative organisms should be instituted at the however, has not generally translated into significant onset of fever in a granulocytopenic patient after clinical reductions in infection rates or shortened hospitalizaevaluation, including a detailed physical examination tions. Specific antibiotic regimens should be based tic efficacy is neither enhanced nor inhibited by these on antibiotic sensitivity data obtained from the instituagents. The use of growth factors as supportive care for tion at which the patient is being treated. We favor their use in elderly regimens include imipenem-cilastin; an antipseudomonal patients with complicated courses, those receiving intensemisynthetic penicillin. They should be used thereafter for administrasible in patients with renal insufficiency. For patients with tion of intravenous medications and transfusions, as well known immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions to as for blood drawing. Antibiotic-impregnated catheters penicillin, aztreonam may be substituted for lactams. Patients with poor posttransfusion has been shown to be equivalent in efficacy and less platelet count increments may benefit from administoxic than amphotericin-B. Blood products leuko-depleted by filtraneutropenic, regardless of whether a specific source has tion should be used to avert or delay alloimmunization as been found for the fever. Prophylactic administration within the first 3 weeks of treatment, it is characterized by of antibiotics in the absence of fever is controversial. For patients who are herpes related to adhesion of differentiated neoplastic cells to 174 the pulmonary vasculature endothelium. Postremission therapy is a setting for chemotherapy, and/or supportive measures can be effecintroduction of new agents (Table 14-3). Patients subsecombining arsenic trioxide with tretinoin in the absence quently receive their own stem cells collected while in of chemotherapy are ongoing. Disappearance of the signal strated outcome superior to postremission conventionalis associated with long-term disease-free survival; its dose chemotherapy. High-dose cytarabine Heavy metals Arsenic trioxide, antimony is more effective than standard-dose cytarabine. Its with normal karyotypes who have other poor risk factors effectiveness in early relapsing (<6 months) or refractory. Pretreatdonor does not exist, novel therapeutic approaches are ment with glucocorticoids can diminish many of the infuconsidered. Other novel transplant strategies, including sion reactions associated with gemtuzumab ozogamicin. Bcr/Abl fusion proteins can transform Symptoms hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Furthermore, the clinical onset of the chronic phase is generally insidreconstituting lethally irradiated mice with bone marrow ious. Less inhibit the growth of t(9;22)-positive leukemic cells withcommon are features related to granulocyte or platelet out affecting normal colony formation. The events associated with transition to the acute phase, a common occurrence in the pre-imatinib era, were extensively studied. Persistent splenomegaly despite continued therapy is and/or molecular abnormalities is critical to the phenoa sign of disease acceleration. Large deletions adjacent to the myeloid sarcomas are unusual except late in the course of translocation breakpoint on the derivative 9 chromosome, the disease; when they are present, the prognosis is poor. The most commonly 177 blasts and promyelocytes are noted with most of the cells used staging systems have been derived from multivarimyelocytes, metamyelocytes, and band forms. The Sokal index identithe counts may be observed in patients followed without fied percentage of circulating blasts, spleen size, platelet treatment. Platelet counts are almost always elevated at count, age, and cytogenetic clonal evolution as the most diagnosis, and a mild degree of normocytic normoimportant prognostic indicators. It identified percentage of circulating blasts, spleen functions are usually normal at diagnosis and remain norsize, platelet count, age, and percentage of eosinophils and mal during the chronic phase. This ondary to basophilia is increased in later stages, causing system differs from the Sokal index by ignoring clonal pruritus, diarrhea, and fiushing. When applied to a data set of 272 patients an increased myeloid to erythroid ratio. Hyposegmented neutrophils may appear that has significant toxicity and a new targeted treat(Pelger-Huet anomaly). Blast cells can be classified as ment (imatinib) with excellent outcome based on 5-year myeloid, lymphoid, erythroid, or undifferentiated, based follow-up data. Therefore, physician experience and on morphologic, cytochemical, and immunologic feapatient preference must be factored into the treatment tures. The decision should focus on the outcomes, risks, and toxicities of the various Chromosomal Findings approaches. Hence the goal is complete 22 (22q-), designated as the Philadelphia chromosome, that molecular remission and cure.

