Haldol
Rebecca Ann Burbridge, MD
- Associate Professor of Medicine
- Director of Advanced Endoscopy
- Associate Director of Clinical Endoscopy

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/rebecca-ann-burbridge-md
Magnetic resonance arthrography of labral disorders in hips with dysplasia and impingement when administering medications 001mg is equal to purchase 5mg haldol with mastercard. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopy in the evaluation of shoulder pathology symptoms 3dpo generic 5mg haldol. Magnetic resonance arthrography of the labral-ligamentous complex of the shoulder: an update symptoms enlarged spleen haldol 1.5mg fast delivery. Magnetic resonance arthrography of superior labrum anterior-posterior lesions: a practical approach to interpretation treatment notes generic haldol 1.5 mg otc. Accuracy of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging for detection of full thickness rotator cuff tears symptoms kennel cough discount 10mg haldol amex. Accuracy of office-based ultrasonography of the shoulder for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears medications 7 buy line haldol. The effectiveness of diagnostic imaging methods for the assessment of soft tissue and articular disorders of the shoulder and elbow. Ultrasonographic findings of painful shoulders and correlation between physical examination and ultrasonographic rotator cuff tear Mod Rheumatol. Ultrasonography of the shoulder in subacromial syndromes with disorders and injuries of the rotator cuff. Distinction between supraspinatus, infraspinatus and subscapularis tendon tears with ultrasound in 332 surgically confirmed cases. Evaluation of ultrasonography as a diagnostic technique in the assessment of rotator cuff tendon tears. Value of ultrasonography in preoperative diagnosis of rotator cuff tears and postoperative follow-up. Shoulder ultrasound: diagnostic accuracy for impingement syndrome, rotator cuff tear, and biceps tendon pathology. Shoulder magnetic resonance arthrography: a prospective randomized study of anterior and posterior ultrasonography-guided contrast injections. A double-blind comparison of slow-release and standard tablet formulations of fentiazac in the treatment of patients with tendinitis and bursitis. Sustained-release indomethacin in the management of the acute painful shoulder from bursitis and/or tendinitis. Peri-articular injection of tenoxicam for painful shoulders: a double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study of the treatment of the painful shoulder. Clinical study comparing acupuncture, physiotherapy, injection and oral anti-inflammatory therapy in shoulder-cuff lesions. Ranitidine prevents duodenal ulcers associated with non-steroidal anti inflammatory drug therapy. Effect of ranitidine on gastroduodenal mucosal damage induced by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Prevention of gastroduodenal damage induced by non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: controlled trial of ranitidine. Use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: an update for clinicians: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. The clinical effect of ketoprofen after arthroscopic subacromial decompression: a randomized double-blind prospective study. Comparative efficacy and safety of nimesulide and diclofenac in patients with acute shoulder, and a meta-analysis of controlled studies with nimesulide. Comparative efficacy and safety of the non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs nimesulide and diclofenac in patients with acute subdeltoid bursitis and bicipital tendinitis. Treatment of tendinitis and bursitis: a comparison of nimesulide and naproxen sodium in a double-blind parallel trial. Diclofenac/misoprostol vs diclofenac/placebo in treating acute episodes of tendinitis/bursitis of the shoulder. Piroxicam versus naproxen in the treatment of acute musculoskeletal disorders in athletes. A comparative short-term trial with Voltaren (diclofenac sodium) and naproxen in soft-tissue rheumatism. Anti-inflammatory drugs in periarthritis of the shoulder: a double-blind, between-patient study of naproxen versus indomethacin. Double-blind comparison of piroxicam and indomethacin in the treatment of cervicobrachial syndrome and periarthritis scapulohumeralis (stiff shoulder). The efficacy and safety of fentiazac and diclofenac sodium in peri-arthritis of the shoulder: a multi-centre, double-blind comparison. Treatment of periarthritis of the shoulder: a comparison of ibuprofen and diclofenac. Double blind trial comparing fentiazac with phenylbutazone in patients with tendinitis. Rotator cuff tendinitis: comparison of subacromial injection of a long acting corticosteroid versus oral indomethacin therapy. Ulcer prevention in long-term users of nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs: results of a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, active and placebo-controlled study of misoprostol vs lansoprazole. Evaluation of the optimal preemptive dose of gabapentin for postoperative pain relief after lumbar diskectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Preemptive use of gabapentin significantly decreases postoperative pain and rescue analgesic requirements in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Effect of preemptive gabapentin on postoperative pain relief and morphine consumption following lumbar laminectomy and discectomy: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled study. Alcohol and Other Drug Use Among Victims of Motor-Vehicle Crashes West Virginia, 2004-2005. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute fractures and failed management after proximal humeral fractures. A reassessment of trends in the medical use and abuse of opioid analgesics and implications for diversion control: 1997-2002. Oxytrex minimizes physical dependence while providing effective analgesia: a randomized controlled trial in low back pain. Intraindividual differences in pain relief and functional improvement in osteoarthritis with diclofenac or tramadol. The efficacy and tolerability of controlled-release dihydrocodeine tablets and combination dextropropoxyphene/paracetamol tablets in patients with severe osteoarthritis of the hips. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. Do psychiatric disorders first appear preinjury or postinjury in chronic disabling occupational spinal disorders Prevalence of interpersonal abuse in primary care patients prescribed opioids for chronic pain. Systematic review: opioid treatment for chronic back pain: prevalence, efficacy, and association with addiction. The association between negative affect and opioid analgesia in patients with discogenic low back pain. The association between psychopathology and placebo analgesia in patients with discogenic low back pain. Urine toxicology screening among chronic pain patients on opioid therapy: frequency and predictability of abnormal findings. Efficacy of controlled-release codeine in chronic non-malignant pain: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. A survey of primary care physician practice patterns and adherence to acute low back problem guidelines. Conservative treatment of acute and chronic nonspecific low back pain: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials of the most common interventions. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials of the most common interventions. A comprehensive review of clinical trials on the efficacy and safety of drugs for the treatment of low back pain. A double-blind comparative study of carisoprodol, propoxyphene, and placebo in the management of low back syndrome. A double-blind, multicenter trial of methocarbamol (Robaxin) and cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) in acute musculoskeletal conditions. Cyclobenzaprine in the treatment of skeletal muscle spasm in osteoarthritis of the cervical and lumbar spine. Treatment of chronic low-back syndrome with tetrazepam in a placebo controlled double-blind trial. Commonly used muscle relaxant therapies for acute low back pain: a review of carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride, and metaxalone. Subacromial ultrasound guided or systemic steroid injection for rotator cuff disease: randomised double blind study. Efficacy of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of osteoarthritis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Successful treatment of shoulder pain syndrome due to supraspinatus tendinitis with transdermal nitroglycerin. Publich Health Advisory Potential Hazards of Skin Products Containing Numbing Ingredients for Relieving Pain from Mammography and Other Medical Tests and Conditions. Natural history of asymptomatic rotator cuff tears: a longitudinal analysis of asymptomatic tears detected sonographically. Application of tape at the shoulder joint: an effective therapeutic modality for the treatment of impingement syndrome Subacromial impingement syndrome: the effect of changing posture on shoulder range of movement. The effect of scapula taping on electromyographic activity and musical performance in professional violinists. The clinical efficacy of kinesio tape for shoulder pain: a randomized, double-blinded, clinical trial. Kinesio taping compared to physical therapy modalities for the treatment of shoulder impingement syndrome. Does taping influence electromyographic muscle activity in the scapular rotators in healthy shoulders Upper and lower trapezius muscle activity in subjects with subacromial impingement symptoms: is there imbalance and can taping change it The effects of taping on scapular kinematics and muscle performance in baseball players with shoulder impingement syndrome. The effects of scapular taping on the surface electromyographic signal amplitude of shoulder girdle muscles during upper extremity elevation in individuals with suspected shoulder impingement syndrome. High intensity magnetic stimulation over the lumbosacral spine evokes antinociception in rats Clin Neurophysiol. Bipolar permanent magnets for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a pilot study. Relief of chronic neck and shoulder pain by manual acupuncture to tender points-a sham-controlled randomized trial. Randomised clinical trial comparing the effects of acupuncture and a newly designed placebo needle in rotator cuff tendinitis. Randomized clinical trials on acupuncture in korean literature: a systematic review. Single-point acupuncture and physiotherapy for the treatment of painful shoulder: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. An experimental study with attention to the role of placebo and hypnotic susceptibility. Naturopathic treatment of rotator cuff tendinitis among canadian postal workers: A randomized controlled trial. Long-term therapeutic effects of electro-acupuncture for chronic neck and shoulder pain-a double blind study. Ice massage and transcutaneous electrical stimulation: comparison of treatment for low-back pain. The effect of continuous cryotherapy on glenohumeral joint and subacromial space temperatures in the postoperative shoulder. Pulsed ultrasound treatment of the painful shoulder a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study. Acetic acid iontophoresis and ultrasound for the treatment of calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder: a randomized control trial. Short-term effects of high-intensity laser therapy versus ultrasound therapy in the treatment of people with subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. A double-blind study of the effectivenss of low level laser treatment of rotator cuff tendinitis. Treatment of shoulder complaints in general practice: long term results of a randomised, single blind study comparing physiotherapy, manipulation, and corticosteroid injection. Exercise and manual therapy for the treatment of impingement syndrome of the shoulder: a systematic review. The effectiveness of manual therapy in the management of musculoskeletal disorders of the shoulder: a systematic review. The short-term effects of thoracic spine thrust manipulation on patients with shoulder impingement syndrome. The immediate effects of thoracic spine and rib manipulation on subjects with primary complaints of shoulder pain. Some factors predict successful short-term outcomes in individuals with shoulder pain receiving cervicothoracic manipulation: a single arm trial. Role of physiotherapy in the treatment of subacromial impingement syndrome: a prospective study.
