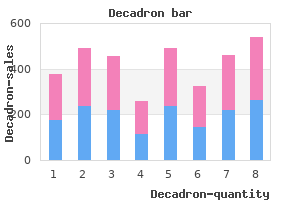
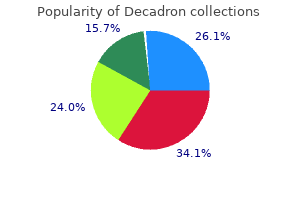
Decadron
Ziad Obermeyer MD
- Acting Associate Professor, Health Policy and Management

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/ziad-obermeyer/
Preece V acne oral medication order decadron with visa,and Pearson T (2015) Stoma Site selection: Getting it right for the patient acne face wash buy discount decadron 1mg online. Royal College of Nursing (2003) Documentation in Colorectal and Stoma Care Nursing skin care doctors orono buy cheap decadron 4mg on line. Slater R (2011) Optimising patient adjustment to stoma formation: Siting and self management acne yahoo answers purchase decadron 1 mg fast delivery. Sari Guidelines (2005) Guidelines for hand hygiene in the Irish Heath care setting acne clothing order decadron without a prescription. Siassi M skin care pakistan buy cheap decadron 0.5 mg on-line, Hohenberger W, Weiss M (2008) Quality of life and patients expectations after closure of temporary stoma. Taylor C, Lopes De Azevedo G, Gabe S (2012) Rehabilitation needs following stoma formation: a patient survey. Walsh C, Marren R, Boyce M, Rowe D, Cooney B (2008) Revised edition (2016) Guidelines on the management of intestinal failure. Letterkenny University hospital, Co Donegal Walsh C (2016) Improving awareness of the management and treatment of Intestinal failure. I was given adequate verbal and written information in order to make a decision about my planned surgery in language I understood. My family/partner/ carer was included in any decision making to a level acceptable to me. I was offered a meeting with another stoma patient and given information about support groups available to me. The ward staff encouraged and supported me to become independent with my stoma care. My family/partner/carer was included in all aspects of my stoma care to a level agreeable to me. I felt confdent to manage the stoma after discharge and received the appropriate support. I felt supported emotionally after discharge and was provided with information on support groups and meeting another patient. I was offered follow up appointments and appliance review with in an appropriate time frame and in line with local policy. It is intended for use within Ireland but readers are advised that practices may vary within Hospital Group/ Community settings. The information has been compiled from professional resources and every effort has been made to provide accurate and expert information, however it is impossible to predict all of the circumstances in which it may be used. However, we this review has been accepted as a thesis together with 6 previously published do have local data from the Capital Region of Denmark, suggest papers by University Copenhagen 7th of February 2013 and defended on 14th of April ing an incidence rate of 4000 stoma creations per year in Den 2013. There are different disease-related reasons for construction Official opponents: Peter Bytzer, Niels Qvist & Eva Carlson. These are primarily can cer, inflammatory bowel disease and traumas, where the treat Correspondence: Surgical Department, Herlev Hospital, Herlev Ringvej 75, 2730 Herlev, Denmark. Additionally, the enterostoma may be perma nent or temporary, and both types may be constructed in the Dan Med J 2013;60(10): B4732 small intestine as well as the colon. Moreover, living with a stoma is not a uniform condition, as the adaptation to living with a stoma is affected by several 1. It is questioned whether and how these Focus group interview: Impact of a temporary stoma on factors may affect the individual person, covering amongst many: patients everyday-lives: feelings of uncertainty while late and early complications (4,5) related to stoma creation, waiting for closure of the stoma. Journal of Clinical Nurs stoma type (6), gender (7), age (8), underlying disease (9,10), ing 2012: in press. Some of these factors are stabilizing forces Learning to live with a Permanent Intestinal Ostomy: Im and some of them may lead to different problems, such as; ban pact on everyday life and Educational Needs. Journal of daging, dehydration, sexual problems, skin problems, develop Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2012: in press. All these problems may have a tients with a stoma lack information and support and are harmful effect on the adaptation to living with a stoma and on restricted in their social and sexual life: a systematic re health related quality of life. International Journal of Colorectal Diseases 2012: stoma may also be surrounded by positive feelings as it is part of in press. Patient educa tance of the stoma may be placed in the background by other tion has a positive effect in patients with a stoma a sys adjacent processes, for instance, parenteral nutrition (17), com tematic review. Health related quality of life However, the physical changes do seem to have significance to increases when patients with a stoma attend patient the individual, both emotionally, socially and psychologically (3). Decreased costs with patient may affect the individual, and adaptation to living with a stoma education after stoma creation. In addition, we were impelled to explore, assess and evalu Stoma creation is a surgical operation where the surgeon makes ate how the establishment of a specific patient education an artificial opening on the abdomen from where the bowel is program aimed at rehabilitation and adaptation to a life with a taken out. It is a radical treatment with permanent physical signs stoma would affect health related quality of life of the partici of bodily change (1). Furthermore, we do not have data on demographic vari that could inform health professionals, and be applied in the ables in persons who have had a stoma created, nor do we have clinical setting. Furthermore, to mixed methods approach (21), and concentrates on patients with explore methods of how to intervene with focus on establishing a stoma as well as concepts of health related quality of life and and testing a patient education program lead by stoma therapists patient education. The literature search was directed by these from the Department of Surgery, Herlev Hospital. The objectives when using education aimed at temporary adaptation to life with a different scientific research methods were to provide power to stoma (paper 1). The strategy was first to collect manent stoma, and the recommendations for patient and analyze the qualitative data, followed by the collection and education aimed at adaptation to life with a stoma (pa analysis of quantitative data. To review the literature exploring and describing how and description of the studies in the ph. It was compre stoma creation affects spouses or near relatives of a pa hensive and reflected the open and explorative approach of the tient with a stoma (paper 3). We conducted when establishing a patient education program aimed at focus group interviews with a phenomenological and hermeneu patients with a stoma (paper 5). Furthermore, to assess tic approach, and we analyzed the interviews according to quali the health economic effects when establishing a patient tative content analysis. On the basis of our initial literature search education program aimed at patients with a stoma (pa and on the interviews, we reviewed the literature systematically per 6). Additionally, we systematically reviewed the specific approach in the thesis is the description and discus the literature in order to identify evidence on the effect of patient sion of central themes related to living with a stoma, and to edu education as there seems to be a large quantity of studies de cational processes connected with it. The ject is implemented as a mixed methods study in which search was aimed at including both quantitative and qualitative qualitative interview studies and two systematic literature review results, but eventually only included quantitative studies (paper identified interventions, which were subsequently tested in a 4). The case/control study was planned on the basis of the inter clinical case/control study. Finally the case/control study was views, on the opening literature search and the systematic re made subject to an economic analysis. Moreover, the formed by registered nurses, who have specialized training in this relevancy of some concepts and theories: health related quality special area of the surgical treatment and care (26). Their primary of life, patient education and the underlying educational assump role is informing and preparing patients and relatives pre tions and theories are presented, and tied to the patient with a operatively, and in addition they stay in contact with patients stoma. The current After a short presentation of the included papers, and a more approach to colostomy care, which has changed little over the extensive discussion of strengths and limitations related to each years, is based on the patients need to be self-sufficient and paper, the thesis moves on to discussing the following themes: being in personal control. The aim is to let the person at risk of Educational strategies for patient education programs aimed at living a restricted life due to social, physical or mental restricting patients with a stoma, health economic assessments related to conditions have the possibility to live a self-determining and clinical research, patient reported outcome and the assessment coherent life. Some of the central issues are training by specialist of health related quality of life. Nevertheless, although patients in Denmark in general have a broad access to stoma