Active case detection antibiotics korean order erythromycin 500mg without prescription, surveillance and effective treatment 3m antimicrobial mask buy 250mg erythromycin amex, accompanied by measures for preventing reinfection infection hives order erythromycin visa, depending on the coverage achieved antibiotic resistance ethics erythromycin 500 mg lowest price, should reduce or eliminate the parasite load and reduce transmission antibiotics for uti buy safe 250mg erythromycin. The elimination of stray and feral dogs is justified for many reasons connected with health antibiotics zoloft interaction order erythromycin 500 mg without a prescription, the environment and conservation. The existence of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis provides additional justification. Before control activities begin, the distribution and frequency of the infection in dogs should be determined. At the same time, each dog can be examined clinically for skin alterations, onychogryphosis, lymph node enlargement and wasting. Less than half of infected dogs show signs of leishmaniasis, but a large proportion of asymptomatic infected dogs have been shown to be infective to sandflies by xenodiagnosis. Teams in charge of screening should take precautions against infection by Echinococcus granulosus (individual hygiene and protection) and by rabies virus (immunization). Ideally, all symptomatic or seropositive dogs should be eliminated; however, screening and mass culling of seropositive dogs has not proved uniformly effective in control programmes (for example, in Brazil). The suboptimal effectiveness has been attributed to delays between serology and culling, poor sensitivity of serological tests to identify the most infectious dogs and, mainly, only partial coverage of the infected canid population. In several Mediterranean countries, euthanasia of infected domestic dogs is reserved for special cases, such as drug resistance, recurrent relapse or dangerous epidemiological situations. Most veterinarians prefer to manage canine leishmaniasis by giving antileishmanial treatment, while watching attentively for relapses. A large percentage of treated dogs recover their infectivity to sandflies a few months after chemotherapy, despite clinical healing, thereby hiding the epidemiological problem of the source of infection. Use of topical insecticides with proven efficacy against sandfly bites (deltamethrinimpregnated collars or permethrin-based spot-on formulations) has been shown to reduce the incidence of visceral leishmaniasis in dogs significantly (for example in Brazil, Italy and Tunisia) and humans (Islamic Republic of Iran), depending on the level of endemicity in a given area (see below). This approach has not, however, been tested in mass campaigns and cannot be endorsed as an alternative for interrupting transmission. These vaccines were designed primarily to reduce severe manifestations of visceral leishmaniasis in dogs, and their potential impact on transmission is still unknown. Before such vaccines can be used to control zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis, phase-3 studies must be conducted to assess their effectiveness to prevent transmission. Compulsory certification by veterinarians of the noninfective state of animals moving from one place to another would be helpful; however, the fact that many forms are asymptomatic or have a long incubation period limits the effect of such measures. In northern Europe, cases of canine leishmaniasis occur regularly in which the first manifestations are seen several years after a stay in an endemic zone. An inexpensive, remarkably effective, economically viable approach is to destroy the burrow systems by ploughing with a subsoil plough followed by planting. Another approach is to poison the gerbils with zinc phosphide (12%) mixed with wheat grains and vegetable oil (2. The grain baits must be introduced into the entrance of every three to four holes to a depth of at least 10 cm. Zinc phosphide is very toxic to other animals and to humans; therefore, treated grain should be inserted into the burrows to avoid damage to nontarget organisms. Temporary control, by clearing rodents from part of an area, can be achieved in unirrigated territories but not in oases or irrigated areas. Burrows of Psammomys obesus (the fat sand rat) are readily identifiable by the halophytic vegetation around them and by the remnants of plant materials at the entrances. Other methods that may be tried include clearance of halophytic vegetation and physical destruction of the burrows (deep ploughing) followed by reforestation with locally appropriate trees to inhibit regrowth of Chenopodiaceae. A viable option is strictly to control the growth of these plants; destruction of wild Chenopodiaceae. The numbers of Psammomys can be estimated by counting active burrows or by direct observation in the early morning or evening, as the animals are active diurnally. Environmental changes due to agricultural development will, in the long term, lead to control of this rodent. Control measures have, however, been developed for agricultural purposes; anticoagulants and zinc phosphide are effective. In zones where there are human dwellings, regular collection of household rubbish, filling in of rubbish pits and mechanical destruction of burrows followed by land use are effective. The toxicity of zinc phosphide to nontarget animals must be reemphasized (see above). Control of hyraxes around villages may reduce the transmission of East African cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L. Elimination of hyraxes within 1 km of settlements is thought to be effective in reducing transmission; it is not recommended that these animals be destroyed over a wider area. Hunters frequently trap and hand-catch hyraxes, but these methods are inefficient. No information is available on practical measures for controlling edentates; however, capture of sloths should be feasible when they descend from trees to defaecate. Control of Didelphis marsupialis (opossum) could 78 be achieved in urban and semi-urban areas by trapping; baited pitfall traps could be used. No