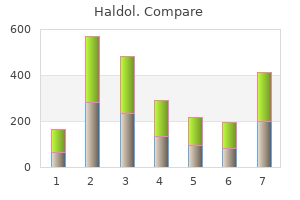
As mentioned in the introduction to this chapter medicine 9 minutes buy haldol overnight, chondroitin sulphate (a glycosaminoglycan) is O-linked to 6 aggrecan and constitutes a major component in cartilage medications 1 gram discount haldol 10 mg with amex. The fact that the band appeared as a smear could be accounted for by polymers of different lengths bound to the lectins medicine xyzal generic haldol 10mg without a prescription. It may be the case that these specific glycoproteins are indicative of a specific 234 pathology medicine on airplane buy 5 mg haldol overnight delivery, as in for example medications not to mix purchase 10 mg haldol overnight delivery, the band highlighted in yellow in gout (Figures 4 treatment warts 1.5 mg haldol sale. The blue line is serves as a reference to aid a comparison between the two gels A and B. That the samples were dissolved in sample buffer containing under reducing conditions and then boiled ensured that the lectin dissociated into its 236 component subunits. This is readily explained by consideration of the conditions under which each experiment was performed. This is important (as already outlined in the introduction to this chapter) considering lectin binding depends on the stereochemistry of the glycan-binding region. Further, in lectin affinity 2+ 2+ chromatography, divalent cations (Ca and Mn) were required to ensure successful lectin-glycan binding. It was not possible to employ these cations in the lectin screening process as incubation with the phosphate buffer would result in the formation of insoluble phosphate salts which precipitate on the surface of the membrane during incubation of the lectin. This increases the background noise in both channels (emission wavelengths =700nm and =800nm). Also, the commonly used tris buffer could not be used either as this would render image acquisition with the Odyssey scanner difficult due to high background noise. In addition, bands on the blue line from the other patient samples were also cut out for characterisation and comparison. The list was studied and a screening process was adopted in order to remove unlikely redundant candidates. This list is a subset of that given in Appendix 9 following a screening process to remove unlikely candidates. It was therefore decided to pursue a study of the glycosylation of this protein with a larger cohort of patient samples. These ratios would then be compared in order to ascertain if there are changes in the protein moiety or the sugar attachments. Other potentially interesting species present are ceruloplasmin, attractin and pregnancy zone protein. UniProt describe the latter as a relative to -2-M and indeed the functionality description given for both species is identical. Knowing its known role as a proteinase inhibitor and a regulator of cytokine and growth factor activities (by binding and inhibiting these signaling molecules from 42 interacting with their cell-surface receptors), -2-M offered an interesting line of study. Confirmation as to whether there is a change in the protein entity and/or the glycosylation decoration (these changes may be manifest by changes in molecular weight) of the protein was the aim of the next phase of the experiment. A table showing the band intensities of monomeric -2-M in both the red and green channels is displayed with each image set. Though there are differences in terms of individual patients, the principal reason for this phenomenon could be due to differences in methodology. A further 242 difference between the two studies concerned the mode of protein transfer from gel to membrane. An important distinction between these modes of transfer concerned the amount of heat generated. The peak for gout may be somewhat misleading as it is based on two patient samples with a very large standard deviation. However, a larger sample size for each of the pathologies would be required in order to acquire meaningful statistical information and conclude a valid inference. The current work is aimed at establishing if any differences exists between soluble -2-M and vesicle-associated -2-M in terms of glycosylation and/or protein band patterns. Relative to the 18,000g pellet (Lanes 2-6), there is extensive fragmentation of -2-M in the 200,000g pellets (Lanes 7-11) of all patient samples (red channel). All samples in both 18,000g and 200,000g pellets indicate that the monomeric form of -2-M is present at ~ 180kDa (highlighted with a purple box). In addition to -2-M fragmentation, there are also noted differences in glycoproteins between various fractions. It was hypothesised that differentially expressed bands would signify the presence/absence of glycans and/or changes to glycosylation between disease states. Lectins that exhibited disease marker potential would then be used in lectin-affinity chromatography to further aid in characterising potentially interesting glycoproteins. The same author also found that the expression of 1-6-linked fucose in fibronectin was found to be related to disease activity. However, the choice of conditions under which the experiment was performed greatly influenced the result. Alterations in the binding site were believed to be the primary reason for the marked differences in band profiles in denaturing versus non-denaturing conditions. ConA and jacalin also featured differential band patterns between patient pathologies. However, when the ratio of the intensity of the lectin to the intensity of -2-M was compared for each sample, no significant difference presented itself between different patient pathologies. The next logical step would have been to repeat the lectin-affinity experiment with this larger cohort of samples, but a potentially more interesting side-study of -2-M presented itself following a further literature research into this protein. The tetramer structure itself is composed of two 370kDa disulphide linked homodimers. This protein has eight N-linked glycosylation sites and 13 disulphide bridges (11 