care they still seem to be marked by psychosocial distress and a tendency of depressive symptoms (36). Patient education and health education During the past 20 years there has been a dramatic increase in public, private and professional interest in preventing disability and death through lifestyle changes and participation in screening programmes (37). Much of this interest in health promotion and disease prevention has been stimulated by the epidemiological transition from infectious to chronic diseases as leading causes of death, the ageing of the population, rapidly escalating healthcare costs, and data linking individual behaviors to increased risk of morbidity and mortality (38). Increased interest in behavioral determinants of health and disease has furthermore drawn atten Figure 1 tion to the importance of health behavior change and resulted in Different methodologies and methods applied in the ph. Orange box: the numerous training programs in public and commercial service initial literature search. The point of view, that the health education in various clinical settings is an instrument of change, has been renewed and in vigorated during the past years (40). The central concern of the information and guidance of patients admitted for crea health promotion and health education is health behavior (41). All major such, the patient with a stoma would be expected to take respon hospitals in Denmark have established an out-patient-clinic for sibility for handling the stoma, for using the correct bandage, and the population (29). There are no uniform requirements either at a generic level or a disease specific level. This could for instance be issues like nutrition, exercise, and ployed in specialized hospitals in Denmark, and the out-patient smoking cessation (42). However, the primary specific symptoms or conditions, the disease specific programs sector in Denmark does also have a part of the responsibility for are aimed at patients with certain diseases and conditions. However, when at the patient having a stoma is offered visits before surgery (if tending a disease specific program the objective is strictly focused not having acute surgery), and during the hospital stay. These on the exact condition, and the correct treatment or prevention visits during hospital stay are often restricted to clinical situations of further development of it (42). After leaving hospital patients are offered visits in aimed at patients with arthritis concluded that a disease oriented the out-patient-clinic and the number of visits varies throughout program may have advantages over a generic program (43). Often patients attend the clinic for a year after relation to stoma creation it would seem natural to include dis stoma creation and some even longer. Furthermore, patients ease specific themes, covering different issues related to the have the offer of telephone support from the enterostoma nurses stoma and the adaptation process. Similar results and experiences in the expert group of enterostoma therapists have been found in a study questioning patients 10 weeks and 1 explored in intensive and dynamic dialogues when establishing year after surgery (33). It has been suggested that some patient education lated quality of life is connected to having rectal cancer rather programmes within the surgical setting have not focused suffi than to having a stoma (59). To some patients creation of a stoma ciently on the need of the individual patient, or on how the needs after surgery for rectal cancer may be preferable to the risk of should be met (48). Effective teaching strategies should be based severe postoperative complications (18). According to a review of on solid knowledge on educational interventions and better re studies published between 1969 and 1992 (9) depression, loneli sults may be reached by involving lay-teachers as well as the ness, suicidal thoughts, and low self-esteem were significantly recognition of the immense effect when organizing education in more prevalent in patients with a stoma compared with patients peer groups (49,50). A follow-up study found sexual impairment in designed to include psycho-social problems related to the specific male Finnish patients undergoing rectal surgery (60), and another condition, shorter lectures with relevant knowledge, as well as study showed negative beliefs about body image (3,61). Therefore, it seemed obvious that the lated quality of life may be affected differently and most probably development of a patient education program should start by reflects the different research designs and methods, which ques exploring the potential participants views and recommendations. It seemed natural brief, one-by-one, with a focus on the methodological strengths to assume that health related quality of life would be a reason and weaknesses. The full-text manuscripts are placed as appendix able outcome, as we wanted to involve a patient oriented per 1-6. Therefore, health related quality of life would give us an ac cess to a more subjective experience of how the disease or the Paper 1: Impact of a temporary stoma on patients everyday condition would inflict on the person (52). The aim of the study was to explore the impact of living with a the aim of gaining the best possible quality of life has be temporary stoma, as well as the issue of adapting to and learning come more accepted as a goal within patient treatment in a to live with a temporary stoma. There are several different aspects and views on the essence of health related Methods quality of life, and in this thesis the perspective has been on We designed a study with a qualitative approach, and set up quality of life connected to certain health related conditions and focus group interviews with a phenomenological hermeneutic how they have affected the individual. However, when looking at perspective in order to grasp essentials of experiences related to a model covering all relevant aspects of quality of life it was cen creation of a temporary stoma. The initial domains identified were life before and Moreover, since quality of life is a complex concept it has after creation stoma, uncertainty, and mastery and personal been suggested (55) that evaluation should assess both generic ity. After an inductive analytical process using qualitative con and disease-specific elements of impairment including physical, tent analysis, the following themes emerged from the data: 1) emotional and social dimensions. Several authors have explored the question of the impact be possible to understand and use the results in the same way as on health related quality of life without reaching a shared conclu in quantitative research (62). A recent Cochrane review regarding quality of life is a method where it is possible to gain access to the way persons in patients after rectal resection for rectal cancer has concluded and groups think, and in our interview the aim was to explore that it was not possible to come to a clear conclusion whether experiences when having a temporary stoma (63). However, the creation of a permanent stoma had an impact on health related term generalizability connects to a quantitative approach to quality of life, primarily because of the small sample sizes (58). There are several factors that determine the sample sizes related quality of life (9,57). Some have reported better quality of in qualitative studies, where the concept of data saturation is the life by avoiding stoma creation, while others have not been able guiding principle for the size of the sample. Health related quality of life may tion of data saturation is tightly connected to both the sampling even be better when having a stoma compared with patients who have had a resection with a bad functional result (19). During the process of analysis we first analyzed such, the use of an analytical method aimed at content seemed the interview with 5 participants and afterwards we analyzed the relevant. However, if we had included an analytical method that interview with 2 participants, and no new codes appeared in the would enable us to understand how the participants interacted analysis. However, it is very difficult to make an exact assessment and how this interaction affected their statements, we would of when data is precisely saturated, as new words and experi probably have been able to point at alternative findings. As such, there could and would be discrepancy between we might have identified other codes. The question remains, the naturalistic view, accepting the world as it is seen by the when to stop, as counting participants does not comply with a participant, and the constructionist view, where nothing is stable, qualitative position and tradition. Participants invest time and resources often with the by another researcher in parallel. Therefore, the researcher has an researcher had to keep a constant awareness on the connection obligation to ensure that the data will be used, which may be between the transcribed interview data and the emerging themes problematic if data becomes repetitive not shedding any further (68). The coding process had to be performed in a rigorous way, light on the issue of investigation. However, the first author presented the analytical coding tree suggested that the item for analysis is not the individual, but the to the second author, and inferences made from the coding tree group (65). Focus group interviewing is a before entering into the sessions were done in cooperation be well-known method within qualitative research, and is especially tween the first and third author.