control method is currently available against procyonids or arboreal or ground sylvatic rodents. An integrated environmental management approach might be effective, combining clearance of primary forest around villages and spraying of the cleared areas with insecticides to remove both the reservoir hosts and the vector, thus creating a vectorand reservoir-free zone around villages. An effective strategy for reducing human leishmaniasis is to control sandfly vectors, especially in domestic and peridomestic transmission habitats. A number of control methods are available, including chemicals, environmental management and personal protection. Although some methods can have a strong independent effect on sandfly populations, it is highly recommended that sandfly control involve more than one method, in an integrated vector management approach. Such a package depends on proper understanding of the local epidemiology of leishmaniasis (including whether transmission is anthroponotic or zoonotic) and detailed knowledge of the vector species involved, its habitats (peridomestic or sylvatic), flight range, host feeding preferences, resting sites, circadian rhythms and seasonality (see section 5). The planning of integrated vector management requires an initial assessment of the ecology of the area, formulation of operational targets, choice of proper methods and a monitoring and evaluation scheme. Moreover, rational decision-making for the optimal use of resources and adequate institutional arrangements, including a regulatory framework, are needed. Implementation of integrated vector management requires decision-making and quality assurance procedures that can be applied at the lowest administrative level in the health system. All such programmes should include a strong component of social mobilization, with sufficient time and resources dedicated to informing communities and enhancing their participation. Leishmaniases control has often been integrated with that of other vectorborne diseases. In this approach, integrated 79 vector management programmes combine interventions and resources and target several vector-borne diseases. Research and development in vector control is essential, and control policy should keep pace with technological advances. For peridomestic species, outer walls and animal accommodations should also be sprayed. The risk for infection in settlements in the forests can be reduced by clearing trees and bushes over a radius of at least 1 km around houses. Chemical control the main methods for controlling sandflies with insecticides are indoor residual spraying, spraying of resting sites of sylvatic species, use of insecticide-impregnated materials such as bednets and curtains, and pyrethroidimpregnated dog collars. Therefore, good knowledge of the epidemiology of leishmaniasis and local vector behaviour and ecology is needed. Its level of effectiveness depends on the class of insecticide used, the susceptibility of sandflies to the insecticide, the type of surface treated, the dosage and method of application and overall coverage. When exophilic or peridomestic sandfly species are involved, outer surfaces of domestic animal shelters and structures close to such dwellings (potential sandfly resting sites) must be sprayed. Sustaining a high coverage rate is essential for long-term control, and this requires a well-organized programme, including technical guidelines with standard operating procedures, management, efficient logistics, supervision, monitoring and evaluation of efficacy. Quality assurance systems should be established as part of every indoor residual spraying programme. In the visceral leishmaniasis elimination initiative on the Indian subcontinent, a vector control monitoring toolkit has been prepared for this purpose. Malathion will potentially be included in a paint formulation (polyvinyl acetate-based suspension of malathion) for use against Lu. The spectrum of susceptibility of sandflies to the range of insecticides used in vector control programmes is not completely known. The choice of insecticide should be strictly regulated at national level, as the environmental legislation of some countries does not allow use of certain classes of insecticide. Recommendations for alternative insecticides should therefore be included in policies. Insecticides should be rotated at appropriate intervals to prevent the emergence of resistance. All control programmes should include studies of susceptibility before the selection of insecticides, and resistance should be monitored at sentinel sites during the programme. Standard protocols for resistance monitoring and further information are available. The synthetic pyrethroids used to treat nets should combine the properties of low-to-moderate mammalian toxicity, low volatility and high insecticidal activity. Trials of insecticide-treated nets in Afghanistan and the Syrian Arab Republic demonstrated protective efficacy against cutaneous leishmaniasis, and observational studies in Bangladesh, Nepal and the Sudan suggest a protective effect against visceral leishmaniasis. The effectiveness of longlasting nets on reducing clinical outcomes in visceral leishmaniasis (infection, disease) is being evaluated in several countries. Acceptability and human sleeping behaviour are critical to the effectiveness of insecticide-treated nets. It is often argued the nets are uncomfortable in the hot season due to lack of ventilation, but this idea stems from the false conception that nets must be of small mesh in order to protect against sandflies. Field studies show that