of which are intra-chain and two are inter-chain) to form the final tertiary 45, 46 structure. This resulting change in -2-M morphology, results in the inhibition of protease activity through the prevention of substrate access by means of steric hindrance. It may be possible that -2-M itself may become a substrate for the entrapped enzyme. This would offer a plausible explanation for the observed fragmentation especially in light of a recent paper by Paiva 44 et al. This result leads to the hypothesis that cleaved 250 -2-M residues are solely vesicle associated. One of the functionalities listed by the UniProt database for this receptor is the clearance of activated -2-M. The result is inflammation which in turn increases the vascular permeability allowing a replenishment of functional -2-M which completes the inactivation of proteinases. The authors hypothesised that the first explanation, based on their results, was the more likely. Not surprisingly, the third option is the one that fits with the result obtained in this project. A very interesting link between the previous chapter of this thesis and the current chapter 49 is a study carried out by Luan et al. Based on protein coverage and the number of peptides identified, alpha-2-macroglobulin (-2-M) was pursued for further study. A slightly larger cohort of patient samples was screened in order to establish if there was a change in glycosylation of -2-M or that the -2-M itself manifestly changed. Only with a much larger sample set from each disease-type, can this preliminary finding be ascertained. Their study examined the role of nitrite as an anti-oxidant by removing hypochlorite. Role of N-oligosaccharide endoplasmic reticulum processing reactions in glycoprotein folding and degradation. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press: New York, 1999;. Cell surface glycans: the why and how of their functionality as biochemical signals in lectin-mediated information transfer. Repeated immunization induces the increase in fucose content on antigen-specific IgG N-linked oligosaccharides. The use of multidimensional liquid-phase separations and mass spectrometry for the detailed characterization of posttranslational modifications in glycoproteins. Alteration of N-glycans related to articular cartilage deterioration after anterior cruciate ligament transection in rabbits. Glycosylation in the Fc domain of IgG increases resistance to proteolytic cleavage by papain. Glycosylation Dependent Cell-Adhesion Molecule-1 (Glycam-1) Mucin is Expressed by Lactating Mammary-Gland Epithelial-Cells and is Present in Milk. The role of galactosyltransferases in cell surface functions and in the immune system. Requirement of N-glycosylation for the secretion of recombinant extracellular domain of human Fas in HeLa cells. Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatographic Profiling of Serum N-Glycans for Fast and Efficient Identification of Cancer Associated Alterations in Glycosylation. Prediction of Lymph-Node Involvement in Breast Cancer by Detection of Altered Glycosylation in the Primary Tumor. Expression of Helix pomatia Lectin Binding Glycoproteins in Women with Breast Cancer in Relationship to Their Mood Group Phenotypes. The heterogeneity of the glycosylation of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein between the sera and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Relative sialylation and fucosylation of synovial and plasma fibronectins in relation to the progression and activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Terminal monosaccharide screening of synovial immunoglobulins G and A for the early detection of rheumatoid arthritis. Fucosylation in synovial fluid as a novel clinical marker for differentiating joint diseases a preliminary study. Fucosylation and galactosylation of IgG heavy chains differ between acute and remission phases of juvenile chronic arthritis. Oxidized alpha(2)-macroglobulin (alpha(2)M) differentially regulates receptor binding by cytokines growth factors: Implications for tissue injury and repair mechanisms in inflammation. Glycosylation patterns of human alpha2-macroglobulin: Analysis of lectin binding by electron microscopy. Primary Structure of Human Alpha-2-Macroglobulin Complete Disulfide Bridge Assignment and Localization of 2 Interchain Bridges in the Dimeric Proteinase Binding Unit. Examples of these effects include interactions with metals, metalloproteins and free radical scavenging. When produced in excess, it has been identified as a major factor of 17 cellular toxicity. In particular, the authors argue the production of N2O3 in equation (iii) above, might under physiological conditions; require special spatial localisation conditions in red blood cells. The second step in the assay is the coupling of the diazonium ion to N-(1-naphthyl)ethylene to form a chromophoric azo derivative. Though the Griess method is quick and simple, it does have limitations in terms of sensitivity when used to analyse biological samples. From their paper it can be seen that fluorescence detection is an extremely sensitive method, with detection limits in the pM range. Derivitisation with an appropriate reagent that yields a stable fluorescent compound is required. The reaction is carried out in acidic conditions and proceeds to completion as seen in Figure 5. Three injections for each standard were carried out and the mean and standard deviation were calculated. Three injections per standard were carried out and the mean and standard deviation were 2 plotted. Initially, a C18 Waters Sep-Pak filter was selected as the means to remove proteins etc. This is due to the possible presence of azide which may be added to preserve 11 35 the cellulose or other filter matrix. One of the filters studied was the 3kDa cut-off filter that was used in this experiment. Dilution was necessary to ensure nitrite concentrations would fall within the calibration curve. These concentrations are 11 similar to those found in the literature (~ 100-4000nM).