If bleeding persists after direct cutdown access the wound should be reexplored Recent operation acne yellow sunglasses discount generic decadron canada. When an operative site is explored for bleeding it is best to leave the site open with active drainage and a plastic seal closure skin care 3m purchase decadron 4mg mastercard, rather than surgical closure of the skin skin care 90036 order generic decadron on-line. There is a moderate risk of wound infection acne products purchase decadron 8mg without prescription, but that risk is much lower than the risk of ongoing bleeding skin care wholesale buy generic decadron 1 mg on-line. Bleeding post chest tube placement: Bleeding is a common complication even if all appropriate steps are taken during tube placement skin care images cheap decadron 8 mg online. Accumulated blood should be evacuated, even if this requires a lower, more posterior tube. Evacuating the blood quantifies the rate of bleeding and decreases the risk of a hemothorax and later organized clot. If it is the tube should be removed, but thoracotomy will probably be need to control the bleeding and air leak. Bleeding from the nasopharynx, mouth, trachea, rectum, or bladder commonly occurs with minor trauma associated with patient care. It is difficult to control bleeding in these areas by direct pressure but full nasal packing or traction on a Foley catheter with a large balloon in the bladder may stop major bleeding. After ruling out retained products of conception, the bleeding may be controlled by oxytocin, or creating a balloon tamponade within the uterus. If the site of bleeding can be reached by an endoscope or arterial catheter, local measures should be attempted. The coagulopathy is corrected as much as possible, and then operation is indicated if uncontrolled bleeding persists. The same is true for spontaneous bleeding into other solid organs (liver, kidney, retroperitoneal tissue) or bleeding into the thorax or peritoneal space. This may stop the bleeding but may also result in clotting in the circuit, so whenever anticoagulation is turned off a primed circuit should be immediately available. When an operation is necessary, coagulation should be optimized (anticoagulation minimized) as described above. Even small operations like chest tube placement are done with extensive use of electrocautery. The trachea is exposed through a small incision, all with extensive electrocautery. The smallest opening in the trachea is made between rings, preferably with a needle, wire, and dilation technique. Subsequent bleeding (common after a few days) should be managed by complete reexploration until bleeding stops. Maintain blood flow and anticoagulation, stop the sweep gas, and cap off the oxygenator. If lung function is adequate at acceptable ventilator settings for an hour or more the patient is ready for decannulation. In this circumstance the usual practice is to infuse low dose heparinized saline into the cannulas and reassess frequently. Decannulation the cannulas can be removed whenever the patient is ready, but ideally after the heparin has been turned off for 30 to 60 minutes. The cannulae are removed and the vessels simply ligated (or occasionally repaired). If the femoral artery has been cannulated by cutdown, vascular repair will be required. Venous and arterial cannulae placed by percutaneous access can be removed directly and bleeding controlled by topical pressure. When removing a venous cannula, air can enter the venous blood through the side holes if the patient is breathing spontaneously. This is prevented by a Valsalva maneuver on the ventilator, or by short-term pharmacological paralysis when removing the venous cannula. The definition of irreversible heart or lung damage depends on the patient and the resources of the institution. In each case, a reasonable deadline for organ recovery or replacement should be set early in the course. Fixed pulmonary hypertension leading to right ventricular failure in a patient with respiratory failure has been considered an indication of futility in the past. These patients may require months of support, so should be managed in facilities equipped for providing months of support. Bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy and airway lavage are facilitated by extracorporeal support and should be used as indicated. Management of air leaks Chest tube placement is frequently accompanied by bleeding complications and need for thoracotomy, so a conservative approach is often taken to pneumothoraces. As in any bronchopleural fistula, the first objective is to evacuate the pleural space so that the lung contacts the chest wall, leading to adhesions with closure of the visceral pleura. In some cases, it may be necessary to manage the airway by continuous positive airway pressure at 10, 5, or even 0 cm/H2O for hours or days leading to total atelectasis. When the air leak has sealed, airway pressure is gradually added until conventional rest settings are reached. Bronchopleural fistula with a massive air leak directly from a bronchus or the trachea (after lung resection or trauma for example) should be managed initially as outlined above, but direct endoscopic or thoracotomy closure is often required. If the cardiac output and hemoglobin concentration are adequate, arterial saturation as low as 75% is safe and well tolerated. In choosing the cannulation approach in such patients it is important not to undersize the cannula so that the maximum flow is less than the required flow to facilitate oxygenation. Almost all such patients are managed with placement of an inferior vena caval filter. As long as renal perfusion is adequate pharmacologic diuresis can be instituted and maintained even in septic patients with active capillary leak. Continuous hemofiltration can and should be added to the circuit if pharmacologic diuresis is inadequate. The hourly fluid balance goal should be set (typically -100 to 300 cc/hr for adults) and maintained until normal extracellular fluid volume is reached (no systemic edema, within 5% of dry weight). Although normal renal function can usually be maintained, the life threatening condition is respiratory failure. If respiratory function is tenuous the vascular access catheters can be left in place as described in V. There is a tendency to drift into positive fluid balance, more sedation, increasing ventilator settings which should be carefully avoided. This condition has the characteristics of chronic irreversible obstructive lung disease; however, this condition almost always reverts to normal within 1-6 weeks. Lung biopsy is best done by thoracotomy (or thoracoscopy) rather than transbronchially because of the risk of major hemorrhage into the airway with transbronchial biopsy. Examples are vasculitis, autoimmune lung disease, bronchiolitis, obliterans, Goodpasture syndrome, rare bacterial, fungal or viral infections. However, we do not know what the survival is in similar patients managed with conventional care in the centers reporting to the registry. Clinical research in acute fatal illness: lessons from extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Referral to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation center and mortality among patients with severe 2009 influenza A (H1N1). Tai Pham, Alain Combes, Hadrien Roze et al, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1)?induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Cohort Study and Propensity-matched Analysis. Even the most seasoned clinician, standing at the bedside of the patient in extremis, can be unclear about the cause of shock and the optimal initial therapeutic approach. Traditional physical examination techniques can be misleading given the complex physiology of shock. Therefore, diagnosis and initial care must be accurate and prompt to optimize patient outcomes. Ultrasound technology has been rapidly integrated into Emergency Department care in the last decade. Studies have demonstrated that initial integration of bedside ultrasound into the evaluation of the patient with shock results in a more accu rate initial diagnosis with an improved patient care plan. Thus, bedside ultrasound has become an essential component in the evaluation of the hypotensive patient. The classic example of this class of shock is sepsis, in which the vascular system is vasodilated to the point that the core vascular blood volume is insufficient to maintain end organ perfusion. Other examples of distributive shock include neurogenic shock, caused by a spinal cord injury, and anaphylactic shock, a severe form of allergic response. The third major form of shock is cardiogenic shock, resulting from pump failure and the inability of the heart to propel the needed oxygenated blood forward to vital organs. Cardiogenic shock can be seen in patients with advanced cardiomy opathy, myocardial infarction, or acute valvular failure. This type is most commonly caused by cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax, or large pulmonary embolus. Many patients with obstructive shock will need an acute intervention such as pericardiocentesis, tube thoracostomy or anticoagulation, or thrombolysis. For example, patients with tamponade, cardiogenic shock and sepsis (when myocardial depression compounds this form of distributive shock) may all present with distended neck veins and respiratory distress. Because of this diagnostic challenge, practitioners used to perform Swan-Ganz catheterization in hypotensive patients, providing immediate intravascular hemodynamic data. Although the data obtained from these catheters was detailed and often helpful at the bedside, large studies demonstrated no improvement in mortality in the patients who received such prolonged invasive monitoring. The first, and most crucial, step in evaluation of the patient in shock is determination of cardiac status, termed for simplicity the pump (Table 1). First, the pericardial sac can be visualized to determine if the patient has a pericardial effusion that may be compressing the heart, leading to a mechanical cause of obstructive shock. Determination of the size and contractility status of the left ventricle will allow for those patients with a cardiogenic cause of shock to be rapidly identified. A heart that has an increased size of the right ventricle relative to the left ventricle may be a sign of acute right ventricular strain from a massive pulmonary embolus in the hypotensive patient. Integration of lung ultrasound techniques can quickly allow the clinician to identify a pneumothorax, which in the hypotensive patient may represent a tension pneumothorax requiring immediate decompression. Tension pneumothorax presum ably limits venous return into the heart due to increased pressure within the chest cavity. Next the clinician should turn to evaluation of the venous side of the vascular system. The femoral and popliteal veins can be exam ined with a high frequency linear array transducer for compressibility. A smaller foot print phased-array transducer is ideal for this examination as it permits the intercostal scanning required of the heart. The tradi tional views of the heart for bedside echocardiography are the parasternal long and short-axis views, the subxiphoid view, and the apical 4-chamber view (Fig. The par asternal views are taken with the probe positioned just left of the sternum at intercostal space 3 or 4. The subxiphoid 4-chamber view is obtained with the probe aimed up toward the left shoulder from a position just below the subxiphoid tip of the sternum (Fig. The apical 4-chamber view of the heart is best evaluated by turning the patient into a left lateral decubitus position and placing the probe just below the nipple line at the point of maximal impulse of the heart. The heart should be imaged in the planes described here, with close attention to the presence of fluid, usually appearing as a dark or anechoic area, within the pericardial space (Fig. Small effusions may be seen as a thin stripe inside the pericardial space, whereas larger effusions tend to wrap circumferentially around the heart. Pericardial effusions can result in hemodynamic instability, due to increased pres sure within the sac leading to compression of the heart. Because the pericardium is a relatively thick and fibrous structure, acute pericardial effusions may result in cardiac tamponade despite only small amounts of fluid. In contrast, chronic effusions can grow to a large volume without hemodynamic instability. Thinking of the heart as a dual chamber in-line pump, the left side of the heart is under consider ably more pressure, due to the high systemic pressures against which it must pump. The right side of the heart is under relatively less pressure, due to the lower pressure within the pulmonary vascular circuit. Thus, most echocardiographers define tampo nade as compression of the right side of the heart (Fig. High pressure within the pericardial sac keeps the chamber from fully expanding during the relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle and thus is best recognized during diastole. As either chamber may be affected by the effusion, both the right atrium and right ventricle should be closely inspected for diastolic collapse. Diastolic collapse of the right atrium or right ventricle appears as a spectrum from a subtle inward serpentine deflection of the outer wall to complete compression of a chamber. This phenomenon is more commonly seen in patients following heart surgery, in whom a clot can form in only one area of the sac. However, a large review from the Mayo Clinic looked at 1127 pericardiocentesis procedures, and found that the optimal placement of the needle was where the distance to the effusion was the least and the effusion size was maximal. The subxiphoid approach was only chosen in 20% of these proce dures, as the investigators recognized the large distance the needle had to travel through the liver to enter the pericardial sac. If the apical approach is selected, the patient should optimally be rolled into a left lateral decubitus position to bring the heart closer to the chest wall, and after local anesthesia, a pericardiocentesis drainage catheter should be introduced over the rib and into the pericardial sac. To maximize success and to avoid complications, the transducer should be placed in a sterile sleeve adjacent to the needle, and the proce dure performed under real-time ultrasound guidance. Whereas in the past echocardiographers used radionuclide imaging to determine ejection fraction, published studies have demonstrated that visual determination of contractility is roughly equivalent. As an example, a vigorously contracting ventricle will almost completely obliterate the ventricular cavity during systole. In comparison, a poorly contracting heart will have a small percentage change in the movement of the walls between diastole and systole. In these hearts, the walls will be observed to move little during the cardiac cycle, and the heart may also be dilated in size, especially if a long-standing cardiomyopathy with severe systolic dysfunction is present.