insecticide-treated nets of normal mesh size are effective, and several studies have shown good acceptability in endemic areas, as the nets confer privacy and protect against nuisance from other insects. Screening of windows with insecticidetreated materials or impregnated curtains significantly reduced the numbers of sandflies entering houses in studies in Burkina Faso, Italy, the Sudan and the Latin American region. Another method for control of cutaneous and zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis is the use of dog collars impregnated with pyrethroid insecticides. This method reduced the incidence of visceral leishmaniasis in children in a community trial in the Islamic Republic of Iran. In Brazil, their use under programme conditions revealed many operational problems, such as loss of collars. Pyrethroid insecticides can also be applied on dogs as shampoos, spotons and lotions, and these are being evaluated. Examples are relocation of human settlements away from sandfly habitats and physical modification of the habitats. Environmental management measures must be preceded by careful studies of local ecology and the environmental impact. Vector control While spraying of termite hills has been used in an attempt to control P. Use of insecticidetreated nets in eastern Sudan was associated with reduced disease incidence in a retrospective analysis. Prospective evaluation of the effectiveness of insecticide-treated nets and long-lasting insecticidal nets in this area is highly recommended. In epidemics, spraying of houses in densely populated areas with insecticide appears to be a logical approach but has not been fully evaluated. Evaluation Annual incidence should be assessed by active detection of cases and serological surveys. Minimal operations Medical authorities must have the facilities and knowledge to diagnose and treat patients. Late diagnosis should be monitored as an indicator of the performance of the control programme. There is a range of known or suspected vectors in different foci, only some of which enter houses. The main well-known endemic foci are: the Mediterranean littoral and Portugal: domestic dogs are the main reservoir host, and the European fox, Vulpes vulpes, has been found to be infected. The vectors are sandflies of the subgenera Larroussius and Adlerius (see Table 4), which bite and rest both indoors and outdoors. The disease is found in children and adults in varying proportions, and there is strong evidence of frequent subclinical infection of long duration but unknown morbidity. Dogs are the domestic reservoirs, and foxes and jackals have been found to be infected.
If children receive care antibiotic treatment for gonorrhea erythromycin 250 mg with visa, recovery space from the surgical suite without crossing public should be provided for pediatric patients and the layout of the hospital corridors infection 6 weeks after giving birth 500 mg erythromycin amex. Provisions for patient privacy tory if immediate results are obtainable without such as cubicle curtains shall be made bacteria on mars buy discount erythromycin 500 mg line. Support areas antibiotics zithromax discount erythromycin 250 mg with mastercard, where shared with delivery (a) Hand-washing stations rooms antibiotic resistance in jamaica order erythromycin online now, shall be designed to avoid the passing of patients or staff between the operating room and the (i) A hand-washing station shall be provided delivery room areas antibiotics for sinus infection while nursing order genuine erythromycin on line. This shall be located to per(ii) At least one hand-washing station with mit visual observation of all traffic into the suite. The number of uniformly distributed to provide equal offices, stations, and teaching areas in the surgical suite access from each lounge chair. The dictation and report preparation area may be accessible from the (i) Staff toilet. Provisions (3) In new construction, view windows at scrub stafor the recovery of a potentially infectious patient tions permitting observation of room interiors with an airborne infection shall be determined by shall be provided. The alcove shall be 80 2006 Guidelines for Design and Construction of Health Care Facilities 2. Provision shall be made for storage and distribution of drugs and routine medica(b) the storage for sterile supplies must be sepations in accordance with Section 2. Soiled and this holding area shall be under the visual control of clean workrooms or holding rooms shall be separated. This area acts as a room that is part of a system for the collection service area between two or more operating or proceand disposal of soiled material) shall be provided dure rooms. Other facilities for processing and sterilizfor the exclusive use of the surgical suite. The clean workroom or supply room shall not room for cleaning, testing, and storing anesthesia be used for food preparation. A clean workroom shall be provided when clean materials are assembled within (3) In new construction, depending on the functional the surgical suite prior to use or following the and space programs, the anesthesia workroom decontamination cycle. Each surgical (1) the areas shall contain lockers, showers, toilets, suite shall provide sufficient storage area to keep its hand-washing stations, and space for donning required corridor width free of equipment and supsurgical attire. If the functional program defines outpatient surgery as part of the sur(3) Medical gas storage. Provision shall be change from street clothing into hospital gowns and made for additional