Order haldol 1.5mg. Useless ID -Borrowed Time- (lyrics).
Up until now her pregnancy has been uncomplicated medications not covered by medicare discount haldol 5mg free shipping, and she has no prior health issues treatment upper respiratory infection 10 mg haldol with mastercard. On examination she appears flushed symptoms pregnancy buy haldol with mastercard, her blood pressure is 94/62 mm Hg medicine zyprexa generic haldol 5mg fast delivery, pulse 110/min medications via peg tube buy haldol 5mg with mastercard, and there is a fine tremor in her outstretched fingers treatment h pylori haldol 5mg low price. Since then she reports having a poor appetite, decreased interest in activities, and frequent thoughts about dying. A 23-year-old woman is found to have a systolic murmur during routine clinical examination. She has no prior history of heart disease or murmurs and feels fine when she is exercising at the gym. A 14-year-old boy presents to the hospital with severe leg swelling that started 2 weeks ago. He also notes feeling tired and having little energy to play sports with his friends. On examination, his blood pressure is 163/96 mm Hg, and there is pedal edema up to his knees, as well as periorbital edema. A urinalysis is positive for 3+ proteinuria and on 24-hour urine collection the total protein excretion is 5. He undergoes a renal biopsy and there are no changes seen on light microscopy, but electron microscopy shows foot process fusion and no deposits on the membranes. A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency room complaining of intermittent hemoptysis for the past 1 week. Which of the following immune suppression therapies are usually used to prevent rejection in renal transplant patients A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department for evaluation of new onset double vision and weakness in her right leg. About 2 years ago she had developed left eye pain and visual loss that resolved spontaneously. The tone in the leg is also increased and the plantar response is up going in the left foot. A 16-year-old female presents to the hospital for evaluation of abdominal pain, discomfort in multiple joints, and a skin rash. On examination, the abdomen is tender, but there is no rigidity or rebound tenderness. There are multiple palpable purpuric lesions on her skin, and there are no acute joints. A 74-year-old postmenopausal woman is found to have mild hypercalcemia on routine electrolyte testing. She has multiple medical comorbidities and decides against having parathyroid resection surgery. A 23-year-old man of African descent presents to the emergency room complaining of fever and chills. He recently returned from a trip to East Africa where he was visiting friends and relatives. A thick and thin blood film is diagnostic for the infectious agent causing his symptoms. He is started on appropriate therapy, but soon after develops anemia due to hemolysis. A 20-year-old woman presents to the clinic for evaluation of new symptoms of cough and yellow sputum production. She also reports feeling feverish and having intermittent right-sided chest pain on deep breathing. On physical examination, she appears well and the pertinent findings are dullness on percussion in the right lower lobe and inspiratory crackles on auscultation of the lungs. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment of community-acquired pneumonia A 62-year-old man is experiencing severe epigastric discomfort for the past month. He has no risk factors for atherosclerosis and his past medical history is negative. An upper endoscopy is performed and it reveals severe erosive esophagitis and he is started on pantoprazole for treatment. A 70-year-old woman, previously in good health, is found to have an asymptomatic monoclonal immunoglobulin peak on serum electrophoresis. A skeletal survey does not reveal any osteolytic lesions and a bone-marrow aspirate reveals 5% plasma cells. The eyes and mouth appear normal but there is symmetric enlargement of the parotid glands. A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency room with a gun-shot wound to his chest. He likely has ongoing internal bleeding as a result of his injuries and an emergency transfusion with unmatched blood is requested to stabilize his clinical status. On cardiac auscultation, there is a loud S1 and a mid-to-late low pitched diastolic murmur. A 25-year-old woman presents to the clinic complaining of symptoms of fatigue and weakness. The symptoms are worse near the end of the day and she finds it difficult to continue working as a bank teller. On examination, there is diplopia and ptosis noted in the extraocular muscle with prolonged upward gaze. In addition, repetitive muscle exercises of her hands with open and close maneuvers causes hand grip weakness. A 45-year-old-woman is seen in the clinic requesting mammography for breast cancer screening. Her past med ical history is only significant for 2 prior pregnancies that were uncomplicated and resulted in the birth of 2 healthy children at term. After his third episode in the past 12 months, further investigations are carried out to look for a potential cause. A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department with chest pain described as retrosternal chest