Decadron 0.5 mg generic. Epionce Renewal Lite Facial Lotion Review | The Skin Spot.
The preventive and therapeutic potential of nutrition and exercise are currently being evaluated acne 2015 heels buy cheap decadron 8mg. To date skin care for rosacea cheap decadron uk, hormone replacement trials consistently demonstrate lack of benefit with regard to cardiovascular outcomes despite benefits suggested by fundamental and observational data acne prevention cheap 1 mg decadron with visa. Devices are used to prevent fatal consequences of ventricular fibrillation in patients at high risk of sudden death acne rash decadron 4 mg for sale, improve ventricular function in heart failure patients with intraventricu lar conduction delays acne at 40 8mg decadron otc, and improve survival in selected end-stage heart failure patients who are ineligible for heart transplantation acne y embarazo order decadron 0.5 mg otc. The development of drug-eluting stents holds promise of significant reduction of restenosis even in patients with a tendency for a hypercellular response to coronary interventions. Current projects encompass developing new strategies for acute and chronic heart disease, cardiomyopathies of different etiologies. Examples of therapies and approaches include diet, exercise, and pharmacologic management of dyslipidemias, genetic susceptibility and directed treatment, diagnosis and management of arrhythmias; surgical and medical man agement of heart failure; and novel imaging of atherosclerosis. It supports epidemiologic studies, clinical trials, demonstration and education research, disease prevention and health promotion research, and basic and applied research in behavioral medicine. Studies on increasing the implementation of interventions known to be effective are of par ticular interest. Clinical trials are used to evaluate the effectiveness of various medical procedures and thera peutic agents in patients with coronary heart disease, hypertension, and heart failure. Research in behavioral medicine focuses on biopsychologic and sociocultural factors involved in heart, lung, and blood diseases. Areas of interest include central nervous system regulation of the cardiovascular system; identification of psychosocial factors (social support, depression, and hostility) affecting disease etiology, treatment, and rehabilitation; and effects of psy chosocial and behavioral interventions on risk factors (smoking, adverse diet, physical inactiv ity), disease outcomes, and quality of life. Study participants are from all levels of health and from all ages and racial groups. Investigators are conducting long-term epidemiological studies of heart and vascular, lung, and blood diseases in defined populations in the United States and other countries. Another area of interest is the incidence of and mortality from car diovascular, lung, and blood diseases. Research strategies apply family, longitudinal, demo graphic, and vital statistics to study their natural history, etiology, and epidemiology. Additional studies are underway to identify genetic factors influencing coronary and aortic calcification and individual variability in the inflammatory response and to investigate gene-environment interaction, collaborative approaches to linkage analysis, and population screening for genetic diseases. Scientists are attempting to find and characterize genes linked to risk factors that are associated with insulin resistance syndrome and diabetes. Research strategies include family and longitudinal studies in racially diverse populations. The pro grams use two strategies: one focuses on individuals at high risk; the other focuses on the general public. The four largest programs have coordinating committees consisting of national medical, public health, and voluntary organizations and of other federal agencies. These committees help to plan, implement, and evaluate program efforts in professional, patient, and public education. Special attention is directed to reducing health disparities among people with hypertension. It is committed to raising public awareness of the importance of adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. Research has identified steps that individuals can take to control their blood pressure and to lower their risk for heart disease. For example, certain dietary habits can decrease blood pressure and can prevent it from rising. In 2002, community and professional activities focused on updating the Primary Prevention Report, encouraging communities to hold local events to mark May as National High Blood Pressure Education Month, and redesigning and expanding the Your Guide to Lowering High Blood Pressure Web page. From 1983 through 1995, the percentage of the public who had their cholesterol checked rose from 35% to 75%, showing that 70 to 80 million more Americans were aware of their cholesterol levels in 1995 than in 1983. Moreover, in 1995, physicians reported initiating diet and drug treatment at much lower cholesterol levels than in 1983. Since 1978, the intake of saturated fat, total fat, and cholesterol among the general public decreased significantly, resulting in an impres sive decline in average blood cholesterol levels. It developed a Web-based kit of materials derived from the guidelines to support cholesterol education for Cholesterol Month 2002 and throughout the year. The advisory provides reassurance that the benefits of statins far outweigh the risks if patients are properly selected and attention is paid to possible side effects. Since its inception, the program has taught health care providers in emergency departments and emergency medical services sys tems about the importance of reducing the interval between a heart attack and treatment. Available treatments, if administered soon after heart attack symptoms start, can save lives and minimize heart muscle damage in heart attack survivors. The American Dietetic Association, in partnership with the project, is providing nutrition consultation. A major goal of the Institute is to eliminate health disparities and to increase the quality and years of healthy life of all Americans. The Institute is collaborating with the Baltimore City Cardiovascular Health Partnership on a project that has a two-pronged strategy consisting of a population-wide public education campaign and a targeted subgroup outreach and educa tional approach to build and reinforce positive cardiovascular health lifestyle skills and C-19 Public Health Action Plan to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke behaviors. The targeted population consists of blacks who reside in Baltimore City public housing developments. As advocates for change, they have increased the number of Latinos in their communities who are engaging in heart healthy behaviors. In 2002, tribal heart health teams received training on topics related to cardiovascular health, including physical activity, obesity, smoking prevention, nutrition, high blood choles terol, and high blood pressure, as well as on theories of team building, evaluation, and com munity interaction and intervention. Since then, they have initiated community outreach education activities on cardiovascular health and disease. In addition, they have developed connections with local organizations to aid them with their missions. The assessments will guide the Institute in its development of culturally and language-appropriate materials and activi ties for these groups. More than a score of trials, involving more than 20,000 partici pants, have assessed antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, thrombolysis, carotid endarterec tomy, hormone replacement, and psychosocial interventions. Until the completion of that trial in 1995, physicians had nothing to offer their patients that could reduce brain injury from stroke. Initial evidence suggests that African Americans may experience more severe strokes and greater residual physical deficits. A Stroke Disparities Planning Panel was held in June 2002, and a follow-up workshop was held in November 2002 to identify specific research needs and areas of opportunity. Additionally, as a result of the Stroke Disparities Workshop, several new prevention and intervention programs are underway or planned. The symposium drew more than 400 professionals representing wide areas of the health care system to draft guidelines on how to treat stroke on an emer gency basis. The participants made recommendations for change in five key areas: pre hospital systems, emergency departments, acute hospital care, hospital systems, and public education. The proceedings from the meeting were published and distributed nationally in an effort to increase the number of stroke patients who can benefit from treatment and the number of hospitals that can offer rapid treatment to their patients. The Know Stroke cam paign is a multifaceted public education program designed to raise awareness of the signs and symptoms of stroke and the need to act quickly to seek medical care. These organizations are using Know Stroke materials in educational sessions at hospitals, senior centers, and other places that serve those at the highest risk for stroke. About 400 participants from many organizations attended this meeting, which was designed to address the problem of the relatively few number of patients nationwide who are receiving acute treatment for their strokes. Both the American Stroke Association and the National Stroke Association were co-sponsors of the meeting. The attendees were to develop workable plans of action to get more stroke patients treated rapidly. The objective of this innovative model is to facilitate translation of basic research findings into clinical practice. This is done in set tings where patients