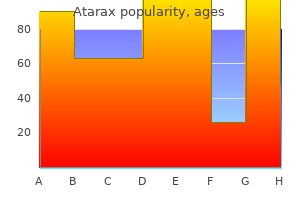
Atarax
Howard Mark Lederman, M.D., Ph.D.
- Director, Immunodeficiency Clinic
- Professor of Pediatrics

https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0000112/howard-lederman
Surgery consists the Norwood surgical procedure and a few centers perform cardiac transplantation for this lesion anxiety 8 weeks postpartum purchase atarax cheap. A 2 year old infant is noted to have mild cyanosis who assumes a squatting position during long walking anxiety symptoms unreal buy generic atarax pills. An infant with a marked cyanotic congenital heart defect with decreased pulmonary vascularity should be treated with: a anxiety 6 months after giving birth purchase atarax 25mg amex. Cyanotic congenital heart-disease with decreased pulmonary blood flow in children (cardiology) anxiety 4 hereford bull 10 mg atarax sale. He also has some shortness of breath with lying down flat when he is trying to sleep anxiety 19th century atarax 10mg line. Heart sounds are tachycardic with a holosystolic murmur 3/6 heard at apex with radiation to axilla anxiety symptoms in 5 year old boy purchase atarax 10mg with visa. He has difficulty with range of motion but can flex his knee 30 degrees passively. Due to the significant cardiac disease with elements of congestive heart failure he is switched to corticosteroids and improves. His heart size decreases over the next 2 weeks, and when it normalizes he is switched back to salicylates for a total treatment duration of 8 weeks. The terms of Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease are sometimes confused. In Hawaii, the ethnic groups at greatest risk are those of Polynesian heritage, with Samoan children being at greatest risk (4-6). The symptoms may be dampened by giving aspirin or other non-steroidal antiinflammatory medications too early, thus not allowing the manifestations to fully develop. Occasionally, the first joint does not resolve completely by the time the second joint becomes involved, and this is termed "additive arthritis", and also fulfills a diagnosis of migrating polyarthritis. Knees and ankles are most often involved, although elbows and wrists can also be involved. Metatarsophalangeal joints can be involved and one can screen for their involvement by squeezing them together, across the foot, and eliciting pain. These findings are important to note, especially in a child with possible symptoms of orthopnea. The murmur of mitral stenosis is a diastolic murmur, although it is described as occurring in mid-diastole, rather then later in diastole like aortic insufficiency. Thus, chorea is often termed a "subacute" phenomenon of rheumatic fever (as opposed to acute rheumatic fever). Despite this lack of evidence of inflammation these patients can develop cardiac disease. For example, they can be located at the tips of the elbows, around the joints, and the bony prominences of the spinal column. It is worthwhile spending some time looking for the nodules as their presence heralds severe carditis (9). Individual lesions usually last for hours and then disappear, which is why it seen so infrequently. If this rash is found, careful cardiac exams should be done, as these children are at greater risk to develop carditis. When evaluating a child with acute onset arthritis, the differential diagnosis can be quite overwhelming. For example, you should be able to describe the type of arthritis you are observing. They can be very painful, but yet if you do not move them, the child is still fairly comfortable. If it is confusing to such well trained individuals, just think of the frustration parents may feel when trying to understand the treatment regiment. Use enteric coated tablets if available, and ask patients to eat prior to taking the aspirin. If the carditis is mild and the child is asymptomatic from a cardiovascular standpoint, then salicylate therapy is usually given. Prednisone is usually given for 2 to 3 weeks followed by aspirin while the corticosteroids are tapered. Antibiotics for prophylaxis against alpha-hemolytic viridans streptococci valvular infection is important prior to and following any dental or gastrointestinal procedure. The development of persistent cardiac disease is dependent on the amount of inflammation suffered by the cardiac structures during the acute period of disease and by the number of recurrences. Each recurrence will cause increased damage to valvular components and an increased likelihood of mitral stenosis, and the need for valve replacement. A classic study demonstrated that with increased carditis severity, there is an increased risk of subsequent cardiac disease (see below). However, the modified Jones criteria can be extremely helpful in assisting the clinician in this process. Special writing group of the committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis, and Kawasaki disease of the council on cardiovascular disease in the young of the American Heart Association. Discontinuing rheumatic fever prophylaxis in selected adolescents and young adults. Collaborative Writing Group United Kingdom and United States Joint report on rheumatic heart disease: the evolution of rheumatic heart disease in children. Cardiac exam reveals tachycardia, and a loud, harsh, blowing, grade 3/6, holosystolic murmur, heard best over the lower left sternal border, but no frictional rubs and no gallops. On hospital day 3, the Staph aureus is methicillin/oxacillin sensitive, so his antibiotics are changed to oxacillin. Carditis (inflammatory conditions of the heart) includes myocarditis, pericarditis and endocarditis. Pericarditis and myocarditis are usually viral or post-viral, but they may be due to rheumatic fever as well. Infective Endocarditis Prior to the era of antibiotics, patients suffering from infective endocarditis had mortality rates of nearly 100%. Some hypothesize the reason for this is due to the current increase in survival rate of children with congenital heart disease. It is theorized that the cause of infective endocarditis stems from the hemodynamically turbulent flow which causes endothelial thickening that provides a place for a platelet and fibrin thrombus to develop. Alphahemolytic streptococci (which includes strep viridans) are responsible for 75% of subacute endocarditis and S. The clinical course of infective endocarditis varies from an acute to subacute course and is usually based on the offending microorganism. Traditionally, the microorganisms which are responsible for acute infective endocarditis include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In the pediatric setting, the clinical distinctions are still useful, perhaps more so than in the elderly population. In 20% of infective endocarditis, a new cardiac murmur or change in a preexisting murmur