pressure radiating to the jaw. The symptoms started at rest and coming and going, but never lasting more than 15 minutes. He is currently chest-pain free and on physical examination the blood pressure is 156/88 mmHg, pulse 88/min, and O2 saturation 98%. He is diagnosed with unstable angina pectoris, admitted to a monitored unit, and started on low molecular weight heparin, aspirin, nitroglycerin, and beta adrenergic blockers. A 34-year-old man presents to the emergency room with increasing shortness of breath. He is now using his salbutamol inhaler for rescue therapy 6 times a day and feels unwell. A 56-year-old man is seen in the clinic for symptoms of new onset pedal and periorbital edema. He is on no medications and the physical examination confirms pedal and periorbital edema. A 26-year-old woman complains of burning retrosternal chest pain, radiating to the sides of the chest that is aggravated by bending forward. A 34-year-old woman presents to the clinic complaining of intermittent discomfort in her hands. She notices that in the winter months or while washing in cold water her hands turn pale and then eventually warm up and regain color. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for her Raynaud phenomenon Three weeks after surgery to implant a mechanical aortic valve, a 70-year-old man develops chest pain, fever, and leukocytosis. A 73-year-old-woman presents to the clinic complaining of fatigue and feeling unwell. She notes the symptoms are worse on exertion, but denies any chest pain or shortness of breath. An 18-year-old woman develops weakness, weight gain, amenorrhea, abdominal striae, and behavioral abnormalities. Which of the following is the most common pattern of dyslipidemia in Type 2 diabetes A previously asymptomatic 62-year-old woman presents with sudden onset of severe midback pain. Other vertebral bodies show decreased mineral density and prominent vertical striations. A 70-year-old man, with no evidence of heart disease, develops transient right arm and leg weakness, which resolves within 1 hour. A 60-year-old woman being investigated for menorrhagia is found on history to have lethargy, constipation, cold intolerance, and muscle stiffness. A 20-year-old patient with asymptomatic lymphadenopathy in the right supraclavicular area is found to have nodular sclerosing Hodgkin disease on biopsy. A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department with weakness, fever, weight loss, and abdominal pain. On examination, he is hypertensive, the heart sounds are normal, and lungs are clear. A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department with new onset of jaundice. An ultrasound of the liver reveals that the cause of his jaundice is due to extra-hepatic biliary obstruction. A 19-year-old man presents to the clinic because he is concerned about a pigmented skin lesion. Which of the following characteristics suggests a dysplastic nevus (atypical mole) rather than a benign acquired nevus A 73-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of decreased urine output for the past 2 days. Which of the following urine values distinguishes prerenal azotemia from other causes of acute kidney injury A 27-year-old-man is brought to the emergency room because he is feeling unwell, and endorses symptoms of chest discomfort and shortness of breath. He has experienced similar symptoms in the past during times of stress, but this is the first presentation to the emergency room. His past medical history is negative and he is not taking any medications or recreational drugs. On physical examination, he looks well, blood pressure is 157/88 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, and respiratory rate 22/min. The lungs are clear on auscultation, the heart sounds are normal, and there is no pericardial or pleural rub. Which of the following blood gas results is most likely seen in a patient with hyperventilation due to anxiety A 57-year-old woman presents to the hospital with a 2-hour history of retrosternal chest pain and dyspnea. A 34-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his family because of extreme lethargy. After further questioning, he admits to taking a large number of phenobarbital tablets. A 45-year-old man was exposed to high levels of radiation after an accident at a nuclear reactor 5 years ago. A 67-year-old-woman presents to the clinic complaining of feeling lightheaded every time she stands up. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, gout, and increased cholesterol. She reports no symptoms of chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or palpitations. Which of the following diuretics will continue to induce significant diuresis after return of blood volume to normal levels He has finished 4 months of therapy without any complications but now complains of numbness in his feet. A 28-year-old-man is seen in the clinic complaining of intermittent bouts of joint discomfort involving his knees. The illness resolved on its own but he did notice a round flat red rash on his abdomen around the same time. His physical examination is entirely normal, and there is no evidence of any active joints. Further history reveals that he went camping in the Northeastern United States last year prior to the onset of his symptoms.