with acute ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are evaluated and treat ed very rapidly after the onset of their symptoms. The goal of the repository will be the elucidation of genetic factors associated with neu rological diseases, including stroke. Genetic studies of neurological disorders are increas ing in number and complexity. Such studies require a large and diverse sample and accompanying information base. The comprehensive report from this meeting will serve as a guide for planning research in stroke prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation for the coming years. This appendix outlines this process and identifies the many partners who participated. Organization the planning process for the Action Plan included several key partners, public health experts, and heart disease and stroke prevention specialists in the United States and abroad. These participants were asked to contribute in several ways, including as members of a Working Group, one of five Expert Panels, or a National Forum. D-1 Public Health Action Plan to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke For the Expert Panels, each of which was chaired by an extramural public health expert, 45 national and international experts contributed to formulation of the recommendations and proposed actions steps. For the Working Group, which also was chaired by an extramural public health expert, 20 national and international experts served. The panels identified relevant concerns and problems, proposed solutions, and offered recommendations appropriate to their topics. Working Group the Working Group was responsible for initial critical review of the draft outline of the plan and the development process. Members also formulated the instructions for the Expert Panels, nominated members for the National Forum, and reviewed the final reports of the Expert Panels. In addition, they assessed the proposed implementation process and consid ered all input from the National Forum in preparing the final document. National Forum National Forum participants were responsible for reviewing the draft plan from the perspec tives of a wide range of partners, constituencies, and other interested parties. They also were asked to assess priorities for the many proposed action steps and to consider the potential contributions of partners to implementing the plan. D-3 Public Health Action Plan to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke the Working Group met first in December 2001 to provide input to the draft outline, draft implementation plan, and Expert Panel instructions and to recommend members for the National Forum. During its second meeting in late May 2002, members reviewed and dis cussed the reports of the five Expert Panels and the implementation plan. Each Expert Panel was convened for two meetings, the first during January?February 2002 and the second during March?May 2002. These meetings included preliminary discussions, interim work, and final discussions, which led to completed position papers for each panel that will be published separately. In preparation for the first meeting, panelists received selected background material and were asked to prepare a written statement on their topics. This material was compiled and distributed to all members of each panel before the meeting. During the first meeting, participants discussed their designated component of the plan and identified approximately five issues of foremost importance regarding that component. This discussion facilitated development of a set of premises, which each panel used as the basis for their recommenda tions. Preventing heart disease and stroke requires a robust and effective public health infra structure. Recent events have underscored the need for improved public health infra structure in the United States. The current public health infrastructure urgently needs to be transformed to allow initiation of programs that are large enough and have the necessary competencies to achieve the goals of the plan. Technical capacity does not assure its own implementation, and a societal commitment cannot suc ceed without technical capacity. Surveillance is needed at national, state, and especially local levels, with indicators established for community and individual measures. These answers are also critical for setting priorities for data collection systems. Many older adults remain at high risk for continued progression of atherosclerosis and high blood pressure or recurrence of heart attacks or strokes unless adequate preventive measures are taken. Thus, preventive measures are important in childhood and adoles cence (or earlier) and throughout early, middle, and later adult years. All are appropriate, and each has elements especially suited to particular settings. Prevention effectiveness studies are needed to investigate inter D-5 Public Health Action Plan to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke ventions, addressing such aspects as the percentage of disease occurrence that can be pre vented, costs and cost-effectiveness, feasibility (strengths/weaknesses/opportunities/threats), specific target populations, multiple levels (local, state, national), multiple settings (com munities, work sites, schools, families), specific behaviors or health states studied as out comes. The roles of these and other potential partners in implementing the research agenda are an important aspect of implementing the plan. A more optimistic view recognizes and responds to the importance of a global context in addressing health and security. Better health?achieved through improvements in basic living conditions, income, education, and social services (including health care)?is a key element to achieving a better and safer world for everyone. Eliminating health inequalities and increasing the quality and years of healthy life are strategic goals for the global community in this century. The second meeting of each panel focused on making specific recommendations for the Action Plan. Areas of consensus and difference were identified, and salient points were incor porated in a set of recommendations and corresponding action steps. The recommendations and action steps constituted the primary products of the Expert Panels. D-6 Development of the Plan the National Forum was appointed in spring and summer 2002 and received the draft plan in August 2002. The members met September 4, 2002, to discuss the proposed action steps and the interests of their respective agencies, organizations, and constituencies in imple menting the plan. Advisory Board of the First International Conference on Women, Heart Disease and Stroke.
One very reliable choice for other modalities such as digital subtraction (Figures 1 skin care natural tips buy cheap decadron line, 2) acne products generic decadron 0.5 mg visa. The calcium score the acquired image data undertake further scan shows and allows calculation of the post-processing techniques to achieve the amount of calcifcation in the coronary best possible diagnostic images for the A B artery wall acne 6 months after giving birth buy 8mg decadron with visa. The great speed of computing unique spectral characteristics when pene A B processing has allowed vendors to produce trated by diferent x-ray energy levels acne medication accutane generic decadron 8mg with mastercard. This model-based iterative reconstruction algo property could enable the mapping of the rithms for image processing acne 5 pocket jeans 8mg decadron free shipping. The radiogra iodine (and thus blood) distribution within pher can hereby maximise image quality in the myocardium at a lower radiation dose order to make a more accurate diagnosis but without dynamic information of the possible by increasing the spatial resolution acne before period best buy for decadron, myocardium. This allows of coronary stenosis expressing the amount system software to select a kV according of coronary fow still attainable despite the to patient size and to reduce the mA in the presence of a stenosis and could potentially anterior-posterior position. They Recent technical advances can assess aim to reach a quick and accurate diagnosis, dynamic myocardial perfusion by scanning with a minimum of radiation dose. The radiographer their department, establishing the criteria, Computed Tomogra cal radiographer until also has to demonstrate adequate compre knowledge and skills to have for a success phy Department of 2006. Athanasios Plo and has completed a Master of Science in digital ipate, annual events also take place, where tas Iatriki S. Since the emergence of the cath lab in the Radiographers share the knowledge and 1980s, the use of percutaneous intervention, a minimally invasive proce skills necessary to assist in a collection? Today, coronary1 strates poise and a level of composure not during and after the procedure angioplasty is performed on more than 2 million patients in the world common among other medical imaging annually2. The anxiety of the patient the radiographer also coordinates access damental role in the multi-professional teams who treat patients with during these life-changing procedures is to supporting imaging such as computed life and limb threatening diseases. Fortunately, the European Federa nostic and interventional procedures are they enable. Although increasingly com become astute in this clinically complex envi and critical information necessary for a vital member of the cath lab team and plex procedures demand longer fuoros ronment. In addition to the cardiac continues to defne the cardiac cath lab niques ensure that the radiation doses to ble the radiographer to contribute to the care cath lab, you will also fnd radiographers is angioplasty and the use of coronary patients