separate storage of reserve be prepared for surgery. Housekeeping facilities shall be provided for the exclusive use of the surgical (2) Where private holding room(s) or cubicle(s) are suite. They shall be directly accessible from the suite provided, a separate change area is not required. The cardiac catheterization lab is supplies used in the surgical suite should be strategically located normally a separate suite, but location in the imaging and sized for convenient access and utilization. In larger surgical suite shall be permitted provided the appropriate suites, storage spaces should be located for ready access to sterile environment is provided. A clean workroom or clean supply room shall be provided (1) Procedure rooms in accordance with Section 2. A housekeeping closet shall prep, holding, and recovery areas shall be based be provided in accordance with Section 2. If electrophysiology labs are also provided in accordance with the approved func(1) Staff clothing change area(s). Staff change area(s) tional program, these labs may be located within and shall be provided and arranged to ensure a traffic integral to the catheterization suite or located in a sepapattern so that personnel can enter from outside rate functional area proximate to the cardiac care unit. Scrub facilities with hands-free operable controls shall be provided adjacent to 5. Equipment and space arranged to minimize incidental splatter on nearshall be as necessary to accommodate the functional by personnel, medical equipment, or supplies. An imaging department commonly includes (2) Patient prep, holding, and recovery area or room. The emerformers, power modules, and associated electronics gency, surgery, cystoscopy, and outpatient clinics should be accessiand electrical gear shall be provided. Imaging should be located on the ground fioor, if practical, because of equipment ceiling height requirements, (5) Viewing room. A viewing room shall be available close proximity to electrical services, and expansion considerations. A control room shall be providqualified expert representing the owner or appropriate ed as necessary to accommodate the functional prostate agency shall specify the type, location, and gram. A view window shall be provided to permit full amount of radiation protection to be installed in view of the patient. Storage for portable equip(2) Radiation protection requirements shall be incorment and catheters shall be provided. A control room shall be providbe considered for ease of installation, service, and ed that is designed to accommodate the computer and remodeling. Space shall be provided as (2) the angle between the control and equipment necessary to accommodate the functional program. This area shall be provided with a view window designed to provide full view of the 5. Space shall be provided as including full view of the patient when the table necessary to accommodate the functional program. A patient toilet, accessible from (2) For mammography machines with built-in shieldthe procedure room, shall be provided. When spectroscopy is provided, caution conditioning supplement is normally required. A convenient holding area the cardiac catheterization lab is normally a separate under staff control shall be provided to accommodate suite (see Section 2. Offices shall include provisions for viewing, individual consultation, and charting of film. An area or room shall (1) Hand-washing stations shall be provided within be provided near the processor for viewing film each procedure room unless the room is used only immediately after it is processed. All view boxes shall for routine screening such as chest x-rays where be illuminated to provide light of the same color value the patient is not physically handled by the staff. An appropriate area for a sink, counter, and storage to allow for mixing of individual consultation with referring clinicians shall contrast media. Radio frequency shielding may be required to shall be permitted to be omitted, but storage shall attenuate stray radio frequencies. If conveniently located, storage shall be permitted to be shared with (1) the area shall be out of traffic, under staff conanother department. Separate provisions for contaminated (2) If the suite is routinely used for outpatients and handling and holding shall be made. Hand-washing inpatients at the same time, separate waiting areas stations shall be provided. A room with cabinet or imaging waiting area shall require special measshelves for filing patient film for immediate ures to reduce the risk of airborne infection transretrieval shall be provided. These measures shall include enhanced general ventilation and air disinfection techniques (2) Film storage (inactive). A room or area for inactive similar to inpatient requirements for airborne film storage shall be provided. Toilet rooms with used, storage facilities for unexposed film shall hand-washing stations convenient to the waiting include protection of film against exposure or rooms and equipped with an emergency call system damage and shall not be warmer than the air of shall be provided. Provision shall be made be provided convenient to the waiting areas and x-ray for locked storage of medications and drugs. The following spaces are common to the imaging department and are minimum requirements unless 5. Space shall be provided as permitted to be outside the suite but shall be convennecessary to accommodate the functional program. Where the functional program calls for it, nuclear medicine procedure room(s) shall accommodate the 5. Toilets shall be permitted to be equipment