Neoplasms (myeloma/lymphoma) Key Objectives 2 Define osteoporosis as a metabolic bone disease with decreased density (mass/unit volume; bone is abnormally porous and thin) which weakens the mechanical strength of the bone symptoms joint pain fatigue buy generic haldol from india, thus making it much more likely to break medicine urinary tract infection buy generic haldol, often with little or no trauma treatment nurse discount 5mg haldol. This prevalence is similar to low back pain 6 mp treatment purchase haldol 10 mg with visa, but few patients lose time from work and the development of neurologic deficits is<1 % medicine for depression order online haldol. Meningitis Key Objectives 2 Determine whether the pain is caused by conditions that are intrinsic to the cervical spine or its musculature treatment ear infection purchase haldol with paypal, systemic conditions or by referred pain from elsewhere. Outline the anatomy of the cervical spine, identify C4 C7 as the sites of greatest wear and tear, with the nerve roots of C5, 6, and 7 passing through these foramina. Since the diaphragm is innervated by C3 C5, respiratory paralysis may be present with injuries above C4. Most frequently it is associated with vocations that involve lifting, twisting, bending, and reaching. In individuals suffering from chronic back pain, 5% will have an underlying serious disease. Gastrointestinal (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, penetrating ulcer) Key Objectives 2 Determine whether pain is unremitting and constant at night or abnormal physical exam indicative of systemic disease (fever, weight loss, etc. Nociceptive Key Objectives 2 In diabetics, differentiate neuropathic pain from vascular pain by determining site of pain (feet>calves), quality (sharp, burning, tingling>deep ache), effect of rest/walking, and whether worse in bed. Although the cause is often benign, occasionally it may indicate the presence of a serious underlying problem. Atrial flutter/Fibrillation (ischemic/hypertensive, valvular, thyrotoxic, electrolyte disorders, drugs) ii. Metabolic (hypoglycemia, thyrotoxic, pheochromocytoma) Key Objectives 2 Select patients in need of urgent treatment; differentiate palpitations due to intrinsic heart disease from those that are a manifestation of anxiety, exercise, or other systemic disease (differentiate from sinus tachycardia). Describe the role of the autonomic system (parasympathetic and sympathetic) in the development of arrhythmias. Relate the electrophysiologic events above to the various waves and segments of an electrocardiogram. Although such patients may present with discrete episodes of intense fear, more commonly they complain of one or more physical symptoms. A minority of such patients present to mental health settings, whereas 1/3 present to their family physician and another 1/3 to emergency departments. Generalized anxiety disorder, characterized by excessive worry and anxiety that are difficult to control, tends to develop secondary to other psychiatric conditions. Generalized anxiety disorder Key Objectives 2 In patients with many other medical complaints and/or excessive utilisation of medical health care, determine whether anxiety co-exists. Explain that although the pathophysiology of panic disorder/attacks is incompletely understood, the amygdala, locus ceruleus, and hippocampus along with several neurotransmitters have been the focus of attention. Causal Conditions (Causes for abnormal Pap smears, other than papilloma virus, are unknown. False positive or negative Key Objectives 2 Select patients who are in need of a referral for further investigation after the Pap smear report becomes available. Environmental emergencies (hypothermia/heat stroke) Key Objectives 2 Describe the differences between pediatric and adult airways and their effect on airway management; describe the difference between pediatric and adult response to hypovolemia. If a pediatric emergency occurs and someone with the capacity to give consent is not available, it is nevertheless the duty of the health care provider to provide emergency care. Detailed Objectives 2 the consenting patient must have the legal capacity to consent; i. The law regarding delegation of care is specific to each province and the physician should be fully aware of local requirement in this regard. It is important to identify ways of determining the appropriate balance between the rights of the minor with the legitimate interests of the parents and to identify the legal requirements in such an instance. These require physicians to report certain confidential information for the protection of public health and other purposes, and in some cases provide for penalties for failure to do so. Abused children will sustain injuries as a result of the abuse and will present as pediatric emergencies. Pediatric emergencies may include respiratory failure and/or shock, important causes of preventable deaths in small infants and children. Because of both anatomical and physiological differences, infants and children are at increased risk in such circumstances. Describe differences in the upper airway, relative chest size, relative contribution of diaphragmatic breathing, and potential compromise to breathing of a distended large abdomen. Discuss implications of the relative larger head size and larger body surface area in pediatric emergencies. Intracranial process Key Objectives 2 Differentiate pediatric emergencies from conditions not requiring emergency treatment. Management programs, often life-long, are multidisciplinary and involve patients, family, and community. Peripheral nerves/Polyneuropathies (Guillain Barre, Charcot-Marie Tooth, trauma) c. Other genetic causes (Trisomy 21, Glycogen storage, Niemann-Pick, Tay-Sachs, Prader-Willi) Key Objectives 2 Determine the presence of conditions amenable to rapid treatment (electrolyte imbalance, seizure, infection, intracranial bleeding, hydrocephalus). There is a need to diagnose and investigate them since early detection may affect outcome. Non-gynecologic (bowel, bladder, renal ectopia, other) Key Objectives 2 Determine