occurs. Embolic episodes may also be a part of the clinical course, however this is more common in adults than in children. Emboli originating from left-sided endocarditis may cause renal infarcts resulting in frank hematuria, splenic infarcts resulting in left flank pain, or stroke-like symptoms resulting from cerebral emboli. Emboli from right-sided endocarditis may cause chest pain and shortness of breath due to pulmonary embolism. Several sources describe a diagnostic criteria (the Duke criteria) to allow early recognition of endocarditis, when vegetations are still too early to detect. A patient is considered to have infective endocarditis if 2 major criteria or 1 major plus 3 minor criteria are met. The major criteria are: positive blood cultures x2 and endocardial abnormalities on echocardiography. Blood cultures are the most valuable laboratory tests in making the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Therefore, it is very important to obtain blood cultures prior to antibiotic treatment. Echocardiography is most helpful in children with normal cardiac anatomy or with isolated valvular abnormalities. Isolation of the infecting microorganism by blood culture is extremely important, not only in making the diagnosis, but also in planning for treatment. The microorganisms that are revealed from the blood cultures will strongly determine the type of antibiotic regimen to be used. Although antibiotic regimens vary depending on the infective microorganism, one general principle is true in the treatment of infective endocarditis: complete eradication of the infecting microorganism with bactericidal agents will usually require weeks of therapy. Initially when blood cultures are still pending, empiric antibiotics should be started. Obtaining occasional blood cultures during the first 8 weeks after cessation of treatment is warranted, because most relapses occur during this period. These include a significant embolic event, persistent infection, and progressive congestive heart failure especially when the aortic or mitral valve is involved. Prophylactic antibiotics are recommended for children who are at risk to develop infective endocarditis, while undergoing procedures that may induce a bacteremia. At risk patients include those who have significant heart defects associated with turbulent blood flow. The maintenance of optimal dental care and oral hygiene is also important for children at risk for infective endocarditis. Mortality rates are slightly higher in patients with acute staphylococcal infection, fungal infection, and prosthetic valve endocarditis. Myocarditis Myocarditis is defined as an inflammatory response within the myocardium. The categories of myocarditis are divided into infectious myocarditis and generalized autoimmune myocarditis. Any virus may cause this, but the most notable viruses are coxsackie viruses, echovirus, influenza virus, mumps, and rubella. Some speculate infectious myocarditis may result from toxins secondary to the infectious agent, others speculate the mechanism is secondary to an immune reaction. Diminished heart tones may be the only clinical clue pointing toward Page 284 myocarditis. Chest radiographs may show an enlarged heart and depending on the severity of the heart failure, pulmonary venous congestion may be present. Echocardiography may reveal a nonspecific dilation of the heart chambers, most commonly the left ventricle. The main importance of an echocardiogram is to exclude a pericardial effusion and to assess myocardial contractility. Controversy remains on routine endomyocardial biopsies for suspected myocarditis because the pathology is often patchy, therefore a negative biopsy cannot exclude the diagnosis. The treatment of myocarditis most often focuses on the treatment of arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. Treatment of the heart failure consists of bedrest, oxygen, and congestive heart failure treatment. Etiologies include acute bacterial pericarditis, acute viral pericarditis, postpericardiotomy syndrome, acute rheumatic fever and uremia. Moderate pericardial effusion secondary to pericarditis may also show up on x-ray as an enlarged cardiac silhouette but the x-ray will not be able to distinguish pericardial effusion from myocardial dilation. Much like infective endocarditis, the incidence of acute bacterial pericarditis has dramatically declined since the development of antibiotics. The most common settings for acute bacterial pericarditis include septicemia or hematogenous or direct spread into the pericardium from another site, such as with pyelonephritis, osteomyelitis, tonsillitis, bacterial pneumonia and empyema. The common microorganisms responsible for most acute bacterial pericarditis are Haemophilus influenzae type B, Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococcus, meningococcus, streptococcus species and tuberculosis infection. Patients with acute bacterial pericarditis will usually manifest with acute onset of chest pain, high fever, tachycardia, frictional rub, tachypnea and toxemia. Acute bacterial pericarditis often is associated with an infection elsewhere, therefore an intensive search for the primary source is essential. Blood cultures are important and it is recommended that three to five sets should be obtained in the first 1 or 2 days after admission. These blood cultures are positive 4080% of the time and the appropriate antimicrobial agent given for 4 to 6 weeks should be chosen based on the susceptibility testing. Acidfast stains for tuberculosis of the sputum, gastric contents, or urine are considered if blood cultures come back negative. Acute viral pericarditis is often associated with the aforementioned viral myocarditis. The typical signs and symptoms of acute viral pericarditis include a low-grade temperature, chest pain, and a frictional rub. Does the pediatric case presented at the beginning of this chapter meet the Duke Criteria for Diagnosis of infective endocarditis What type of prophylactic antibiotic against infective endocarditis would you prescribe to a nine-year old female, with a past medical history only remarkable for an allergic reaction to penicillin, scheduled for a tooth extraction the next day Which of the following answer is the most severe clinical manifestation commonly found in pediatric myocarditis No antibiotics are needed, because this particular patient has no risk factors for infective endocarditis. Although c may be associated with viral myocarditis, viral pericarditis is most likely self-limiting. The patient immediately becomes briefly bradycardic followed by resumption of a normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 140 beats per minute. An irregular heart rhythm is not an unusual finding in children with or without known cardiac disease.
It can be ately discuss with the children anatomical facts related to helpful to place visual cues in the indoor and outdoor learngender identity and sex differences anxiety symptoms perimenopause cheap 25mg atarax visa. In addition to the health and safety 83 Chapter 2: Program Activities Caring for Our Children: National Health and Safety Performance Standards topics for children in Standard 2 anxiety symptoms adults cheap atarax 25mg online. Participative education for Child care programs should consider offering credit for children: An effective approach to increase safety belt use anxiety of death cheap atarax 10mg on-line. Parental/guardian and safety issues for all age groups served anxiety symptoms while sleeping 10 mg atarax mastercard, should be in a behavior can be modifed by education anxiety symptoms urination safe 10mg atarax. If the facility suggests a referral or resource anxiety chest pain order 25mg atarax overnight delivery, this hearing/vision screening, monitoring growth and should be documented in the childs record. When values collide: Exploring a cross p) Handling loss, deployment, and divorce; cultural issue. Health and safety education for parents/guardians should utilize principles of adult learning to maximize the potential for parents/guardians to learn about key concepts. Parent/guardian attitudes, beliefs, fears, and educational and socioeconomic levels all should be given consideration in planning and con85 Chapter 2: Program Activities Chapter 3 Health Promotion and Protection Caring for Our Children: National Health and Safety Performance Standards guardians and staff can exchange information when face-to3. For children younger than twenty-four months of teacher(s) in conducting a health check. The items in the age, health supervision includes documentation and plotting standard can serve as a checklist to guide learning the proof sex-specifc charts on child growth standards from the cedure until it becomes routine. For children twenty-four months of age and older, parent/guardian to the staff of the child care facility. Bright futures in practice: by the exchange of information, with parental/guardian Nutrition. Growth charts are based on data from naPhysical Activity tional probability samples, representative of children in the general population. Their use by the primary care provider the facility should promote childrens active play every day. All children, birth to six years, should the caregiver/teacher, can direct the caregivers/teachers participate daily in: attention to disease, poor nutrition, or inadequate physical a) Two to three occasions of active play outdoors, activity that requires modifcation of feeding or other health weather permitting (see Standard 3. These incorporate the childs activities during their time at the early outdoor times can be curtailed somewhat during care and education program. Numerous reports suggest that children are not meeting daily recommendations for physical activity, and that chilInfants should have supervised tummy time every day when dren spend 70% (10) to 87% (11) of their time in early care they are awake. Children may only spend about 2% to 3% of time betime (three to fve minutes), increasing the amount of time as ing moderately or vigorously active (11). Very young children are entirely dependent on their caregivTime spent outdoors has been found to be a strong, ers/teachers for opportunities to be active (12-15). The infant will lift his/her head and use his/her arms to try to see your face (27). For training materials and more ideas of effective and ageChildren should have adequate space for both inside and appropriate games for young children, consider the followoutside play. Active start: A statement of physical activity guidelines for Experts disagree about the appropriate amount of physical children birth to fve years. Med Sci Sports Exerc a) the National Association for Sport and Physical Edu38:2086-94. Angloand Mexican-American preschoolers at home and at recess: Activity patterns and environmental infuences. Factors parents use in selecting play spaces for young lines for Americans, 2010 at. Correlates of physical activity at home in Family Child Care Home Mexican-American and Anglo-American preschool children. Variability and tracking of physical activity over 2 yr in Activity young children. The childcare environment and childrens physical preschoolers: Understanding prevalence and measurement issues. Children tummy shown to hinder achievement of developmental milestones, should be observed closely when playing in dirt/soil, so that say physical therapists. Short pose a safety risk, individual child health risk, or signifcant exposure of the skin to sunlight promotes the production of health risk of frostbite or of heat related illness. Nevertheless, some riding in a carriage or stroller; however, infants should be ofweather conditions make outdoor play hazardous. Infants receiving formula and water Warning is issued when wind chill temperatures are life can be given additional formula in a bottle. Children for an All Hazards radio network, making it a single source whom cold weather is an asthma trigger may be helped by for comprehensive weather and emergency information. Some alerts may be delayed or missed because Family Child Care Home of problems on the Internet or the cell-phone network. A children and, over multiple years of exposure, can contribchilds symptoms may include shivering, clumsiness, slurred ute to permanent decreased lung size and function (1,2). Chairs for adults on playgrounds inhibit the promotion of Although general public is not likely to be affected at childrens physical activity. Continuing education activities are a health alert signifying that everyone may experience useful in disseminating knowledge about effective games to more serious health effects. The entire sider incorporating structured activities into the curriculum population is more likely to be affected. N care and education settings offer caregivers/teachers the Engl J Med 351:1057-67. Diesel time and to educate parents/guardians about alternative exhaust particles exert acute effects on airway infammation and activities that families can do with their children (3). Effects of child care sleep environment, staff should immediately move policy and environment on physical activity. Documentation that training has occurred and that are comfortably clothed (not overheated or sweaty), these individuals have received and reviewed the written and that bibs, necklaces, and garments with ties or policy should be kept on fle. Also, the caregiver/teacher devices should be used unless required by the childs should check to ensure that the infants head remains unprimary care provider, and no other items should be covered and re-adjust clothing as needed. Recent research and demonstration active, and ongoing supervision when infants are falling to projects (2) have revealed that: sleep, are sleeping, or are becoming awake. Parents/guardians and caregivers/teachers want infants to Training that includes observations and addresses barritransition to child care facilities in a comfortable and easy ers to changing caregiver/teacher practices would be most manner. Special Care Plans: Some facilities require staff to place Concern about Plagiocephaly: If parents/guardians or infants in a supine position for sleep unless there is docucaregivers/teachers are concerned about positional plagiomentation in a childs special care plan indicating a medical cephaly (fat head or fat spot on head), they can continue to need for a different position. Using pacifers in a sanitary and safe fashion in should be placed (or encouraged to lie down) on their backs group care settings requires special diligence. American Academy of Pediatrics, Task Force on Sudden Infant Family Child Care Home Death Syndrome. The facility should provide an opportunity for, but should not require, sleep and rest. This rest may guardians take the pacifers home with them and bring them take the form of actual napping, a quiet time, or a change back to the facility. There are studies that show is free of fuid after cleaning to ensure the infant does not inthe amount of time young children sleep in a twenty-fourgest it. Pacifers and sudden infant death syndrome: during the time they are in child care). Pacifer use: ing, holding a child while swaying, singing, reading, patting A systematic review of selected parenting web sites. Is sleep duration at home twice a day may be exempted since additional associated with childhood obesity A systematic review and metabrushing has little additive beneft and may expose a child analysis. Local dental health professionals can facilitate compliance with these activities by offering education and Rest Areas training for the child care staff and providing oral health All children should have access to rest or nap areas whenpresentations for the children and parents/guardians. Tooth decay cannot develop without this plaque which contains the acid-producing bacteria in a childs mouth. Red book: 2009 report of the Committee on Infectious their meals and snacks during a full day in child care. However, if children swallow more than recomonly a smear of fuoride toothpaste (rice grain) on the brush mended amounts of fuoride toothpaste on a consistent when brushing. In facilities where tooth brushing is an activity, each child Caregivers/teachers should encourage parents/guardians should have a personally labeled, age-appropriate toothto establish a dental home for their child within six months brush. Adolescent children should be informed about the effect of Toothpaste is not necessary if removal of food and plaque tobacco products on their oral health and additional reasons is the primary objective of tooth brushing. American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Pediatric for fecal contamination of the caregivers/teachers hands, Dentistry. Diapering practices that reduce the frequency and severity of diaper dermatitis will require less application of skin 3. If a cloth diaper with a separate lining is used, the standard: modern disposable paper diapers with absorbent outer covering and inner lining should be changed together material, and single unit reusable diaper systems with an inat the same time as a unit and should not be reused in the ner cotton lining attached to an outer waterproof covering. There is no reason to use the toilet for stool if less they have a care plan noting a different procedure from disposable diapers are being used. Comparison of stool containment in cloth and single-use aggravate diaper dermatitis (2). Reusable cloths Caregivers/teachers should never leave a child unattended should be stored in a washable, plastic-lined, tightly on a table or countertop, even for an instant. A safety strap covered receptacle (within arms reach of diaper or harness should not be used on the diaper changing table. The If an emergency arises, caregivers/teachers should bring cover should not require touching with contaminated any child on an elevated surface to the foor or take the child hands or objects. All cleaning and b) Put soiled disposable diapers in a covered, plasticdisinfecting solutions should be stored to be accessible to lined, hands-free covered can. Childrens hands often stray into the diaper area (the area a) Dispose of the disposable paper liner used on the of the childs body covered by diaper) during the diapering diaper changing surface in a plastic-lined, hands-free process and can then transfer fecal organisms to the envicovered can; ronment. Although gloves disinfectants may require rinsing the change table may not be required, they may provide a barrier against surface with fresh water afterwards. This may reduce the presence of enteric pathogens under the Step 8: Perform hand hygiene according to the procedure in fngernails and on hand surfaces. If caregivers/ later come in contact with uncontaminated surfaces such teachers or children who are sensitive to latex are present in as hands, furnishings, and foors (1,3). Always follow the manufacturers instructions for use, Commonly, caregivers/teachers do not use disposable application and storage. Therefore, the spray bottle enough, there will be less need to remove visible soil from should be put away before hand hygiene is performed, (the surfaces later and there will be enough paper to fold up so last and essential part of every diaper change) (4). Department of Health and Human e) Disposable gloves, if you plan to use them (put Services, Offce of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and gloves on before handling soiled clothing or pull-ups) Evaluation. It is a good idea for the child care Caregivers/teachers should never leave a child unattended facility to request a few extra pair of socks and shoes on a table or countertop, even for an instant. A safety strap from the parent/caregiver to be kept at the facility in or harness should not be used on the changing surface. The procedure for changing a childs stored in a washable, plastic-lined, tightly covered soiled undergarment and clothing is designed to reduce the receptacle (within arms reach of diaper changing contamination of surfaces that will later come in contact tables) until they can be laundered. Posting the multi-step procedure may help objects; caregivers/teachers maintain the routine. Taking the supplies out of their containers and c) If gloves were used, remove them using the proper leaving the containers in their storage places reduces the technique (see Appendix D) and put them into a likelihood that the storage containers will become contamiplastic-lined, hands-free covered can; nated during changing. Put the wipes paper that is large enough to cover the area likely to be into the plastic-lined, hands-free covered can. If the childs clean buttocks are put down on a soiled sura) Dispose of the disposable paper liner used on the face, the childs skin can be resoiled. Infectious organisms are present and detergent, rinse; on the skin and pull-ups or underwear even though they are d) Wet the entire changing surface with a disinfectant not seen. To reduce the contamination of clean surfaces, that is appropriate for the surface material you are caregivers/teachers should use a fresh wipe to wipe their treating. Although gloves may not Step 7: Perform hand hygiene according to the procedure in be required, they may provide a barrier against surface conStandard 3. Red book 2009: Report of the Committee on Infectious Prior to disinfecting the changing table, clean any visible Diseases. Respiratory opportunities for the ingestion of zoonotic parasites that infections transmitted from animals. Hand hygiene with Children and staff members should wash their hands using an alcohol-based sanitizer is an alternative to traditional the following method: handwashing with soap and water when visible soiling is not a) Check to be sure a clean, disposable paper (or present. If a child can not open the door or turn off the faucet, Hand Hygiene they should be assisted by an adult. Hand hygiene warm water also promotes adequate rinsing during handwith an alcohol-based sanitizer is an alternative to handwashing (1). Preventing tion of towel; and the spread of infuenza (the fu) in child care settings: Guidance for b) Incidents of unintentional strangulation have been administrators, caregivers/teachers, and other staff. Handwashing: shown to reduce transmission of organisms that cause Clean hands save lives. Staff members and children should be taught to cover their mouths and noses with a tissue when they cough or sneeze. For guidance on disinfectants, refer to Apcleaning up of spills of human milk, or for diapering; pendix J, Selecting an Appropriate Sanitizer or Disinfectant. Such techniques include fuids containing blood (such as watery discharges from avoiding touching surfaces with potentially injuries) pose a potential risk, because bloody body fuids contaminated materials unless those surfaces contain the highest concentration of viruses. Wearing of gloves to feed or hand creams or lotions (which can cause glove clean up spills of expressed human milk is unnecessary, but deterioration); caregivers/teachers should avoid getting expressed human e) After removing latex gloves, wash hands with a mild milk on their hands, if they have any open skin or sores on soap and dry thoroughly; their hands. If caregivers/teachers have open wounds they f) Practice good housekeeping, frequently clean areas should be protected by waterproof bandages or disposable and equipment contaminated with latex-containing gloves. Hand hygiene Appendix J: Selecting an Appropriate Sanitizer or Disinfectant Appendix L: Cleaning Up Body Fluids and sanitizing of contaminated surfaces is required when gloves are used. Creating a contact dermatitis); Chapter 3: Health Promotion 116 Caring for Our Children: National Health and Safety Performance Standards latex-safe school for latex-sensitive children.