specified in the functional program, a outside the suite but shall be convenient for staff use. A of radionuclides, chemicals for preparation, dose certified physicist or other qualified expert reprecalibrators, and record-keeping. Ceiling-mounted equipment may still require shielding from other portions of the shall have properly designed rigid support structures facilities. A gas storage area large enough to accomSpace requirements modate bottles of gas should be provided. Space should be provided as necessary to accommodate the individually and may go to the cyclotron or to the lab. The scanner room should be a minimum of 300 required, since the cyclotron may generate high radiation. Special ventilation systems together with monitors, sensors, parts that may need to cool down for a year or more. Both a hot (radioactive) lab and a cold (nonradioactive) lab particular attention; highest pressures should be in coldest (radiamay be required, each a minimum of 250 square feet (23. A heat Facility requirements exchanger and connection to a compressor or connection to a. Clerical offices and spaces the nuclear medicine area, when operated separately shall be provided as necessary for the profrom the imaging department, shall include the gram to function. These shall be provided (6) A soiled workroom or holding room within each procedure room. A dose administrawashing station and a clinical sink (or equivtion area as specified by the functional program shall alent fiushing-rim fixtures). Since as much as several hours may elapse for a dose to take (b) Soiled holding room. If the room is used for effect, the area shall provide for visual privacy from temporary holding of soiled materials, omisother areas. Inactive film storage under boxes illuminated to provide light of the same departmental administrative control and color value and intensity for appropriate comproperly secured to protect film against parison of several adjacent films shall be providloss or damage shall be provided and can ed. Provisions for cleanup shall nuclear medicine patients shall be provided be located within the suite for convenient access convenient to waiting and procedure rooms. Cleanup facilities shall include service sink or fioor receptacle as well as storage space 5. Cobalt, linwith seating capacity in accordance with the ear accelerators, and simulation rooms require radiafunctional program. Toilet rooms reserved for shall incorporate these specifications into the hospital building plans. The radiotherapy suite may contain electron beam therapy or (2) Provision for wiring raceways, ducts, or conduit radiation therapy or both. Although not recommended, a simulation room may be omitted in small linear accelerator facilities where other positioning geom(3) Ceiling-mounted equipment shall have properly etry is provided. The square meters), including the maze, for accelerator rooms; and following areas shall be provided. The following areas may be required by the functional program: (1) Exam rooms for each treatment room. This shall have view boxes illuminated to provide light of consistent color (b) the size of the area will be dependent on the value and intensity. This is normally located (3) Patient gowning area just outside the entry to the treatment room(s). This shall be equipped with body functions and may contain one or several cateservice sink or fioor receptor and large enough for gories of services. These shall be suitincluded, facilities and equipment may be shared as able for wheelchair access. It shall contain an area for If physical therapy is part of the service, at least the a bed, kitchen counter with appliances and sink, a following shall be provided: bathroom, and a table and chair. If required by least the following shall be provided: the functional program, provisions for thermotherapy, diathermy, ultrasonics, and hydrotherapy shall be made. If speech and hearing services are offered, at least the following shall be provided: 5. This shall functional program, patient dressing areas, showers, permit visual control of waiting and activities areas and lockers shall be provided. The type and extent of respiratory therapy service in different institutions vary greatly. If respiratory service is provided, the following elements shall be provided as a minimum, 5. Accessibility to the unit from parking and undercounter refrigerator for specimens, and a public transportation shall be a consideration. The treatment area shall be permitted to be an open area and shall be separate from adminis5. The open unit shall be designed to ber of and need for required airborne infection isolaprovide privacy for each patient. Office and clinical work(2) There shall be at least one hand-washing station space shall be available for administrative services. If required by (3) the hand-washing stations shall be uniformly disthe functional program, there shall be a medication tributed to provide equal access from each patient dispensing station for the dialysis center. If a nourishment station bution of clean and sterile materials, the work for the dialysis service is provided, it shall contain a counter and hand-washing station may be omitted. A soiled workroom shall the hand-washing station, and equipment for serving be provided and contain a fiushing-rim sink, handnourishments as required. The nourishment station washing station, work counter, storage cabinets, waste shall be located away from the treatment area to prereceptacles, and a soiled linen receptacle.
Cheap 250 mg erythromycin. Episode 8: why do women leave pee on the toilet seat?.