and staf are as low as possible. Arteries once thought to be for is equipped with knowledge of radiation radiology, paediatrics, neurology and ever occluded are now being restored physics, radiation biology, x-ray image forma electrophysiology. It has minimises patient and clinical personnel aspects of all the equipment utilised during the cath lab require highly coordinated been predicted that 50% of the fnancial exposure. Recent develop return from cardiac cath labs will be from reasonably achievable. This fundamental masters of the delicate interplay of technol ments in cardiac surgery and interven non-coronary procedures by 2020. Heart7 principle of radiation protection is taught ogy and anatomy that is required to achieve tional cardiology and new percutaneous valve repairs and replacements, left atrial to radiographers on their frst day. It is the ographer commits to a career-long contin thesiologists, engineers and nurses. There There are many new interventional tech radiographer who is educationally prepared uing educational process. The cath lab team performs has been associated with an additional risk achievable. Advanced visual isation will include free-foating and 3-D Credentialing in this healthcare setting has holographic images, and robotic systems grown proportionally to the new forms of for peripheral, coronary and electrophysiol treatment that are enabled by advancing ogy procedures will soon become standard technologies. The cath lab department to confrm the placement of a radiographer who earns these secondary catheter in his arm, to the use of sophisti credentials demonstrates not only funda cated three-dimensional imaging to replace mental knowledge but also a dedication to valves in a heart, the radiographer has con their professional development. Steelman is currently the chairman of the He is the author of numerous national and inter American Society of Radiologic Technologists He is the President of the Milan Professional Body of national scientifc papers and articles. He research and training programmes aimed at all represents invasive cardiovascular technologists health professionals. He serves the International Society of improve the teaching and research in diagnostic Radiographers and Radiological Technologists as disciplines especially in the area of interventional a Regional Coordinator of Professional Practice. He was given an shares his writings in books, journals and periodi award by the National Federation of Colleges cals. Therefore, the technical, clinical, and socio-economical stakes are the gold standard for a long time. However, relates to the clinical range of cardiac pulse high when we consider cardiac imaging. Along with the technical devel there is a small but real risk of complications rates. This also examinations have been developed for the dual-source scanners, wider detector cover afects medical physicists3. The optimal usage of equipment described diagnostics and treatment chain of more age, iterative reconstructions and motion-ar by patient fow, the optimal utilisation of equipment features indicated by stable and medically treatable states of tefact corrections have made improvements specialised diagnostic protocols and radiological optimisation (for radia diseases1, 2, 5. For example, given only for a fraction of the overall beam hardening artefacts in the images17?19. The T1 relaxation time (a accurate assessment of myocardial morphol measure of how fast the nuclear spin magne ogy and function possible, but also shows tisation recovers back to its equilibrium state Figure 1 focal fbrosis and infltration. By using and the left main branch follows the interarterial route between the pulmonary branch and the aorta. The post-contrast T1 map showed signifcantly decreased T1 relaxation time (~220 ms) in this area of the myocardium compared to the normal myocardium (~520 ms). However, recent developments in temporal scan window is not a straightfor are used for the optimisation of clinical scans. Cardiac imaging in multi-professionality also makes for excellent prehensive task and is a cornerstone of the radiology may also involve methods where research topics. In standard quality assurance does not provide project33), and further down the line, may any radiological examination there should full coverage through standard metrics. Therefore, more elabo which also includes implementation of new rate quality assurance methods relating to Cardiac imaging in radiology is highly imaging methods and clinical applications. His profes assurance, and radiation protection in diagnostic sional focus is on quality assurance, dosimetry, radiology. The New raphy and cardiac magnetic By Gorka Bastarrika England journal of medicine. Heart disease and stroke Imaging, Society for Cardi statistics-2009 update: a 7 Menke J. Image quality and radiation Cademartiri F, de Feyter P, et the performance and acqui exposure with prospectively al. Presented at the bach S, Agatston A, Berman Magnetic Resonance Imag Society of Echocardiogra scoring: review of evidence doi: 10. Endorsed by Huda W, Ruzsics B, Costello Imaging and North American S0140-6736(11)61335-4. Validation of magnetic By Rozemarijn Vliegenthart By Marc Dewey S1936-878X(17)30993-2. J Cardiovasc Crossing the Borders of 16 Motoyama S, Kondo T, Sarai management of acute coro By Marco Francone, Anna Palmisano and Comput Tomogr 8:183-188. J Am of knowledge on aetiology, care professionals from the Circulation 135:e146-e603. Eur Heart on Exercise, Cardiac Rehabili tomographic angiography for Prognostic implications from a years. J Am Coll Cardiol Cardiovascular magnetic res Angiography of Individuals 8 Task Force M, Montalescot young children: image quality 54:49-57. Efect of Undergoing Invasive Coronary G, Sechtem U et al (2013) and radiation dose reduction. J Am Coll tis: diagnostic value of quanti in patients with suspected 45:1761-1770. Association of Cardiovascular den: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Imaging and the American 1 Sucha D, Symersky P, Tanis Chapter 12: Atherosclerosis. Vascular dial Extracellular Volume by comes after transcatheter or Cardiovasc Imaging. A major subclinical coronary artery Health and Risk Management T1-Mapping to Distinguish surgical aortic-valve replace Sep;8(9):e003703. Normal values Cardiovascular Magnetic Reso for inoperable severe aortic [Epub ahead of print]. Consensus Document on Opti 1 Albus C, Barkhausen J, Fleck E, vascular Imaging. Comprehensive Cardiovascular Imaging Best ber S, on behalf of the German en/education/diploma. J Med Imaging (Bell Kassenarztliche Bundesv manninger J, Prayer F, Pan J, death substrate imaged by the management of patients imaging and functional recov ingham). Machine magnetic resonance imaging: with ventricular arrhythmias ery after reperfused myo gemeinschaft der Wissen learning: from radiomics to From Investigational tool to and the prevention of sudden cardial infarction. J Am Coll 3 Hedgire S, Ghoshhajra B, schaftlichen Medizinischen discovery and routine. Myerson S, Neubauer S, Wie nobel prizes/medicine/laure 9 Good practices in interven Am J Roentgenol. Anxiety levels of tices-in-interventional-fuoros Imaging in the Diagnosis of 2016 Jul;46(4):273-285. Efcacy of noninva 14 Kalisz K, Buethe J, Saboo J, Nezafat R, Salerno M, Schel diology. Artifacts at Car R, Ugander M, van Heeswijk opment recommendations tion of Organisations for Med stable coronary artery disease. Infarct characterization Tesche C, Mangold S, Spandor Society for Cardiovascular Lung: the Journal of Acute and 2018. Curr Treat ping: Techniques and clinical 33 Empir project, Metrology for Options Cardiovasc Med. Cardiovas 22 Krishnamurthy R, Cheong B, Technical challenges of coro cular magnetic resonance and Muthupillai R. This also includes the alignment of logical clinical categories; emergent, urgent, semi-urgent and elective, to standardized provincial priority levels with associated access targets for each procedure. For each algorithm, a brief historical synopsis, description and list of field inputs are provided. It should be noted that patients are not triaged nor monitored clinically based on the access target. Signs and symptoms of anemia may include pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, shortness of breath, palpitations of the heart, soft systolic murmurs, lethargy, and fatigability. Navigational Note: Bone marrow hypocellular Mildly hypocellular or <=25% Moderately hypocellular or Severely hypocellular or >50 Aplastic persistent for longer Death reduction from normal >25 <50% reduction from <=75% reduction cellularity than 2 weeks cellularity for age normal cellularity for age from normal for age Definition: A disorder characterized by the inability of the bone marrow to produce hematopoietic elements. Navigational Note: Disseminated intravascular Laboratory findings with no Laboratory findings and Life-threatening Death coagulation bleeding bleeding consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by systemic pathological activation of blood clotting mechanisms which results in clot formation throughout the body. There is an increase in the risk of hemorrhage as the body is depleted of platelets and coagulation factors. Navigational Note: Hemolysis Laboratory evidence of Evidence of hemolysis and Transfusion or medical Life-threatening Death hemolysis only. Navigational Note: Leukocytosis >100,000/mm3 Clinical manifestations of Death leucostasis; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an increased number of white blood cells in the blood. Navigational Note: Thrombotic Laboratory findings with Life-threatening Death thrombocytopenic purpura clinical consequences. Navigational Note: Asystole Periods of asystole; non Life-threatening Death