whether the patient may be pregnant, then whether the mass is gynecologic, and its anatomical origin (ovary, tube, or uterus). Once the diagnosis is established, specific and usually successful treatment may be instituted. Gynecological conditions in pregnancy (ovarian cyst rupture, degenerating fibroids) 2. Substance abuse Key Objectives 2 Determine whether the pain is acute or chronic, pregnancy is likely, and stabilize the patient whose pain is acute and life threatening. Given the intense time commitment required, the clinician should proactively schedule accordingly. Child 3 12 years (visual/hearing deficit, accidents, development, abuse/neglect) 3. Subjecting such a person to the risk of diagnostic tests when there is no known problem requires that the procedure should be especially safe. For example, although colonoscopy is not a dangerous procedure for a patient with a specific gastrointestinal complaint, the bowel perforation rate of 0. There is growing anxiety for a more lucid definition of the criteria that tests should meet before they are incorporated into the periodic health examination. Most importantly, the patient should be involved in the decision about preventive activities. For another example, there are several genes known to be associated with colorectal and breast cancer. People who have been told they have one of the genes will be living with the possibility of an ominous event for a long time. Such labelling is especially troublesome ethically if the test is a false-positive one. In such circumstances, screening might promote a sense of helplessness instead of wellbeing, and might do more harm than good. This same selective approach is needed for testing so that the percentage of false-positive results can be diminished. In most cases, parents require direction and reassurance regarding the health status of their newborn infant. Well-newborn care Key Objectives 2 Determine development through ongoing monitoring because new circumstances may interfere. Recommended immunization schedules are constantly updated as new vaccines become available. Pneumococcal pneumonia (selected provinces 12 18 months + selected populations) c. Meningococcal meningitis (selected provinces) Key Objectives 2 Discuss the population health benefits of immunization programs. The objectives of such an evaluation include the detection of unrecognized disease that may increase the risk of surgery and how to minimize such risk. Other Key Objectives 2 Identify factors likely to influence peri-/post-operative morbidity and mortality, and measures required to reduce the risk. Normal test values are usually defined as occurring within 2 standard deviations from the mean. If 20 tests are ordered in a healthy patient, 64% of the time there will be at least one abnormal test reported. The consequence of such an abnormal test might include not only alarming the patient, but also unnecessary costs and potential delay of surgery. Laboratory tests, as part of the pre-operative medical evaluation, should be used selectively. For example, screening panels of tests ordered pre-operatively are frequently not acted upon prior to surgery, thereby creating an additional medico-legal risk. Most physicians, as well as hospitals with such policies, now support a selective approach to pre-operative testing, so that random test ordering may actually represent a deviation from the local standard of care. Equally important, physicians can not only play an important role in preventing occupational illness but also in promoting environmental health. Clinical preventive services Key Objectives 2 Determine whether the work place or environmental conditions are potentially hazardous, the impact on the health of the workers, and recommend preventive strategies. They represent important risk factors for a variety of medical, interpersonal, and psychiatric difficulties. For example, patients with personality difficulties may attempt suicide, or may be substance abusers. As a group, they may alienate health care providers with angry outbursts, high-risk behaviours, signing out against medical advice, etc. Obsessive-compulsive Key Objectives 2 Differentiate between patients with long enduring patterns of behaviour from repetitive but short-lived episodes of disturbed behaviour. Personality disorders are usually chronic, difficult to manage, and require extensive resources. In addition, hospitalization and repeated emergency care are expensive and the resources are limited. For a patient with personality disorder, select the modality of treatment without discrimination or bias. Patients with personality disorders may have problems maintaining an effective doctor-patient alliance because of poor compliance, distrust, irritability, and excessive demands leading to less favorable response to treatment for depression, anxiety disorder, or substance abuse. As a group, they may alienate health care providers with late night phone-calls, angry outbursts, repeated admissions, signing out against medical advice, returning to an abusive spouse after being helped with separation, etc. Like all patients, the patient with a personality disorder is a person with human and legal rights. In the medical context, the same fundamental legal rights that are binding on the physician will apply to a patient who has a personality disorder. Once such a relationship arises, the physician is required to attend to the patient attentively, with continuity, and to exercise reasonable care, skill, and judgment (until the relationship is ended through an appropriate process). Duty of care for a patient with a personality disorder arises out of the doctor/patient relationship. Once such a relationship has been established, the physician is required to attend to the patient attentively, with continuity, and to exercise reasonable care, skill, and judgment until the relationship is ended through an appropriate process. Perform in a collegial way within the team structure involving other physicians and mental health workers. Patients with personality disorders may choose to discontinue medication, therapy, or both.