Most patients infected with either species have a self-limited course and recover completely anxiety symptoms bloating discount atarax amex. No antihelminthic drug is proven to be effective and some patients have worsened with therapy anxiety symptoms breathing order atarax with american express. Mebendazole or albendazole each with or without a corticosteroid appear to shorten the course of infection (K Sawanyawisuth and K Sawanyawisuth anxiety in teens cheap 10 mg atarax with visa, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2008; 102:990; V Chotmongkol et al anxiety fatigue purchase atarax 10 mg amex. Gastric anisakiasis can usually be diagnosed and treated by endoscopic removal of the worm anxiety 18 weeks pregnant buy 25 mg atarax mastercard. Enteric anisakiasis is more difficult to diagnose; it can be managed without worm removal as the worms eventually die anxiety pain order 10mg atarax free shipping. Surgery may be needed in the event of intestinal obstruction or peritonitis (A Repiso Ortega et al, Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 26:341; K Nakaji, Intern Med 2009; 48:573). Safety of ivermectin in young children (<15 kg) and pregnant women remains to be established. Exchange transfusion has been used in combination with drug treatment in severely ill patients and those with high (>10%) parasitemia. Immunosuppressed patients and those with asplenia should be treated a minimum of 6 weeks and at least 2 weeks past the last positive smear. Some patients may be co-infected with the etiologic agents of Lyme disease and human granulocytic anaplasmosis. Atovaquone is available in an oral suspension that should be taken with a meal to increase absorption. Oral clindamycin should be taken with a full glass of water to minimize esophageal ulceration. Quinine should be taken with or after a meal to decrease gastrointestinal adverse effects. Use of tetracyclines is contraindicated in pregnancy and in children <8 years old. Tetracycline should be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals and/or dairy products. Mebendazole, levamisole or ivermectin could be tried if albendazole is not available. Metronidazole resistance may be common in some areas (J Yakoob et al, Br J Biomed Sci 2004; 61:75). Nitazoxanide, paromomycin, or a combination of paromomycin and azithromycin may be tried to decrease diarrhea and recalcitrant malabsorption of antimicrobial drugs, which can occur with chronic cryptosporidiosis (B Pantenburg et al, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2009; 7:385). In sulfa-allergic patients, pyrimethamine 50-75 mg daily in divided doses (plus leucovorin 10-25 mg/d) has been effective. In one study, single-dose ornidazole, a nitroimidazole similar to metronidazole that is available in Europe, was effective and better tolerated than 5 days of metronidazole (O Kurt, Clin Microbiol Infect 2008; 14:601). A program for monitoring local sources of drinking water to eliminate transmission has dramatically decreased the number of cases worldwide. The treatment of choice is slow extraction of worm combined with wound care and pain management (Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58:1123). Since family members are usually infected, treatment of the entire household is recommended; retreatment after 14-21d may be needed. Antihistamines or corticosteroids may be required to decrease allergic reactions to components of disintegrating microfilariae that result from treatment, especially in infection caused by Loa loa. Endosymbiotic Wolbachia bacteria, which are present in most human filariae except Loa loa, are essential to filarial growth, development, embryogenesis and survival and represent an additional target for therapy. For patients with microfilaria in the blood, Medical Letter consultants start with a lower dosage and scale up: d1: 50 mg; d2: 50 mg tid; d3: 100 mg tid; d4-14: 6 mg/kg/d in 3 doses (for Loa Loa d4-14: 9 mg/kg/d in 3 doses). A single dose of 6 mg/kg is used in endemic areas for mass treatment, but there are no studies directly comparing the efficacy of the single-dose regimen to a 12-day course. One review concluded that the 12-day regimen did not have a higher macrofilaricidal effect than single dose (A Hoerauf, Curr Opin Infect Dis 2008; 21: 673; J FigueredoSilva et al, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1996; 90:192; J Noroes et al, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1997; 91:78). Diethylcarbamazine should not be used for treatment of Onchocerca volvulusdue to the risk of increased ocular side effects (including blindness) associated with rapid killing of the worms. In heavy infections with Loa loa, rapid killing of microfilariae can provoke encephalopathy. Diethylcarbamazine is potentially curative due to activity against both adult worms and microfilariae. Diethylcarbamazine should not be used for treatment of this disease because rapid killing of the worms can lead to blindness. Skin reactions after ivermectin treatment are often reported in persons with high microfilarial skin densities. Unlike infections with other flukes, Fasciola hepatica infections may not respond to praziquantel. Triclabendazole (Egaten Novartis) appears to be safe and effective, but data are limited (J Keiser et al, Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2005; 14:1513). All patients should be treated with medication whether surgery is attempted or not. S Pasuralertsakul et al, Am Trop Med Parasitol 2008; 102:455; G Molavi et al, J Helminth 2006; 80:425. Some of the listed drugs and regimens are effective only against certain Leishmania species/strains and only in certain areas of the world (J Arevalo et al, J Infect Dis 2007; 195:1846). Medical Letter consultants recommend consultation with physicians experienced in management of this disease. In one open-label study one 10 mg/kg dose of liposomal amphotericin B was as effective as 15 infusions of amphotericin B (1 mg/kg/d) on alternate days (S Sundar et al, N Engl J Med 2010; 362:504). Two other amphotericin B lipid formulations, amphotericin B lipid complex (Abelcet) and amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate (Amphotec)have been used, but are considered investigational for this condition and may not be as effective (C Bern et al, Clin Infect Dis 2006; 43:917). The relapse rate is high; maintenance therapy (secondary prevention) may be indicated, but there is no consensus as to dosage or duration. One study in India used a 14-day course of paromomycin (S Sundar et al, Clin Infect Dis 2009; 49:914). Topical paromomycin should be used only in geographic regions where cutaneous leishmaniasis species have low potential for mucosal spread. A formulation of 15% paromomycin/12% methylbenzethonium chloride (Leshcutan)in soft white paraffin for topical use has been reported to be partially effective against cutaneous leishmaniasis due to L. The methylbenzethonium is irritating to the skin; lesions may worsen before they improve. In a placebo-controlled trial in patients 12 years old, miltefosine was effective for treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis due to L. At this dosage pentamidine has been effective in Colombia predominantly against L. For pubic lice, treat with 5% permethrin or ivermectin as for scabies (see page 10). Permethrin and pyrethrin are pediculocidal; retreatment in 7-10d is needed to eradicate the infestation. Medical Letter consultants prefer pyrethrin products with a benzyl alcohol vehicle. Resistance, which is a problem with other drugs, is unlikely to develop (Med Lett Drugs Ther 2009; 51:57). Malathion is both ovicidal and pediculocidal; 2 applications at least 7d apart are generally necessary to kill all lice and nits. In one study for treatment of head lice, 2 doses of ivermectin (400 mcg/kg) 7 days apart was more effective than treatment with topical malathion (O Chosidow et al, N Engl J Med 2010; 362:896). In one study for treatment of body lice, 3 doses of ivermectin (12 mg each) administered at 7d intervals were effective (C Fouault et al, J Infect Dis 2006; 193:474). Treatment with the usual antimalarials, such as chloroquine and atovaquone/proguanil appear to be effective. Primaquine is given as part of primary treatment to prevent relapse after infection with P. Since this is not always effective as prophylaxis (E Schwartz et al, N Engl J Med 2003; 349:1510), others prefer to rely on surveillance to detect cases when they occur, particularly when exposure was limited or doubtful. Atovaquone/proguanil is available as a fixed-dose combination tablet: adult tablets (Malarone; atovaquone 250 mg/proguanil 100 mg) and pediatric tablets (Malarone Pediatric;atovaquone 62. To enhance absorption and reduce nausea and vomiting, it should be taken with food or a milky drink. The drug should not be given to patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30mL/min). Although approved for once-daily dosing, Medical Letter consultants usually divide the dose in two to decrease nausea and vomiting. The artemisinin-derivatives, artemether and artesunate, are both frequently used globally in combination regimens to treat malaria. It is contraindicated during the 1st trimester of pregnancy; safety during the 2nd and 3rd trimester is not known. The tablets should be taken with fatty food (tablets may be crushed and mixed with 1-2 tsp water, and taken with milk). In Southeast Asia, relative resistance to quinine has increased and treatment should be continued for 7d. Quinine should be taken with or after meals to decrease gastrointestinal adverse effects. Mefloquine should not be used for treatment of malaria in pregnancy unless there is not another treatment option (F Nosten et al, Curr Drug Saf 2006; 1:1). It should be avoided for treatment of malaria in persons with active depression or with a history of psychosis or seizures and should be used with caution in persons with any psychiatric illness. Mefloquine should not be used in patients with conduction abnormalities; it can be given to patients taking blockers if they do not have an underlying arrhythmia. Mefloquine should not be given together with quinine or quinidine, and caution is required in using quinine or quinidine to treat patients with malaria who have taken mefloquine for prophylaxis. Mefloquine should not be taken on an empty stomach; it should be taken with at least 8 oz of water. It has also been reported on the borders between Myanmar and China, Laos and Myanmar, and in Southern Vietnam. Adults treated with artesunate should also receive oral treatment doses of either atovaquone/proguanil, doxycycline, clindamycin or mefloquine; children should take either atovaquone/proguanil, clindamycin or mefloquine (F Nosten et al, Lancet 2000; 356:297; M van Vugt, Clin Infect Dis 2002; 35:1498; F Smithuis et al, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2004; 98:182). Relapses of primaquine-resistant strains may be retreated with 30 mg (base) x 28d. Chloroquine should be taken with food to decrease gastrointestinal adverse effects. If chloroquine phosphate is not available, hydroxychloroquine sulfate is as effective; 400 mg of hydroxychloroquine sulfate is equivalent to 500 mg of chloroquine phosphate. The loading dose should be decreased or omitted in patients who have received quinine or mefloquine. Intrarectal quinine has been tried for the treatment of cerebral malaria in children (J Achan et al, Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45:1446). Travelers should be advised to seek medical attention if fever develops after they return. Insect repellents, insecticide-impregnated bed nets and proper clothing are important adjuncts for malaria prophylaxis (Treat Guidel Med Lett 2009; 7:83). Malaria in pregnancy is particularly serious for both mother and fetus; prophylaxis is indicated if exposure cannot be avoided. Beginning 1-2 d before travel and continuing for the duration of stay and for 1wk after leaving malarious zone. In one study of malaria prophylaxis, atovaquone/proguanil was better tolerated than mefloquine in nonimmune travelers (D Overbosch et al, Clin Infect Dis 2001; 33:1015). Some Medical Letter consultants prefer alternate drugs if traveling to areas where P. Beginning 1-2 d before travel and continuing for the duration of stay and for 4wks after leaving malarious zone. Doxycycline can cause gastrointestinal disturbances, vaginal moniliasis and photosensitivity reactions. Not recommendedfor use in travelers with active depression or with a history of psychosis or seizures and should be used with caution in persons with psychiatric illness. Mefloquine should not be used in patients with conduction abnormalities; it can be given to patients takingblockers if they do not have an underlying arrhythmia. Beginning 1-2 wks before travel and continuing weekly for the duration of stay and for 4wks after leaving malarious zone. Some Medical Letter consultants favor starting mefloquine 3 weeks prior to travel and monitoring the patient for adverse events, this allows time to change to an alternative regimen if mefloquine is not tolerated. For pediatric doses <tablet, it is advisable to have a pharmacist crush the tablet, estimate doses by weighing, and package them in gelatin capsules. There is no data for use in children <5 kg, but based on dosages in other weight groups, a dose of 5 mg/kg can be used. The combination of weekly chloroquine (300 mg base) and daily proguanil (200 mg) is recommended by the World Health Organization ( Studies have shown that daily primaquine beginning 1d before departure and continued until 3-7 d after leaving the malarious area provides effective prophylaxis against chloroquine-resistant P.
Recommendations for Scheduling Pertussis Immunization for Children Younger Than 7 Years of Age in Special Circumstances severe anxiety symptoms 247 best atarax 25 mg. Charts of children for whom pertussis immunization has been deferred should be fagged anxiety symptoms muscle weakness buy atarax 10 mg online, and the immunization status of these children should be assessed periodically to ensure that they are immunized appropriately anxiety symptoms help purchase cheap atarax line. These local and systemic manifestations after pertussis immunization occur within several hours of immunization and subside spontaneously within 48 hours without sequelae anxiety symptoms night sweats cheap atarax generic. Swelling involving the entire thigh or upper arm has been reported in 2% to 3% of vaccinees after administration of the fourth and ffth doses of a variety of acellular pertussis vaccines severe anxiety symptoms 247 order cheap atarax on line. Limb swelling can be accompanied by erythema anxiety symptoms for hiv cheap 25mg atarax mastercard, pain, and fever; it is not an infection. Although thigh swelling may interfere with walking, most children have no limitation of activity; the condition resolves spontaneously and has no sequelae. Bacterial abscess indicates contamination of the product or nonsterile technique and should be reported (see Reporting of Adverse Events, p 44). The Institute of Medicine report titled Adverse Effects of Vaccines: Evidence and Causality links tetanus-containing vaccines to anaphylaxis. Transient urticarial rashes that occur occasionally after pertussis immunization, unless appearing immediately (ie, within minutes), are unlikely to be anaphylactic (IgE mediated) in origin. Seizures associated with pertussiscontaining vaccines usually are febrile seizures. These seizures have not been demonstrated to result in subsequent development of recurrent afebrile seizures (ie, epilepsy) or other neurologic sequelae. It has been noted after receipt of immunizations other than pertussis vaccine and is not known to be associated with sequelae. Appropriate diagnostic studies should be performed to establish the cause of serious adverse events occurring temporally with immunization, rather than assuming that they are caused by the vaccine. Nonetheless, the cause of events temporally related to immunization, even when unrelated to the immunization received, cannot always be established, even after extensive diagnostic and investigative studies. A contraindication is a condition in a recipient that increases the risk for a serious adverse reaction. The only contraindication applicable to all vaccinees is a history of a severe allergic reaction (ie, anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of the vaccine or to a vaccine component (unless the recipient has been desensitized). A precaution is a condition in a recipient that might increase the risk of a serious adverse reaction or that might compromise the ability of the vaccine to produce immunity. However, immunization might be indicated in the presence of a precaution if the beneft of protection from the vaccine outweighs the risk for an adverse reaction. For example, Guillain-Barre syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous dose of tetanus toxoid containing vaccine is a precaution to further doses. The presence of a moderate or severe acute illness with or without a fever is a precaution to administration of all vaccines. Preterm birth is not a reason to defer immunization (see Preterm and Low Birth Weight Infants, p 69). Preterm birth is associated with increased risk of complications and death from pertussis in infancy. Children with a stable neurologic condition (well-controlled seizures, a history of seizure disorder, cerebral palsy) should receive pertussis immunization on schedule. Children with a family history of a seizure disorder or adverse events after receipt of a pertussis-containing vaccine in a family member should receive pertussis immunization on schedule. Because the majority of contraindications and precautions are temporary, immunizations often can be administered later. Tdap can be administered regardless of time since receipt of last tetanusor diphtheria-containing vaccine. Other indicated vaccine(s) that are not available and therefore cannot be given at the time of administration of Tdap can be given at any time thereafter. If further dose(s) of tetanus and diphtheria toxoids are needed in a catch-up schedule, Td is used. The preferred schedule is Tdap followed by Td (if needed) at 2 months and 6 to 12 months, but a single dose of Tdap could be substituted for any dose in the series. Children who receive Tdap at 7 through 10 years of age should not be given the standard Tdap booster at 11 or 12 years of age but should be given Td 10 years after their last Tdap/Td dose. Currently, only 1 lifetime dose of Tdap should be administered to an adolescent or adult. Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria among pregnant and postpartum women and their infants: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Updated recommendations for the use of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccine from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2010. Physicians who provide health care to women should implement a Tdap immunization program for pregnant women who previously have not received Tdap. Physicians should administer Tdap during pregnancy, preferably during the third or late-second trimester (after 20 weeks gestation), or if not administered during pregnancy, Tdap should be administered immediately postpartum. Both Tdap manufacturers have established pregnancy registries for women immunized with Tdap during pregnancy. Health care professionals are encouraged to report Tdap immunization during pregnancy to the following registries: Boostrix, to GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals at 1-888-825-5249; and Adacel, to Sanof Pasteur at 1-800-822-2463. Ideally, these adolescents and adults should receive Tdap at least 2 weeks before beginning close contact with the infant. There is no minimum interval suggested or required between Tdap and prior tetanus or diphtheria-toxoid containing vaccine. If tetanus and diphtheria booster immunization is indicated during pregnancy for a woman who previously has not received Tdap (ie, more than 10 years since previous Td), then Tdap should be administered during pregnancy, preferably during the third or late-second trimester (after 20 weeks gestation). As part of standard wound management care to prevent tetanus, a tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine might be recommended for wound management in a pregnant woman if 5 years or more have elapsed since 1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria among pregnant and postpartum women and their infants: recommendations of the advisory committee on Immunization Practices. Immunizing parents and other close family contacts in the pediatric offce setting. If a Td booster is indicated for a pregnant woman who previously has not received Tdap, then Tdap should be administered. To ensure protection against maternal and neonatal tetanus, pregnant women who never have been immunized against tetanus should receive 3 doses of vaccines containing tetanus and reduced diphtheria toxoids during pregnancy. Tdap should replace 1 dose of Td, preferably during the third or late-second trimester of pregnancy (after 20 weeks gestation). There is no minimum interval suggested or required between Tdap and prior receipt of any tetanus or diphtheria toxoidcontaining vaccine. Adults of any age who previously have not received Tdap, including adults who have or anticipate having close contact with an infant younger than 12 months of age, should be given a single dose of Tdap, with no minimum interval suggested or required between Tdap and prior receipt of a