urgent medical management consequences; urgent indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia without cardiac electrical activity. Navigational Note: Atrial fibrillation Asymptomatic, intervention Non-urgent medical Symptomatic, urgent Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated intervention indicated; device consequences; embolus. Navigational Note: Atrial flutter Asymptomatic, intervention Non-urgent medical Symptomatic, urgent Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated intervention indicated; device consequences; embolus. Navigational Note: Atrioventricular block Non-urgent intervention Symptomatic and Life-threatening Death complete indicated incompletely controlled consequences; urgent medically, or controlled with intervention indicated device. Conduction disorder Mild symptoms; intervention Non-urgent medical Symptomatic, urgent Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences Definition: A disorder characterized by pathological irregularities in the cardiac conduction system. Navigational Note: Cyanosis Present Definition: A disorder characterized by a bluish discoloration of the skin and/or mucous membranes. Navigational Note: Heart failure Asymptomatic with Symptoms with moderate Symptoms at rest or with Life-threatening Death laboratory. Navigational Note: If left sided use Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction; also consider Cardiac disorders: Restrictive cardiomyopathy, Investigations: Ejection fraction decreased. Left ventricular systolic Symptomatic due to drop in Refractory or poorly Death dysfunction ejection fraction responsive controlled heart failure due to to intervention drop in ejection fraction; intervention such as ventricular assist device, intravenous vasopressor support, or heart transplant indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by failure of the left ventricle to produce adequate output. Navigational Note: Mobitz type I Asymptomatic, intervention Symptomatic; medical Symptomatic and Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated incompletely controlled consequences; urgent medically, or controlled with intervention indicated device. Navigational Note: Myocarditis Symptoms with moderate Severe with symptoms at rest Life-threatening Death activity or exertion or with minimal activity or consequences; urgent exertion; intervention intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia Asymptomatic, intervention Non-urgent medical Symptomatic, urgent Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated intervention indicated; consequences; incompletely ablation controlled medically; cardioversion indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with abrupt onset and sudden termination of atrial contractions with a rate of 150-250 beats per minute. Navigational Note: Pericardial effusion Asymptomatic effusion size Effusion with physiologic Life-threatening Death small to moderate consequences consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by fluid collection within the pericardial sac, usually due to inflammation. Navigational Note: Pericardial tamponade Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in intrapericardial pressure due to the collection of blood or fluid in the pericardium. Navigational Note: Pulmonary valve disease Asymptomatic valvular Asymptomatic; moderate Symptomatic; severe Life-threatening Death thickening with or without regurgitation or stenosis by regurgitation or stenosis by consequences; urgent mild valvular regurgitation or imaging imaging; symptoms controlled intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Restrictive cardiomyopathy Imaging findings only Symptomatic without signs of Symptomatic heart failure or Refractory heart failure or Death heart failure other cardiac symptoms, other poorly controlled responsive to intervention; cardiac symptoms new onset of symptoms Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability of the ventricles to fill with blood because the myocardium (heart muscle) stiffens and loses its flexibility. Navigational Note: Sick sinus syndrome Asymptomatic, intervention Symptomatic, intervention Symptomatic, intervention Life-threatening Death not indicated not indicated; change in indicated consequences; urgent medication initiated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with alternating periods of bradycardia and atrial tachycardia accompanied by syncope, fatigue and dizziness.
Circulation 1978;57: rhythmias in adult aortic stenosis: prevalence acne 1cd-9 purchase generic decadron line, mechanisms skin care trade shows cheap decadron online, and clinical relevance acne 101 order decadron no prescription. Nonischemic mitralregurgitation:prognosticvalueofnonsustainedventriculartachycardiaafter bundle-branch reentry by valve surgery acne around nose order decadron 0.5mg line. Comparison of the causes of late death following aortic and Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task mitral valve replacement acne 37 weeks pregnant order discount decadron on-line. Incidence and mechanisms of cardiorespiratory arrests in epilepsy Reg 2005;70:61134?61135 acne around nose safe 8mg decadron. Antipsychotic drugs and the risk of ventricular arrhyth trophy: a nationwide cohort study. Lallemand B, Clementy N, Bernard-Brunet A, Pierre B, Corcia P, Fauchier L, Psychiatry 2005;4:1. Drug-induced diographic abnormalities and sudden death in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Risk of mortality (including sudden cardiac death) and major cardiovas moplegia and pigmentary retinopathy). Report of 2 cases and review of 17 cular events in atypical and typical antipsychotic users: a study with the general published cases. Mortality in myotonic dystrophy patients in the area of prophylactic the risk of sudden cardiac death. Task Force on the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases During Pregnancy of 1995;36:1187?1194. Theblockadeofmineralocorticoidhormonesignalingprovokesdra pregnancy: increased incidence of supraventricular arrhythmias. Obstructive sleep apnea and the risk of sudden cardiac and impact on fetal and neonatal outcomes. Usefulness of sleep-disordered breathing to predict oc sophageal echocardiography. Cheyne-Stokes respiration and obstructive sleep apnoea are inde col 1992;167:506?507. Relationship among the severity of sleep and therapy of peripartum cardiomyopathy: a position statement from the Heart apnea syndrome, cardiac arrhythmias, and autonomic imbalance. Pacing Clin Elec Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on trophysiol 2003;26:669?677. Regitz-Zagrosek V, Blomstrom Lundqvist C, Borghi C, Cifkova R, Ferreira R, apnoea. Am on the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy: the Task Force J Cardiol 1996;77:1310?1314. Day-nightpatternofsudden deathin gene mutations are common in families with both peripartum cardiomyopathy obstructive sleep apnea. Cardiac arrhythmias in structive sleep apnea syndrome: effects of nasal continuous positive airway pres pregnancy: clinical and therapeutic considerations. Clin Pharmacol Ther ous positive airway pressure therapy on cardiovascular outcomes in sleep apnea 2000;68:337?338. Eur Heart J 1993; rhythmias due to transient or correctable causes: high risk for death in follow-up. Monnig G, Kobe J, Loher A, Wasmer K, Milberg P, Zellerhoff S, Pott C, torsade de pointes. Ventricular arrhythmias in patients with myocardial infarction and is Escande D, Franz M, Malik M, Moss A, Shah R. Drugs 1984;28(Suppl 1): and proarrhythmia by non-antiarrhythmic drugs: clinical and regulatory implica 66?76. Azithromycin and the risk of Magnesium in the prevention of lethal arrhythmias in acute myocardial infarction. Unexpected death in patients suffering from eating dis the risk of serious arrhythmia: a population-based study. Co-trimoxazole and sudden death in patients receiving inhibitors events with transvenous implantable cardioverter-de? Martinez Sanchez J, Garcia Alberol A, Almendral Garrote J, Castellanos E, Perez 751. Med Pediatr Oncol 1995;24: sensing errors in third-generation implantable cardioverter-de? Sudden, unexpected death in cardiac transplant recipients: an aut Acta Cardiol 2002;57:381?383. Meta-analysis: age and effectiveness of prophylactic im ing cardiovascular safety at sports arenas: position stand from the European As plantable cardioverter-de? Brullmann S, Dichtl W, Paoli U, Haegeli L, Schmied C, Steffel J, Brunckhorst C, 789. Re commendations for preparticipation screening and the assessment of cardiovas 804. Patterns of functional decline at culardiseaseinmastersathletes:anadvisoryforhealthcareprofessionalsfromthe the end of life. Borjesson M, Urhausen A, Kouidi E, Dugmore D, Sharma S, Halle M, Loh P, Cobbe S, Grace A, Morgan J. Cardiovascular evaluation of middle-aged/senior individuals engaged nearing end of life or requesting withdrawal of therapy. Europace 2010;12: in leisure-time sport activities: position stand from the sections of exercise physi 1480?1489. Palliative care in heart failure: a position statement from Moscatiello M, Tavazzi L, Santinelli V. Wolff?Parkinson?White syndrome in the palliativecareworkshop of the Heart Failure Association of the European So the era of catheter ablation: insights from a registry study of 2169 patients. Earlyrecognitionbyemer Received 28 April 2016 gency medical dispatchers is essential for an effective chain of actions, leading to early cardiopulmonary Received in revised form 21 August 2016 resuscitation, use of an automated external de? Keywords: Method: An observational register-based study collecting data from national cardiac arrest registers in Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest Denmark and Sweden during a six-month period