tetanusor diphtheria-toxoid containing vaccine. Local adverse events after administration of Tdap in adolescents and adults are common but usually are mild. Postmarketing data suggest that these events occur at approximately the same rate and severity as following Td. Syncope can occur after immunization, is more common among adolescents and young adults, and can result in serious injury if a vaccine recipient falls. A history of immediate anaphylactic reaction after any component of the vaccine is a contraindication to Tdap (see Tetanus, p 707, for additional recommendations regarding tetanus immunization). History of Guillain-Barre syndrome within 6 weeks of a dose of a tetanus toxoid vaccine is a precaution to Tdap immunization. If decision is made to continue tetanus toxoid immunization, Tdap is preferred if indicated. A history of severe Arthus hypersensitivity reaction after a previous dose of a tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine administered less than 10 years previously should lead to deferral of Tdap or Td immunization for 10 years after administration of the tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine. This product should not be administered to people with a history of an anaphylactic reaction to latex but may be administered to people with less severe allergies (eg, contact allergy to latex gloves). The immunogenicity of Tdap in people with immunosuppression has not been studied adequately, but there is no safety risk. Bacterial superinfections can result from scratching and excoriation of the area. Pinworms have been found in the lumen of the appendix, but most evidence indicates that they do not cause acute appendicitis. Many clinical fndings, such as grinding of teeth at night, weight loss, and enuresis, have been attributed to pinworm infections, but proof of a causal relationship has not been established. Urethritis, vaginitis, salpingitis, or pelvic peritonitis may occur from aberrant migration of an adult worm from the perineum. Prevalence rates are higher in preschooland school-aged children, in primary caregivers of infected children, and in institutionalized people; up to 50% of these populations may be infected. Female pinworms usually die after depositing up to 10 000 fertilized eggs within 24 hours on the perianal skin. Reinfection occurs either by autoinfection or by infection following ingestion of eggs from another person. A person remains infectious as long as female nematodes are discharging eggs on perianal skin. Humans are the only known natural hosts; dogs and cats do not harbor E vermicularis. The incubation period from ingestion of an egg until an adult gravid female migrates to the perianal region is 1 to 2 months or longer. No egg shedding occurs inside the intestinal lumen; thus, very few ova are present in stool, so examination of stool specimens for ova and parasites is not recommended. Alternatively, diagnosis is made by touching the perianal skin with transparent (not translucent) adhesive tape to collect any eggs that may be present; the tape is then applied to a glass slide and examined under a low-power microscopic lens. Specimens should be obtained on 3 consecutive mornings when the patient frst awakens, before washing. For children younger than 2 years of age, in whom experience with these drugs is limited, risks and benefts should be considered before drug administration. Reinfection with pinworms occurs easily; prevention should be discussed when treatment is given. Infected people should bathe in the morning; bathing removes a large proportion of eggs. Frequently changing the infected persons underclothes, bedclothes, and bed sheets may decrease the egg contamination of the local environment and risk of reinfection. Specifc personal hygiene measures (eg, exercising hand hygiene before eating or preparing food, keeping fngernails short, avoiding scratching of the perianal region, and avoiding nail biting) may decrease risk of autoinfection and continued transmission. All household members should be treated as a group in situations in which multiple or repeated symptomatic infections occur. In institutions, mass and simultaneous treatment, repeated in 2 weeks, can be effective. Bed linen and underclothing of infected children should be handled carefully, should not be shaken (to avoid spreading ova into the air), and should be laundered promptly. Lesions can be hypopigmented or hyperpigmented (fawn colored or brown), and both types of lesions can coexist in the same person. Lesions fail to tan during the summer and during the winter are relatively darker, hence the term versicolor. Common conditions confused with this disorder include pityriasis alba, postinfammatory hypopigmentation, vitiligo, melasma, seborrheic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, pityriasis lichenoides, and dermatologic manifestations of secondary syphilis. Although primarily a disorder of adolescents and young adults, pityriasis versicolor also may occur in prepubertal children and infants. Malassezia species commonly colonize the skin in the frst year of life and usually are harmless commensals. Malassezia infection can be associated with bloodstream infections, especially in neonates receiving total parenteral nutrition with lipids. Skin scrapings examined microscopically in a potassium hydroxide wet mount preparation or stained with methylene blue or MayGrunwald-Giemsa stain disclose the pathognomonic clusters of yeast cells and hyphae (spaghetti and meatball appearance). Growth of this yeast in culture requires a source of long-chain fatty acids, which may be provided by overlaying Sabouraud dextrose agar medium with sterile olive oil. Other topical preparations with off-label therapeutic effcacy include sodium hyposulfte or thiosulfate in 15% to 25% concentrations (eg, Tinver lotion) applied twice a day for 2 to 4 weeks. Oral antifungal therapy has advantages over topical therapy, including ease of administration and shorter duration of treatment, but oral therapy is more expensive and associated with a greater risk of adverse reactions. A single dose of ketoconazole (400 mg, orally) or fuconazole (400 mg, orally) or a 5-day course of itraconazole (200 mg, orally, once a day) has been effective in adults. Some experts recommend that children receive 3 days of ketoconazole therapy rather than the single dose given to adults. For pediatric dosage recommendations for ketoconazole, fuconazole, and itraconazole, see Recommended Doses of Parenteral and Oral Antifungal Drugs, p 831. Exercise to increase sweating and skin concentrations of medication may enhance the effectiveness of systemic therapy. Patients should be advised that repigmentation may not occur for several months after successful treatment. Buboes develop most commonly in the inguinal region but also occur in axillary or cervical areas. Less commonly, plague manifests in the septicemic form (hypotension, acute respiratory distress, purpuric skin lesions, intravascular coagulopathy, organ failure) or as pneumonic plague (cough, fever, dyspnea, and hemoptysis) and rarely as meningeal, pharyngeal, ocular, or gastrointestinal plague. Abrupt onset of fever, chills, headache, and malaise are characteristic in all cases. Occasionally, patients have symptoms of mild lymphadenitis or prominent gastrointestinal tract symptoms, which may obscure the correct diagnosis. When left untreated, plague often will progress to overwhelming sepsis with renal failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, hemodynamic instability, diffuse intravascular coagulation, necrosis of distal extremities, and death. Humans are incidental hosts who develop bubonic or primary septicemic manifestations typically through the bite of infected feas carried by a rodent or rarely other animals or through direct contact with contaminated tissues.
Buy 10 mg atarax fast delivery. anxiety / depression Edit.