in 2013. Data were analysed in two steps; registry data Recognition Emergency medical dispatching were merged with electronically registered emergency call data from the emergency medical dispatch Emergency medical services centres in the two regions. IntheCapital A Spanish translated version of the summary of this article appears as Appendix in the? Main characteristics Item Capital Region of Denmark Skane Region in Sweden Region demographya Population 1. Paramedics (47%) and others (53%), 6 week communication module with no former medical education. Skane Region: priority 1=life threatening symptoms or accident, priority 2=urgent but not life-threatening symptoms. In medical cases, the dispatcher can initiate co-listening caller-relatedfactors;caller?srelationtopatient,languageusedand from a registered nurse. All medical dispatchers receive a 20-week training program that pro Analyses vides a certi? In Denmark, the study was approved by the Danish Data Pro Study design, data collection and de? A request was sent to the Research Ethics Committee in the Capital Region of Denmark, the study was an observational register based study. In Sweden, the study was reviewed and approved by the the Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry23,24 during a 6-month study Ethical Review Board in Lund (? Prior to the study period, the joint study group from the given an option to withdraw consent (opt-out method). Results the data collection was conducted in two phases: Baseline characteristics in both recognised and un-recognised 1. In the Skane Region in Sweden, one subject declined to partic We found that the vast majority of patients were given the ipate and two cases were excluded because the information letter highest priority assigned for the ambulance dispatch, despite the did not reach the recipient. The choice of resources dispatched may play an essential incidence of 44/100,000 citizens/year. Missing dispatch codes nurses and paramedics while the majority in the Skane Region have were common among the audited emergency calls in the Capi no formal medical education despite intentions for a registered tal Region (127/266 calls, 48%). The median call duration was 6-week communication course and simulation training at employ longer for the audited recognised calls compared to the audited ment. Whether these dissimilarities between the two regions play non-recognised calls in both regions. However, we found that recognition performance was Discussion high in both systems after auditing calls despite the differences in professional background and educational level of the medical dis this study aimed at evaluating the accuracy in recognition of patchers. A A high compliance to follow the priority tool and mandatory reason may be a difference in call culture or barriers for calling. This is in contrast to what was anticipated with two calls was high and comparable in both regions. Capital Region, N=294 (recognition not applicable, n=28) Skane Region, N=62 (recognition not applicable, n=9) Recognised, n=164 Non-recognised, n=102 Recognised, n=14 Non-recognised, n=39 Dispatcher-related factors Four most common 1. AnnEmergMed data registration practices, reducing the generalizability of results. Implementing a nationwide criteria-based emergency medical dispatch sys Conclusion tem: a register-based follow-up study. Temporaltrendsincoverageofhis torical cardiac arrests using a volunteer-based network of automated external medical services. Improved outcome in Sweden after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and possible associations with improvements in every link in the chain of survival. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation in monary resuscitation outcome reports: update of the Utstein resuscitation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Circulation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest should be diagnosis related rather than symptom 2015;16:2?39. Tuition of emergency medical dispatchers in the recognition of agonal respira Resuscitation 2015;96:303?9. Sakai), and From a nationwide, prospective, population-based registry of patients with out-of the Department of Emergency Medicine, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine hospital cardiac arrest in Japan, we identified patients from 2005 through 2013 (T. The number of patients in whom survival with a favorable neurologic Address reprint requests to Dr. Iwami at Kyoto University Health Service, Yoshida outcome was attributable to public-access defibrillation was estimated. The percentage of patients receiving public-access defibrillation increased from 1. The percentage of patients who were alive at 1 month Copyright 2016 Massachusetts Medical Society. The estimated number of survivors in whom survival with a favorable neu rologic outcome was attributed to public-access defibrillation increased from 6 in 2005 to 201 in 2013 (P<0. Cardiac cardiac arrest in industrialized countries has been arrest was defined as the cessation of cardiac increasing,5-7 but it remains low (approximately mechanical activity, as confirmed by the absence 10%). Many reports have shown8 cular disease; external factors, including drown that public-access defibrillation by laypersons ing, hanging, trauma, asphyxia, and drug over contributes to improving outcomes after out-of dose; or any other noncardiac factor. Specially trained emer gency life-saving technicians are also allowed to Methods insert tracheal tubes and administer intravenous Study Design, Population, and Settings epinephrine. Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan for bystanders were changed from conventional server. Data Collection and Quality Control Outcome Measures Data were collected prospectively on resuscitation the primary outcome measure was survival with related factors including origin of arrest (cardiac a favorable neurologic outcome at 1 month after or noncardiac), sex and age of the patient, type of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. A favorable neuro bystander (family member or other), first docu logic outcome was defined as a Cerebral Perfor mented cardiac rhythm, time course of resusci mance Category score of 1 or 2. Neurologic outcome was determined to-one pair matching between the group receiv by the physician responsible for the care of the ing public-access defibrillation and the group not patient by a follow-up interview 1 month after receiving public-access defibrillation was per successful resuscitation, with the use of the formed by nearest-neighbor matching without Cerebral Performance Category scale, on which replacement, with the use of a caliper width category 1 represents good cerebral performance; equal to 0. Covariate balances gory 3, severe cerebral disability; category 4, before and after matching were checked by com coma or vegetative state; and category 5, death parison of standardized mean differences. Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests during the Study Period and Patients Included in the Analysis. Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan A 500,000 428,821 400,000 364,959 310,075 300,000 264,165 218,050 200,000 164,343 96,545 100,000 45,417 10,961 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 B 20. All tests were two surviving with a favorable neurologic outcome tailed, and P values of less than 0. The trend in numbers of attribut Study Population able favorable outcomes over time was tested During the study period, 1,050,412 out-of-hos with a linear regression model. Of these, 43,776 patients had ventricular fibrillation as the first docu mented rhythm. A total of 43,762 patients with outcome data (4499 who received public-access defibrillation [10. Patient Characteristics Characteristics of patients with bystander-wit nessed ventricular-fibrillation arrest of cardiac origin who received public-access defibrillation and those of patients who did not receive public access defibrillation are shown in Table 1. The group that received public-access defibrillation was less likely to have a cardiac arrest that was wit nessed by family members than the group that did not receive public-access defibrillation (9. Propensity-score match ing yielded 4221 patients who received public access defibrillation matched to 4221 patients who did not receive public-access defibrillation. Outcomes Table 2 shows outcomes of bystander-witnessed ventricular-fibrillation arrests of cardiac origin with or without public-access defibrillation. The rate of 1-month survival with a favorable neuro logic outcome was significantly higher in the group that received public-access defibrillation than in the group that did not receive public n engl j med 375;17 nejm. Outcomes of Bystander-Witnessed Ventricular-Fibrillation Arrest of Presumed Cardiac Origin with or without Public-Access Defibrillation. Most of this increase was observed out public-access defibrillation (adjusted odds among adults 18 to 74 years of age (from 6 in ratio, 2. Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan We also estimated the number of patients in whom survival with a favorable neurologic out 210 Any age come was attributable to the use of public-access 190 defibrillation. This figure increased steadily dur 170 ing the 9 years of the study, from 6 cases in 2005 150 P<0. As indicated in Figure 1, only the number of patients in whom survival with a favorable neurologic out about half of the out-of-hospital cardiac arrests come was attributed to public-access defibrillation was estimated annually in our study were of cardiac origin, and of these, as follows: the number of patients with ventricular-fibrillation cardiac arrest receiving public-access defibrillation in each year?
Additional information: